Abstract
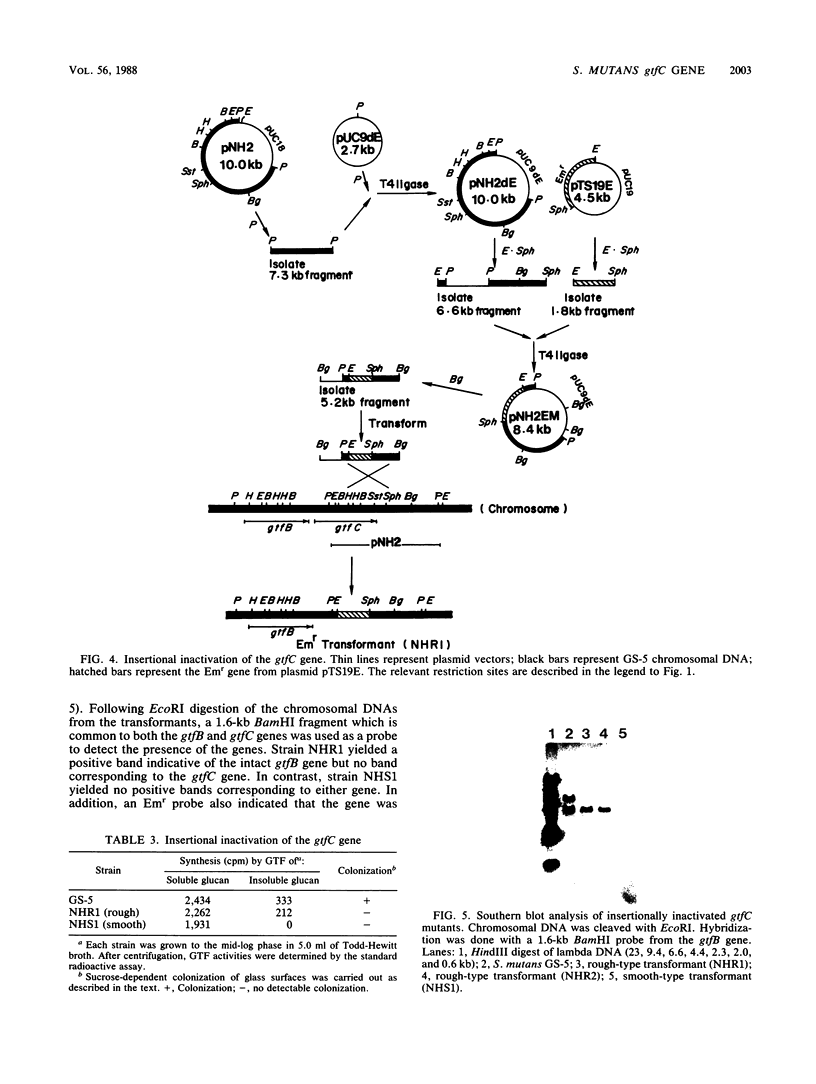
The intact gtfC gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5 was isolated in Escherichia coli in plasmid vector pUC18. The glucosyltransferase activity expressed by the gene synthesized both low-molecular-weight water-soluble glucan and insoluble glucan in a primer-independent manner. Purification of the enzyme by procedures that minimize proteolytic digestion yielded a purified preparation with a molecular weight of 140,000. Insertional inactivation of the gtfC gene with a streptococcal erythromycin resistance gene fragment followed by transformation of strain GS-5 suggested that the gtfC gene product was required for sucrose-dependent colonization in vitro. In addition, evidence for the presence of a third gtf gene coding for soluble glucan synthesis was obtained following the construction of mutants containing deletions of both the gtfB and gtfC genes.
Full text
PDF



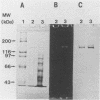
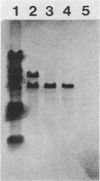
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K. J., Cornish-Bowden A., Cole J. A. Purification and properties of nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):483–493. doi: 10.1042/bj1750483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R., Morrissey P. Cloning and expression of two Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):414–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.414-416.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of Steptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):738–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.738-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Wondrack L. Insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans serotype c strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of basic glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 28;719(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Tsumori H., Shimamura A. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.790-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B. M., White P., Mohan S. B., Cole J. A. Effect of dextran and ammonium sulphate on the reaction catalysed by a glucosyltransferase complex from Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):353–366. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. A., Bleiweis A. S., Small P. A., Jr Adherence inhibition of Streptococcus mutans: an assay reflecting a possible role of antibody in dental caries prophylaxis. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):419–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.419-427.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Wondrack L. M., Kuramitsu H. K. Genetic transformation of putative cariogenic properties in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.722-727.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Jones K. R., Kuramitsu H. K., Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the glucosyltransferase C gene (gtfC) from Streptococcus mutans LM7. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2176–2182. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2176-2182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of a fructosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):166–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.166-170.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tsumori H., Mukasa H. Three kinds of extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans 6715 (serotype g). FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfB gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4263–4270. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4263-4270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Molecular basis for the spontaneous generation of colonization-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):135–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]