Abstract
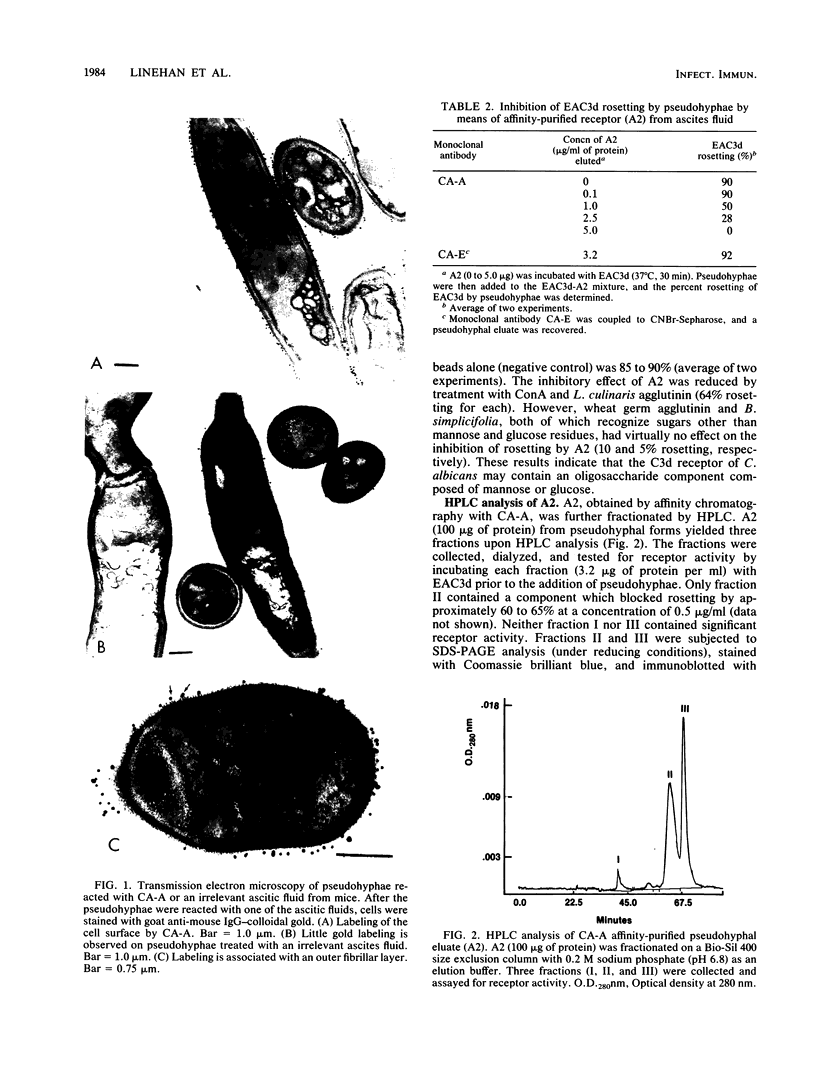
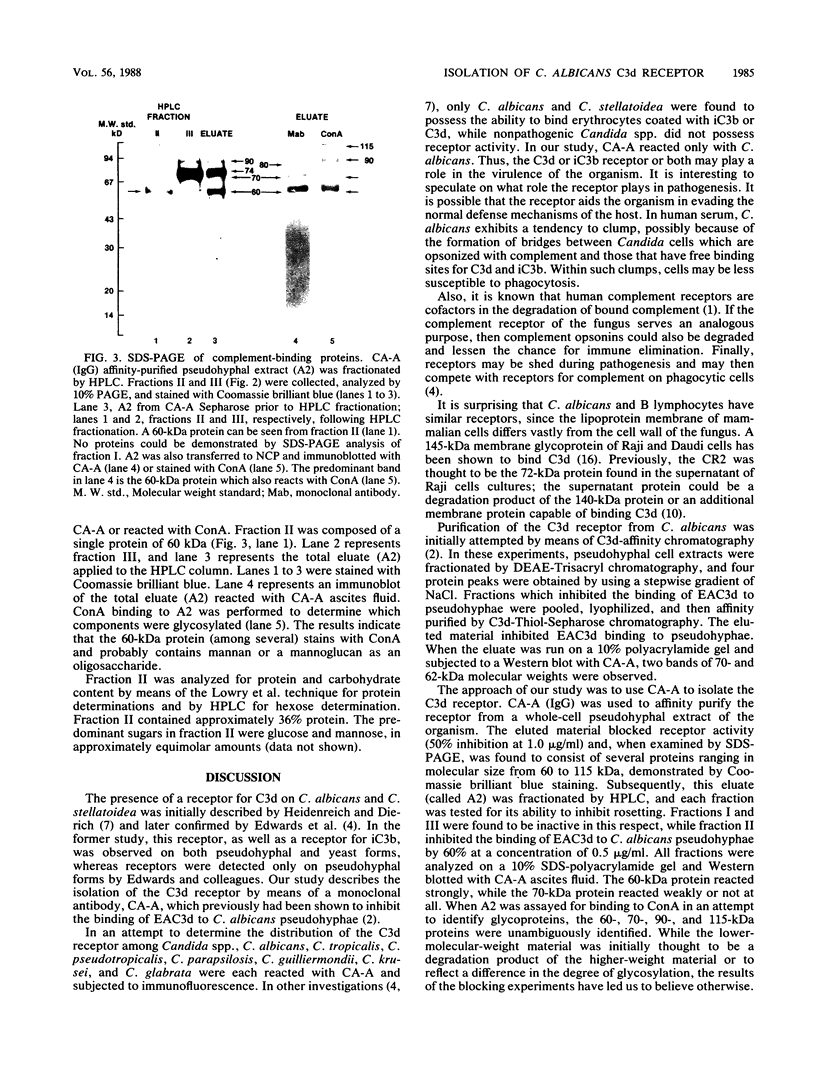
Pseudohyphae of Candida albicans possess a receptor for C3d, a fragment of the complement component C3. This receptor was partially purified by using a monoclonal antibody (CA-A) that previously had been shown to inhibit the binding of C3d to C. albicans pseudohyphae. Purified immunoglobulin G from ascites fluid (CA-A) was coupled to a cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose column, and an affinity-purified fraction (A2) from C. albicans pseudohyphae was obtained. This fraction inhibited rosetting of the EAC3d receptor by pseudohyphae and appeared to contain glycoprotein, since receptor activity could be removed when A2 was incubated with lectins specific for mannose and glucose. A2 was analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and two polypeptides of approximately 60 and 70 kilodaltons (kDa) were consistently identified in reducing gels. The 60-kDa protein was identified as a glycoprotein by concanavalin A binding. A2 was further analyzed by high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC). Of three fractions obtained by HPLC, one containing the 60-kDa protein was found to have receptor activity. When analyzed by HPLC, this protein was found to contain mannose and glucose in approximately equal amounts. Both immunofluorescence and electron microscopy of pseudohyphae treated with CA-A identified A2 as a surface moiety. Thus, the C3d receptor of C. albicans, isolated with CA-A, is a glycoprotein of approximately 60 kDa.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Gaither I. A., Frank M. M. Complement receptors. Clin Immunol Rev. 1981;1(4):471–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Gaither T. A., O'Shea J. J., Rotrosen D., Lawley T. J., Wright S. A., Frank M. M., Green I. Expression of specific binding sites on Candida with functional and antigenic characteristics of human complement receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. Identification of concanavalin A-binding proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate--gel electrophoresis and protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Dierich M. P. Candida albicans and Candida stellatoidea, in contrast to other Candida species, bind iC3b and C3d but not C3b. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):598–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.598-600.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoberg K. A., Cihlar R. L., Calderone R. A. Characterization of cerulenin-resistant mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):102–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.102-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Dobson N. J., Ross G. D. Isolation of lymphocyte membrane complement receptor type two (the C3d receptor) and preparation of receptor-specific antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1828–1832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Inducible proteinase of Candida albicans in diagnostic serology and in the pathogenesis of systemic candidosis. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Aug;13(3):423–435. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Fearon D. T. The identification of N-linked oligosaccharides on the human CR2/Epstein-Barr virus receptor and their function in receptor metabolism, plasma membrane expression, and ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13824–13830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Fearon D. T. Identification of a 145,000 Mr membrane protein as the C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):881–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]