Abstract
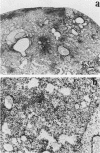
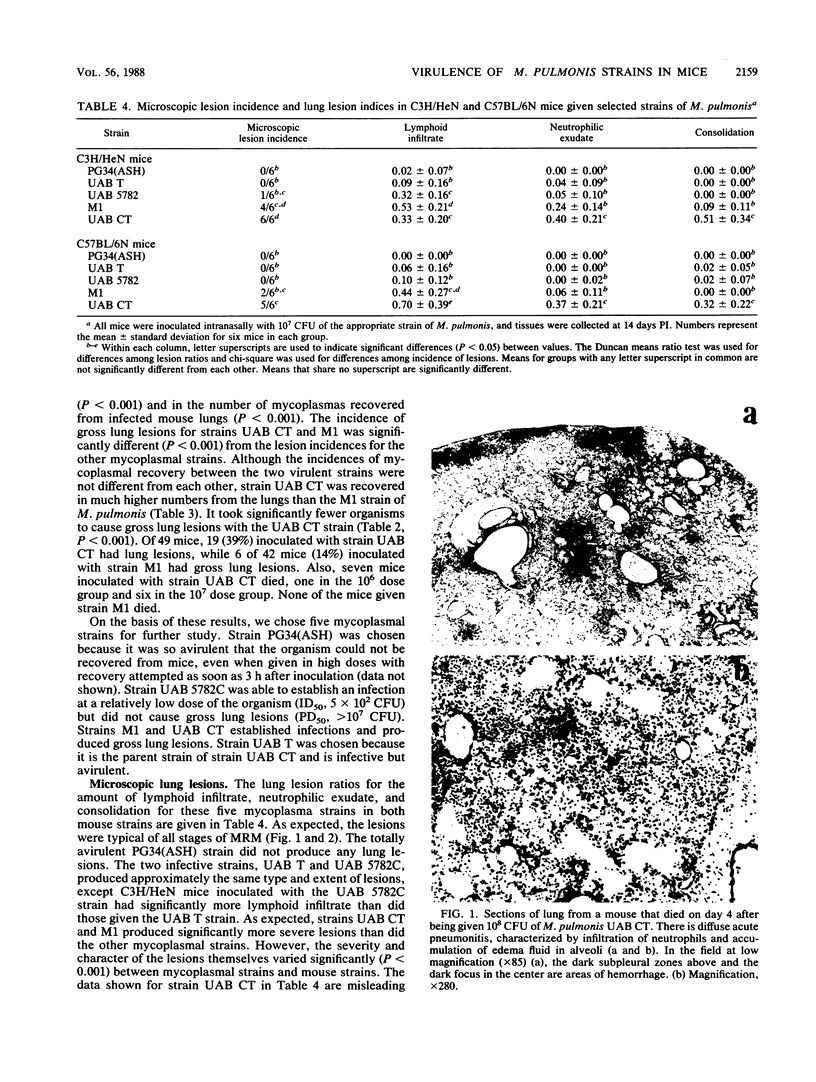
The mouse model of acute murine respiratory mycoplasmosis was used to screen 18 strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis for their ability to establish respiratory infections and produce gross lung lesions in the susceptible C3H/HeN mouse strain. All experiments were designed to minimize host, environmental, and microbial differences to ensure that experimental results would reflect differences in mycoplasmal virulence. There were differences in the 50% infectious dose (range, 3 X 10(2) to greater than 10(7) CFU) and the 50% gross pneumonia dose (range, 10(3) to greater than 10(7) CFU) among the 18 mycoplasmal strains. Only 10 strains (UAB CT, M1, UAB 5782C, UAB 6510, 66, UAB T, UAB 8145D, Nelson C, Peter C, and Negroni) established respiratory infections, and only 2 of the 10 strains (UAB CT and M1) produced gross lung lesions. Strains UAB CT, UAB T, M1, UAB 5782C, and PG34(ASH) were chosen for qualitative and quantitative evaluation of lung lesions in C3H/HeN and C57BL/6N mice. Lesion incidence and severity was dependent on the mycoplasmal strain and the mouse strain. Microscopic lesions varied among mycoplasmal strains and mouse strains in the amount of lymphoid infiltrate, neutrophilic exudate, and consolidation, as well as overall severity. The most virulent strain, UAB CT, produced acute pneumonitis in the 10(7) CFU dosage group and required a threshold dose of 10(3) CFU to consistently produce microscopic lung lesions. These results suggest that M. pulmonis virulence is multifactorial and different strains of mycoplasmas yield disease expressions that differ both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barden J. A., Tully J. G. Experimental arthritis in mice with Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):5–10. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.5-10.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broderson J. R., Lindsey J. R., Crawford J. E. The role of environmental ammonia in respiratory mycoplasmosis of rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Oct;85(1):115–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H. Derrick Edward Award Lecture. The pathogenic potential of mycoplasmas: Mycoplasma pulmonis as a model. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S18–S34. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Parker R. F., White H., Dziedzic D., Taylor G., Davidson M. K., Cox N. R., Cassell G. H. Strain differences in susceptibility to murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in C57BL/6 and C3H/HeN mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):647–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.647-654.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Thorp R. B., Maddox P. A., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in F344 and LEW rats: evolution of lesions and lung lymphoid cell populations. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):720–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.720-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Thorp R. B., Parker R. F., White H., Dziedzic D., D'Arcy J., Cassell G. H. Development of an aerosol model of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):194–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.194-201.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Cassell G. H., Gambill G., Cox N., Watson H., Davidson M. Diagnosis of murine mycoplasmal infections by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):717–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice R. A., Robillard N. F., Carski T. R. Immunofluorescence identification of Mycoplasma on agar by use of incident illumination. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1205–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1205-1209.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. The pleuropneumonia group of organisms: a review, together with some new observations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. A., Cassell G. H. Detection of antibodies to Mycoplasma pulmonis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):161–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.161-170.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G. Variation in the virulence of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis related to susceptibility to killing by macrophages in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):289–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Cassell H. Experimental Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in pathogen-free mice. Models for studying mycoplasmosis of the respiratory tract. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jul;72(1):63–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Haemadsorption and haemagglutination by mycoplasmas. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):465–478. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Tully J. G., Ginsburg H. Lymphocyte activation by various Mycoplasma strains and species. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.310-317.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Ota T., Atobe H. [Studies on Mycoplasma of roden origin--Mycoplasma from chronic respiratory diseases in rats]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1967 Dec;22(11):618–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinson D. M., Schoeb T. R., Lindsey J. R., Davis J. K. Evaluation by scoring and computerized morphometry of lesions of early Mycoplasma pulmonis infection and ammonia exposure in F344/N rats. Vet Pathol. 1986 Sep;23(5):550–555. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Nakagawa M., Muto T., Imaizumi K. Strain difference of mouse in susceptibility to Mycoplasma pulmonis infection. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1978 Dec;40(6):697–705. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.40.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Nakagawa M., Suzuki E., Kinoshita K., Imaizumi K. Synergistic effect of Sendai virus on Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in mice. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1981 Feb;43(1):43–50. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.43.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeb T. R., Davidson M. K., Lindsey J. R. Intracage ammonia promotes growth of Mycoplasma pulmonis in the respiratory tract of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):212–217. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.212-217.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeb T. R., Kervin K. C., Lindsey J. R. Exacerbation of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in gnotobiotic F344/N rats by Sendai virus infection. Vet Pathol. 1985 May;22(3):272–282. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeb T. R., Lindsey J. R. Exacerbation of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis by sialodacryoadenitis virus infection in gnotobiotic F344 rats. Vet Pathol. 1987 Sep;24(5):392–399. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G. BIOCHEMICAL, MORPHOLOGICAL, AND SEROLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MYCOPLASMA OF MURINE ORIGIN. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:171–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Davies H. A., Manchee R. J., Mouches C., Bove J. M. Mycoplasmal adherence with particular reference to the pathogenicity of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J. Interaction of Mycoplasma pulmonis with mouse peritoneal macrophages and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–30. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rask-Nielsen R. Mycoplasma in leukemic and nonleukemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., Cox N. R., Davidson M. K., Blalock D. K., Davis J. K., Dybvig K., Horowitz S. A., Cassell G. H. Mycoplasma pulmonis proteins common to murine mycoplasmas. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. S., Davis J. K., Cassell G. H. Polyclonal activation of rat splenic lymphocytes after in vivo administration of Mycoplasma pulmonis and its relation to in vitro response. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.594-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]