Abstract
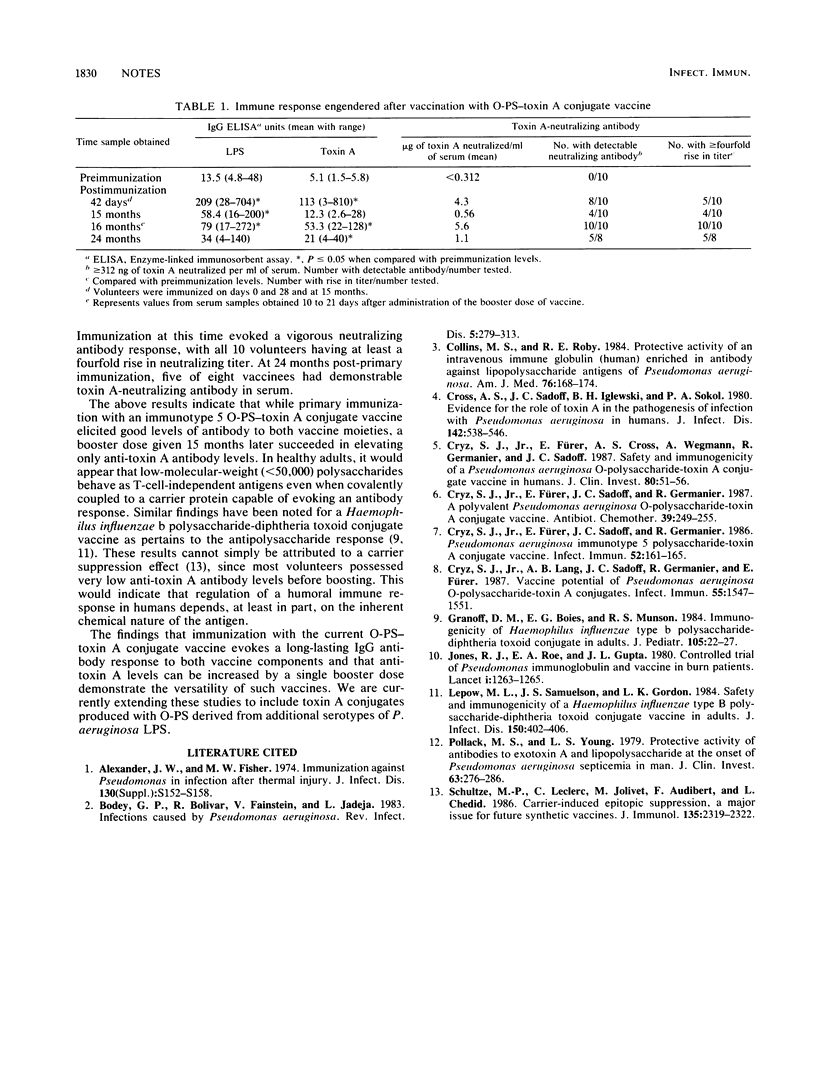
Healthy adult volunteers were vaccinated on day 0 and 28 and at 15 months with a Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 5 O polysaccharide-toxin A conjugate vaccine. Immunization resulted in mild, transient local reactions in less than 20% of the subjects. Maximal immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody titers to both toxin A and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were seen at day 42, at which time 50% of the vaccinees showed a fourfold or greater rise in toxin A-neutralizing titers. By 15 months postvaccination, both antitoxin A and anti-LPS IgG antibodies had markedly declined. A booster dose of vaccine administered at 15 months evoked a vigorous anti-toxin A IgG antibody response with 100% of the volunteers showing a fourfold or greater rise in neutralizing antibody titer compared with preimmunization levels. In contrast, there was no significant elevation of anti-LPS IgG antibody levels. At 24 months postimmunization, only anti-toxin A antibody levels were significantly higher than preimmunization levels.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. S., Roby R. E. Protective activity of an intravenous immune globulin (human) enriched in antibody against lipopolysaccharide antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Med. 1984 Mar 30;76(3A):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Furer E., Sadoff J. C., Germanier R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype 5 polysaccharide-toxin A conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.161-165.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Cross A. S., Wegmann A., Germanier R., Sadoff J. C. Safety and immunogenicity of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-polysaccharide toxin A conjugate vaccine in humans. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):51–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI113062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Sadoff J. C., Germanier R. A polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-polysaccharide-toxin A conjugate vaccine. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:249–255. doi: 10.1159/000414350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Lang A. B., Sadoff J. C., Germanier R., Fürer E. Vaccine potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-polysaccharide-toxin A conjugates. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1547–1551. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1547-1551.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Boies E. G., Munson R. S., Jr Immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide--diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine in adults. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Controlled trial of Pseudomonas immunoglobulin and vaccine in burn patients. Lancet. 1980 Dec 13;2(8207):1263–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepow M. L., Samuelson J. S., Gordon L. K. Safety and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide-diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine in adults. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):402–406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutze M. P., Leclerc C., Jolivet M., Audibert F., Chedid L. Carrier-induced epitopic suppression, a major issue for future synthetic vaccines. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2319–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley J., Fisher A., Fisher M. W. Immunization against Pseudomonas in infection after thermal injury. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S152–S158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



