Abstract
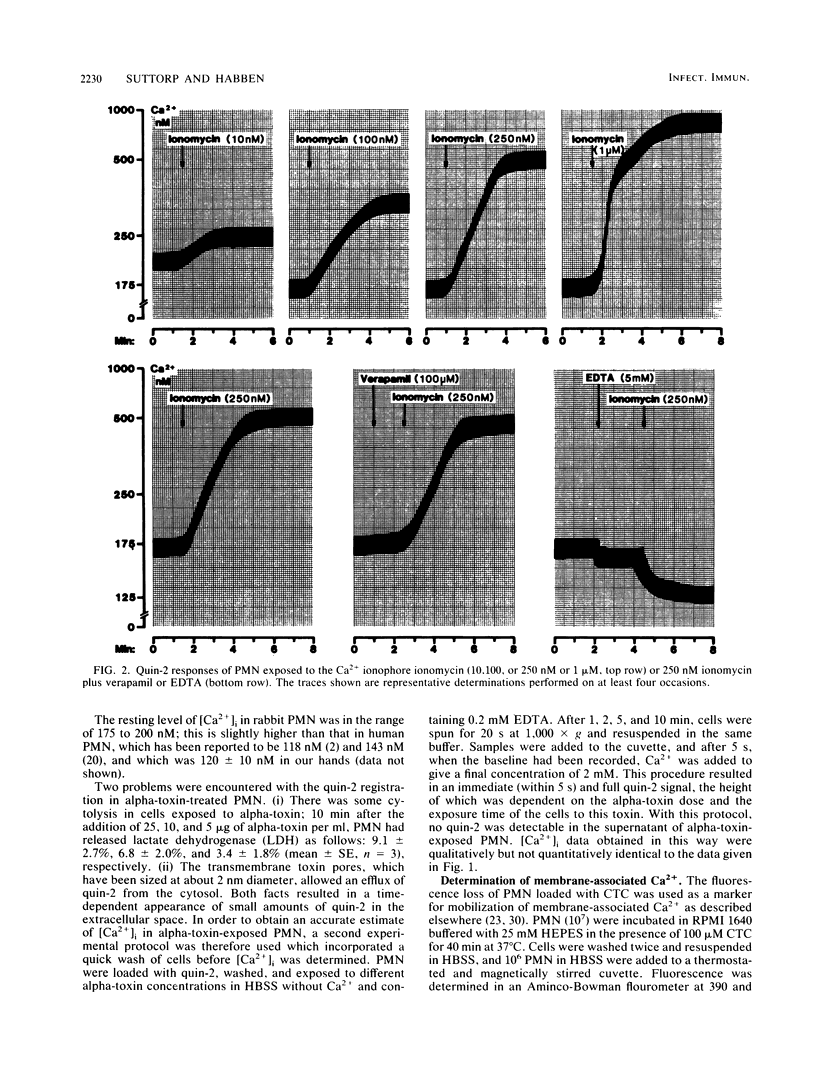
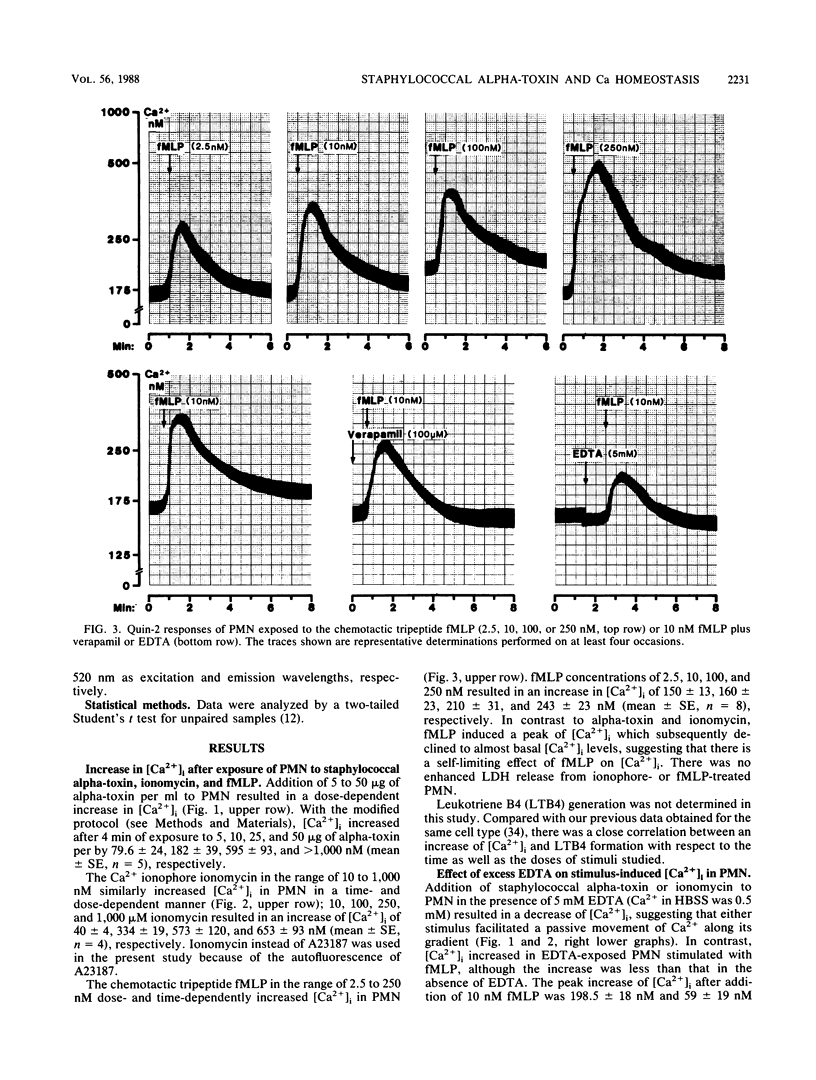
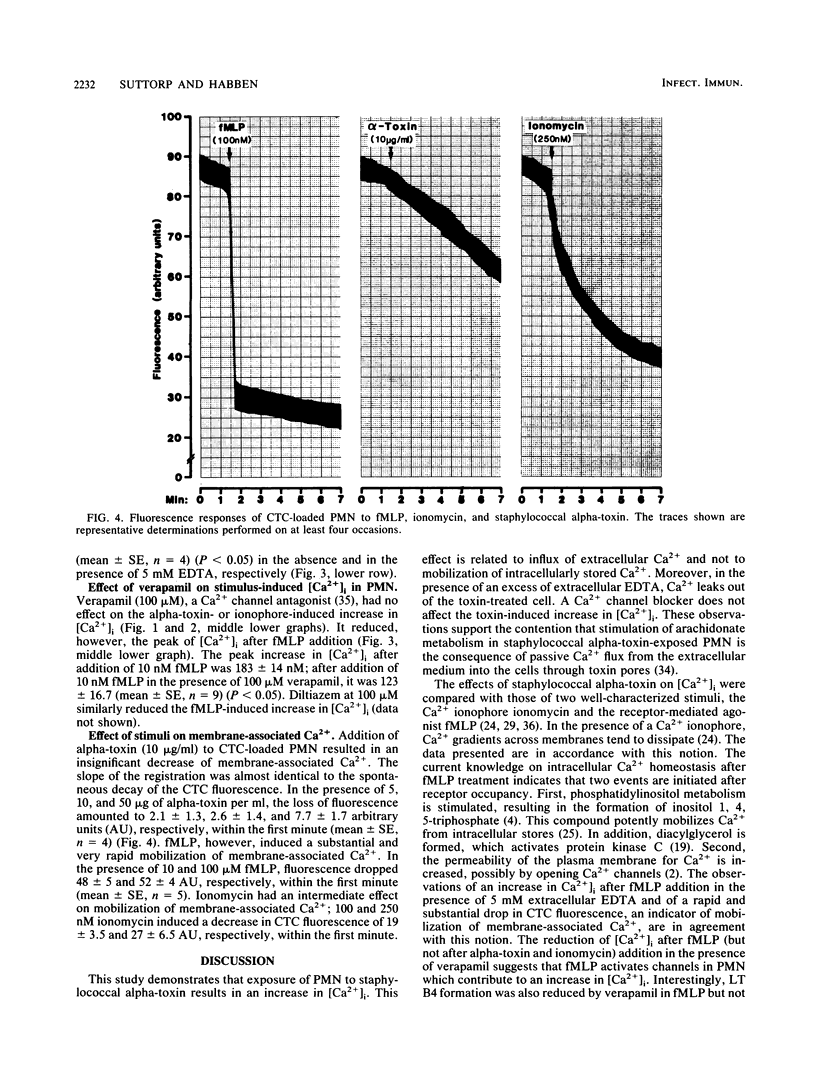
Staphylococcal alpha-toxin, a channel-forming protein, stimulates leukotriene B4 formation in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) (N. Suttorp, W. Seeger, J. Zucker-Reimann, L. Roka, and S. Bhakdi, Infect. Immun. 55:104-110, 1987). The concept was advanced that transmembrane toxin pores act as Ca2+ gates allowing passive Ca2+ influx into the cell, thus initiating stimulus response coupling. A critical step in this hypothesis is the demonstration of an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration [( Ca2+]i). [Ca2+]i and membrane-associated Ca2+ were therefore monitored in quin-2- or chlorotetracycline-loaded PMN exposed to alpha-toxin. The effects of the Ca2+ ionophore ionomycin and the chemotactic tripeptide formylmethionyl-leucylphenylalanine (fMLP) were studied in parallel. All stimuli increased [Ca2+]i in dose- and time-dependent manner. In the presence of an EDTA excess there was a decrease of [Ca2+]i due to an efflux of Ca2+ in alpha-toxin- and ionomycin-treated cells, while addition of fMLP still induced an increase of [Ca2+]i. In the presence of verapamil, a Ca2+ channel blocker, [Ca2+]i was reduced after stimulation with fMLP but not with alpha-toxin or ionomycin. Addition of fMLP and ionomycin but not of alpha-toxin to PMN resulted in a rapid and substantial mobilization of membrane-associated Ca2+. The collective data demonstrate that exposure of PMN to staphylococcal alpha-toxin results in an increase in [Ca2+]i which is due to an influx of extracellular Ca2+ and not to a mobilization of intracellularly stored Ca2+. The concept of initiating stimulus response coupling by Ca2+ influx through transmembrane pores may be generally applicable to other channel-forming cytolysins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Minimal requirements for exocytosis. A study using PC 12 cells permeabilized with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12730–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson T., Dahlgren C., Pozzan T., Stendahl O., Lew P. D. Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Füssle R. Correlation between toxin binding and hemolytic activity in membrane damage by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.318-323.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Sziegoleit A. Mechanism of membrane damage by streptolysin-O. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.52-60.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bianca V., Grzeskowiak M., De Togni P., Cassatella M., Rossi F. Inhibition by verapamil of neutrophil responses to formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine and phorbol myristate acetate. Mechanisms involving Ca2+ changes, cyclic AMP and protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 30;845(2):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Ionic channels in leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Mar;39(3):241–254. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro R., Pozzan T., Romeo D. Monitoring of cytosolic free Ca2+ in C5a-stimulated neutrophils: loss of receptor-modulated Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ uptake in granule-free cytoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Sinner A., Reichwein J., Bhakdi S. Quantitation of monomeric and oligomeric forms of membrane-bound staphylococcal alpha-toxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2933–2939. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2933-2939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Wollheim C., Seger R. A., Pozzan T. Cytosolic free calcium changes induced by chemotactic peptide in neutrophils from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):231–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P., Campbell A. K. The recovery of human polymorphonuclear leucocytes from sublytic complement attack is mediated by changes in intracellular free calcium. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):205–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2310205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Involvement of membrane calcium in the response of rabbit neutrophils to chemotactic factors as evidenced by the fluorescence of chlorotetracycline. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):179–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Lew D. P., Wollheim C. B., Tsien R. Y. Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.6310757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B., Lew P. D. Ca2+ homeostasis in permeabilized human neutrophils. Characterization of Ca2+-sequestering pools and the action of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13777–13782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichwein J., Hugo F., Roth M., Sinner A., Bhakdi S. Quantitative analysis of the binding and oligomerization of staphylococcal alpha-toxin in target erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2940–2944. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2940-2944.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Bauer M., Bhakdi S. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin elicits hypertension in isolated rabbit lungs. Evidence for thromboxane formation and the role of extracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):849–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI111502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Suttorp N., Hellwig A., Bhakdi S. Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Hyslop P. A., Oades Z. G., Omann G. M., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G. Signal transduction and ligand-receptor dynamics in the human neutrophil. Transient responses and occupancy-response relations at the formyl peptide receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11461–11467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Noble P., Freed R., Weissmann G. Metabolic requirements for maintenance of the chlortetracycline-labeled pool of membrane-bound calcium in human neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):415–422. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Dewein E., Bhakdi S., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced PGI2 production in endothelial cells: role of calcium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C127–C134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Uhl J., Lutz F., Roka L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin stimulates prostacyclin production in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells: membrane attack and calcium influx. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zinsky S., Bhakdi S. Complement complex C5b-8 induces PGI2 formation in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C13–C21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zucker-Reimann J., Roka L., Bhakdi S. Mechanism of leukotriene generation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):104–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.104-110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggle D. J., Janis R. A. Calcium channel ligands. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:347–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Baggiolini M. Calcium fluxes and calcium buffering in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10163–10168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



