Abstract
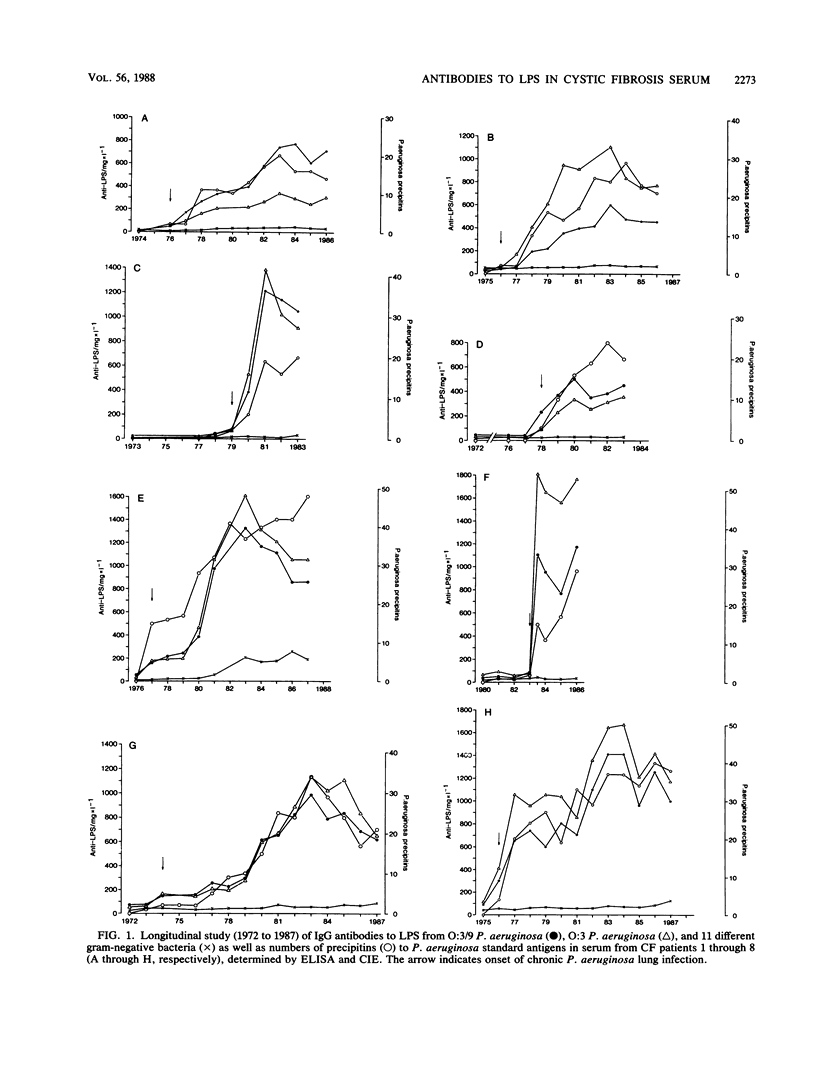
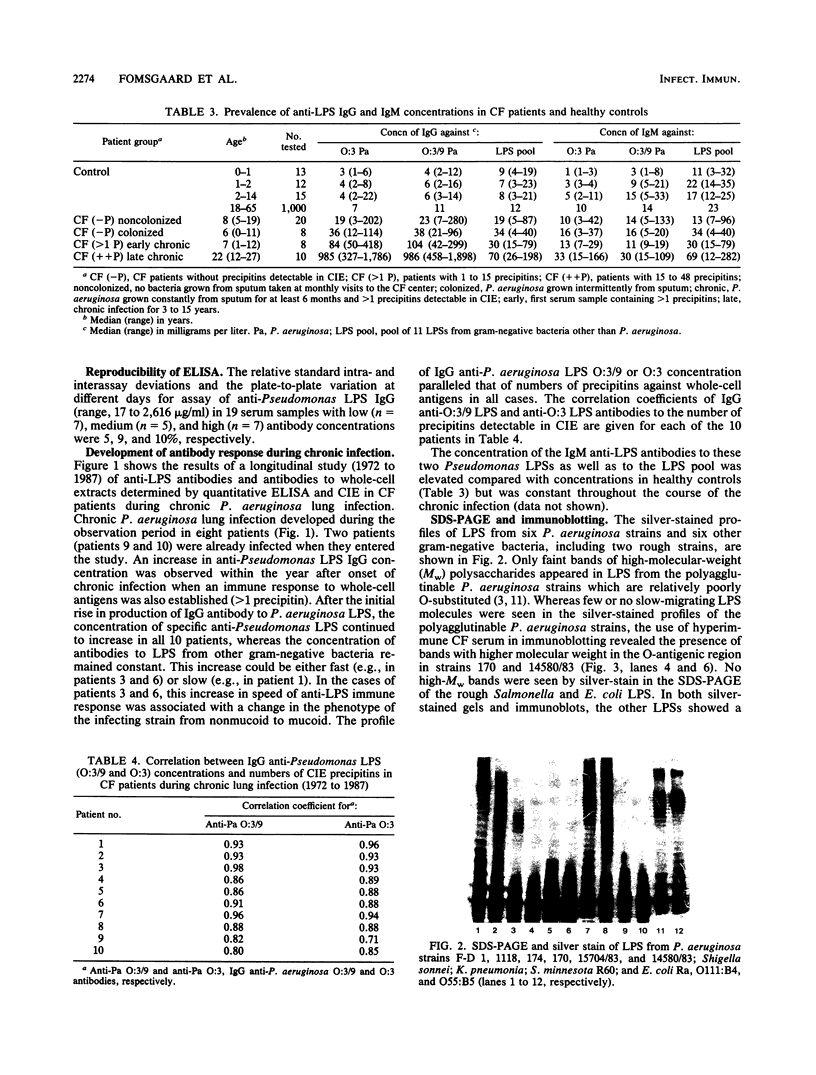
Antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa from 10 cystic fibrosis patients with chronic P. aeruginosa lung infections were quantitatively and qualitatively analyzed. The development of specific antibodies in patient serum was evaluated in a longitudinal study (1972 to 1987). The concentrations and specificities of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibodies to purified lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa and to a variety of other gram-negative bacteria were studied by immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques. Results were compared with the number of immunoprecipitates to P. aeruginosa whole-cell extracts detected by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. IgG, but not IgM, anti-Pseudomonas LPS concentrations increased significantly at the onset of chronic infection and continued to increase during the course of the infection. There was a good positive correlation between the concentration of IgG anti-Pseudomonas LPS antibodies and the number of crossed-immunoelectrophoresis precipitins. The increases in IgG anti-LPS antibody concentrations were much higher to Pseudomonas LPS than to other LPSs. Binding studies demonstrated an increase in binding of IgG anti-Pseudomonas LPS during infection, whereas the binding of other anti-LPS antibodies decreased. Immunoblotting studies confirmed that antibodies reacted strongly with Pseudomonas LPS and weakly with Escherichia coli core-lipid A. The specificity of the reaction with Pseudomonas LPS increased with the duration of infection. It is concluded that anti-LPS response in cystic fibrosis patients during chronic P. aeruginosa infection demonstrates a marked increase in IgG anti-Pseudomonas LPS antibody concentration, specificity, and affinity. The anti-LPS enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is proposed as a routine test to diagnose and to follow the course of chronic P. aeruginosa lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF






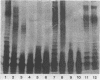
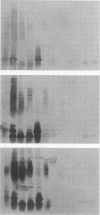
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Döring G., Høiby N. Longitudinal study of immune response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.197-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Comparative immunochemistry of lipopolysaccharides from typable and polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.821-826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Dinesen B., Baek L. Anti-lipopolysaccharide antibodies measured by enzyme-immunoassay in Danish blood donors. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1987 Feb;95(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Dinesen B. ELISA for human IgG and IgM anti-lipopolysaccharide antibodies with indirect standardization. J Immunoassay. 1987;8(4):333–350. doi: 10.1080/15321818708057032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Feldt-Rasmussen B., Deckert M., Dinesen B. Micro-ELISA for the quantitation of human urinary IgG. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;47(2):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Nielsen R., Froberg K. D., Baek L., Deghn H. K. Endotoxinaemia in toxic shock syndrome treated with anti-endotoxin antibodies. Lancet. 1987 Feb 28;1(8531):514–515. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Flensborg E. W., Beck B., Friis B., Jacobsen S. V., Jacobsen L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitins determined by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1977 Apr;58(2):65–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Sompolinsky D. Antibody response in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection to a 'common antigen' from P. aeruginosa analysed by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Jun;88(3):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Rosendal K. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients treated at a cystic fibrosis centre. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Straus D. C., Hilton C. B., Bass J. A. Antibodies to proteases and exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis: Demonstration by radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):49–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E., Høiby N., Lam K., Baek L., Costerton J. W. Immunogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens examined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):88–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.88-98.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N. Diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Todd H. C., Mackintosh C. A., Im S. W. Evaluation of three serological tests for detection of antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human sera. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):190–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02013596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Kania S. A., Warren H. S. Cross-reactivity of rabbit antibodies to lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli J5 and other gram-negative bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):954–964. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimakoff J., Høiby N., Rosendal K., Guilbert J. P. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and the role of contamination of the environment in a cystic fibrosis clinic. J Hosp Infect. 1983 Mar;4(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(83)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., McCabe W. R. Effects of IgM and IgG antibody in patients with bacteremia due to gram-negative bacilli. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):37–45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]