Abstract
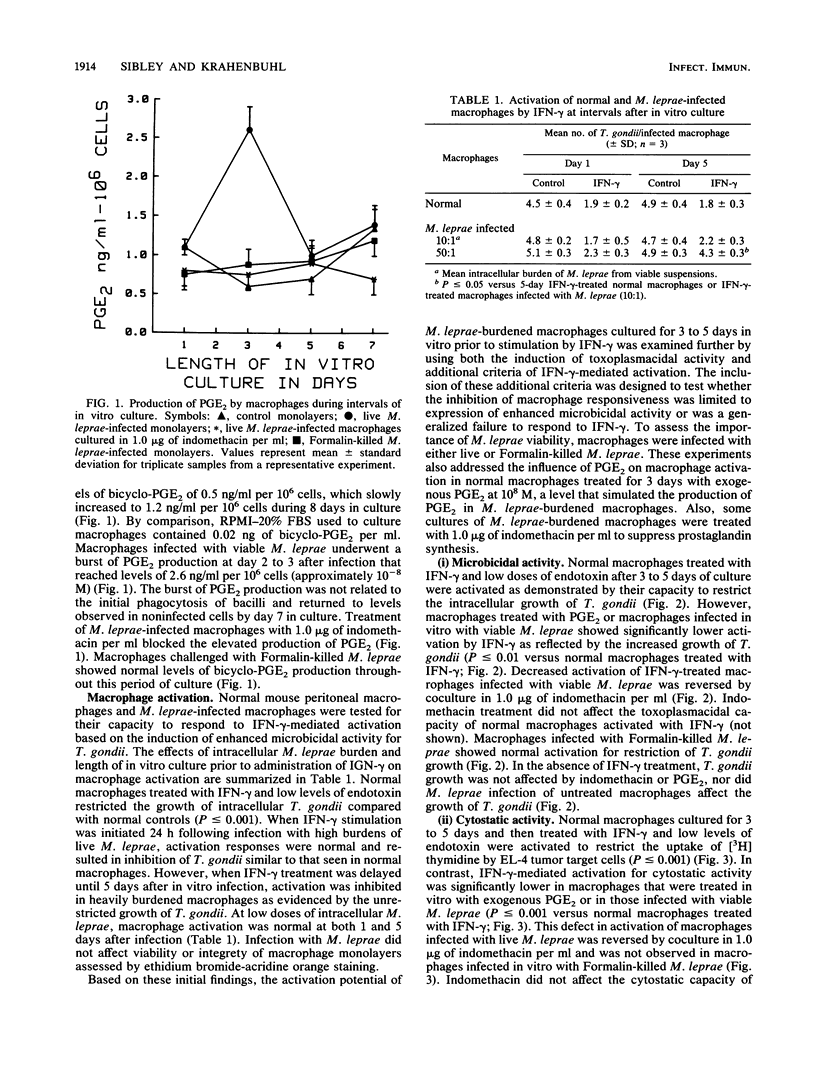
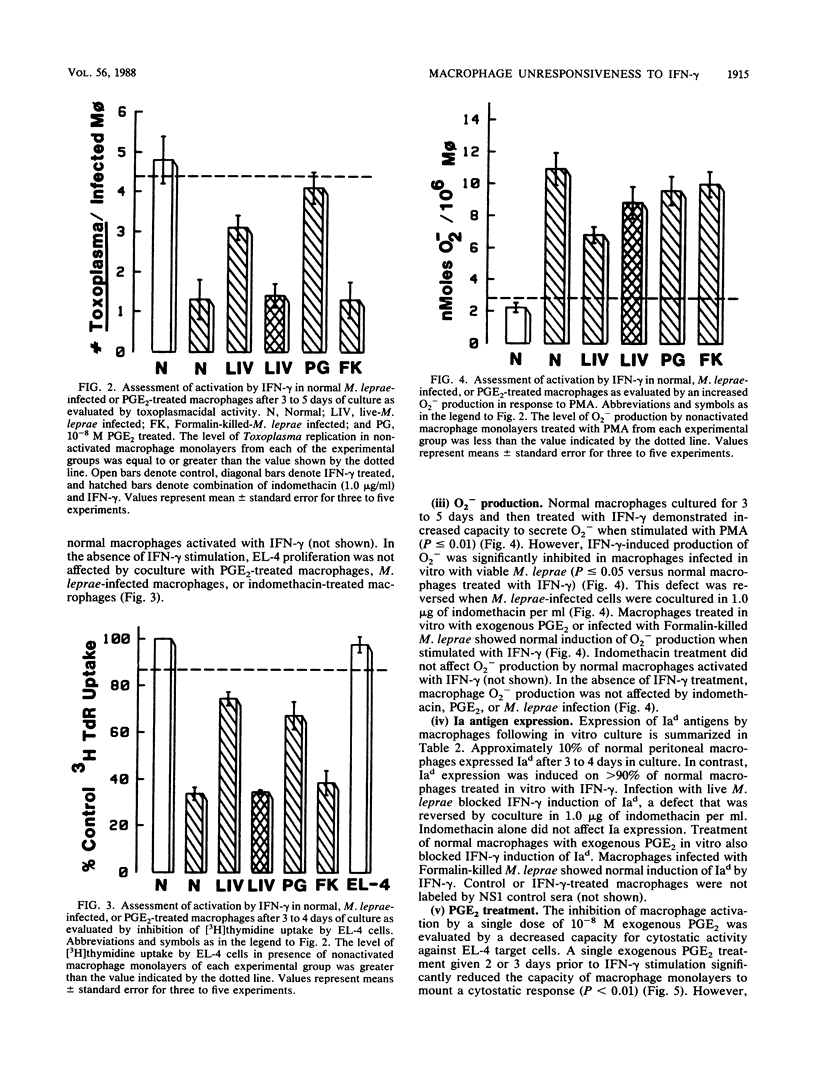
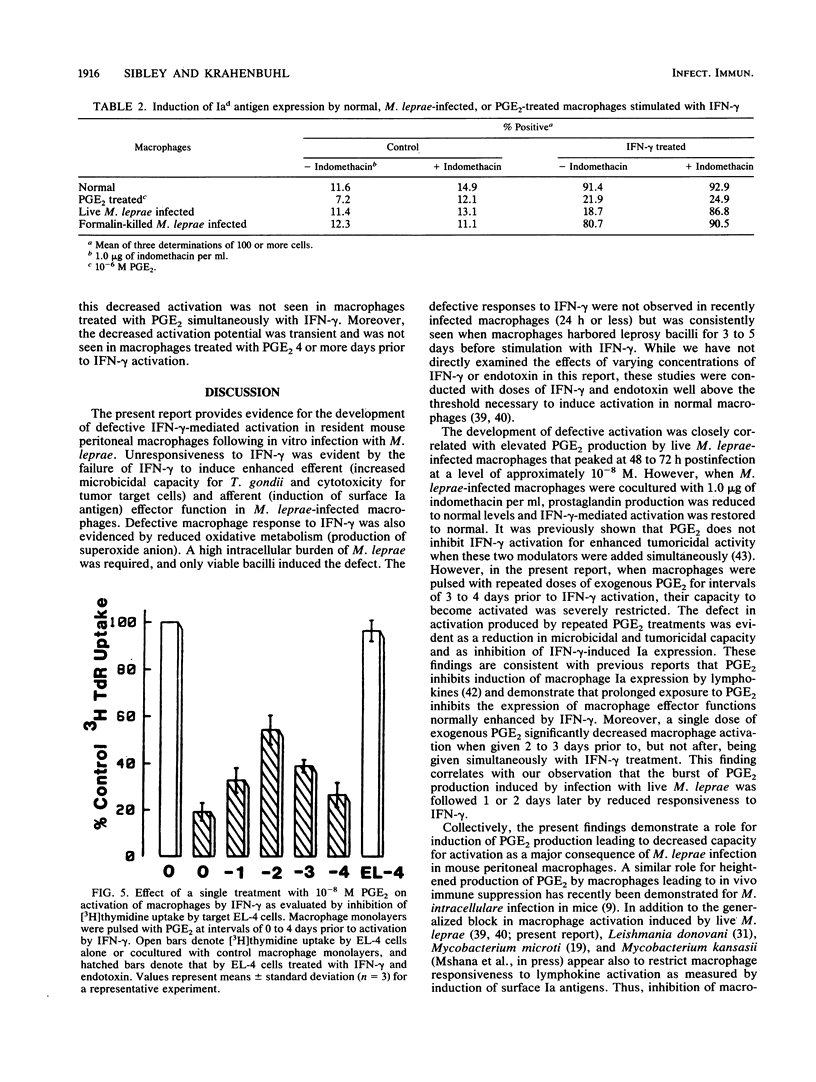
We have previously demonstrated that Mycobacterium leprae-burdened granuloma macrophages isolated from infected nude mice are refractory to activation by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). To explore further both the afferent and efferent functional capacity of M. leprae-infected macrophages, we examined the IFN-gamma-mediated activation of resident mouse peritoneal macrophages infected in vitro with live or dead M. leprae. When IFN-gamma was administered within 24 h of M. leprae infection, macrophages were fully activated. However, defective activation was evident at 3 to 5 days postinfection in macrophages that were heavily burdened with viable M. leprae. This defect was evident by four parameters of activation in which IFN-gamma failed to stimulate the enhancement of microbicidal activity, cytotoxicity for tumor target cells, O2- production, and surface Ia antigen expression. The development of defective activation closely followed an increase in macrophage production of prostaglandin E2. Defective activation of M. leprae-burdened macrophages was reversible by indomethacin, and a similar block in IFN-gamma activation was observed in three of these four parameters in normal macrophages treated with exogenous prostaglandin E2. Thus, infection of mouse macrophages with M. leprae appears to restrict IFN-gamma-mediated activation at least in part by induction of inhibitory levels of prostaglandin E2.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal S., Vemuri N., Mahadevan P. R. Macrophage membrane alterations in leprosy as determined by change in sialic acid level. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1986 Mar;19(3):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I. Functional significance of the regulation of macrophage Ia expression. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Feb;14(2):138–143. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdi T. J., Mistry N. F., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Alterations in the membrane of macrophages from leprosy patients. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):121–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.121-127.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. II. Parasite destruction in macrophages activated by supernates from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. B., Tolson T. A., Yoder L., Loesch J., Krahenbuhl J. L. Lesional modulation of peripheral monocyte leucotactic responsiveness in leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):289–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. R., Sharma S. D., Remington J. S. Oxygen-independent killing by alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1113–1131. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehl S., Ruby J., Job C. K., Hastings R. C. The growth of Mycobacterium leprae in nude mice. Lepr Rev. 1983 Dec;54(4):283–304. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19830035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Cline M. J., Levy L. Leukocyte antimicrobial function in patients with leprosy. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):380–386. doi: 10.1172/JCI107570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. K., 3rd, Hedegaard H. B., Zlotnik A., Gangadharam P. R., Johnston R. B., Jr, Pabst M. J. Chronic infection due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in mice: association with macrophage release of prostaglandin E2 and reversal by injection of indomethacin, muramyl dipeptide, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1820–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., Hastings R. C. Rapid in vitro metabolic screen for antileprosy compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):780–783. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. On the metabolism of prostaglandins E 1 and E 2 in man. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6713–6721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Mustafa A. S., Helle I., Waters M. F., Leiker D. L., Godal T. Reversal by interleukin-2 of the T cell unresponsiveness of lepromatous leprosy to Mycobacterium leprae. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:77–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer T. J., Nelson K. E., Crispen R. G., Andersen B. R. Mycobacterium leprae fails to stimulate phagocytic cell superoxide anion generation. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):514–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.514-520.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Levis W. R., Cohn Z. A. Defective production of monocyte-activating cytokines in lepromatous leprosy. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):666–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Godzik C. A., Cohn Z. A. Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Nathan C. F., Gandhi R., Horwitz M. A., Levis W. R., Cohn Z. A. Effect of recombinant interferon-gamma on hydrogen peroxide-releasing capacity of monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with lepromatous leprosy. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):983–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Sims M., Feldmann M. Regulation of macrophage accessory cell activity by mycobacteria. II. In vitro inhibition of Ia expression by Mycobacterium microti. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):28–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. P., Jones P. P. Induction of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line by immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Cytostatic effects of activated macrophages on tumor target cells: inhibition of cytotoxic action of ARA-C. J Immunopharmacol. 1980;2(3):325–348. doi: 10.3109/08923978009046465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Rothman W., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. F., Bloom B. R. Delineation of a human T cell subset responsible for lepromin-induced suppression in leprosy patients. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1183–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Horwitz D. A., Husmann L. A., Gillis S., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ identification of cells in human leprosy granulomas with monoclonal antibodies to interleukin 2 and its receptor. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mshana R. N., Hastings R. C., Krahenbuhl J. L. Infection with live mycobacteria inhibits in vitro detection of Ia antigen on macrophages. Immunobiology. 1988 Apr;177(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(88)80090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Narayanan R. B., Mehra N. K., Sharma A. K., Gupte M. D. Concanavalin A induced suppressor activity in human leprosy. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):319–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Van Rood J. J., Mehra N. K., Vaidya M. C. Natural suppressor cells in human leprosy: the role of HLA-D-identical peripheral lymphocytes and macrophages in the in vitro modulation of lymphoproliferative responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):203–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Kaplan G., Levy E., Sarno E. N., Kushner P., Granelli-Piperno A., Vieira L., Colomer Gould V., Levis W., Steinman R. Defective gamma interferon production in leprosy. Reversal with antigen and interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Torres B. A., Johnson H. M., Gray P. W. Recombinant mouse gamma interferon induces the priming step in macrophage activation for tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2011–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Kaplan G., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Arachidonic acid metabolism by human monocytes. Studies with platelet-depleted cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):393–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., McMaster W. R. Parasite-accessory cell interactions in murine leishmaniasis. II. Leishmania donovani suppresses macrophage expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex gene products. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1926–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridel P. R., Jamet P., Robin Y., Bach M. A. Interleukin-1 released by blood-monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with leprosy. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.303-308.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: development of macrophage cytotoxic activity requires completion of a sequence of short-lived intermediary reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P. R., Birdi T. J., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Role of macrophages in defective cell mediated immunity in lepromatous leprosy. I. Factor(s) from macrophages affecting protein synthesis and lymphocyte transformation. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Jun;48(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Franzblau S. G., Krahenbuhl J. L. Intracellular fate of Mycobacterium leprae in normal and activated mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):680–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.680-685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L. Defective activation of granuloma macrophages from Mycobacterium leprae-infected nude mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Jan;43(1):60–66. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L. Mycobacterium leprae-burdened macrophages are refractory to activation by gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):446–450. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.446-450.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Krahenbuhl J. L., Weidner E. Lymphokine activation of J774G8 cells and mouse peritoneal macrophages challenged with Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.760-764.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Prostaglandins modulate macrophage Ia expression. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):163–165. doi: 10.1038/299163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffet S. M., Russell S. W. Macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing: regulation of expression of cytolytic activity by prostaglandin E. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):424–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



