Abstract
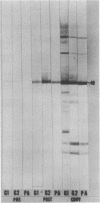
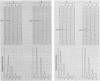
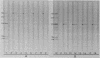
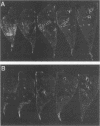
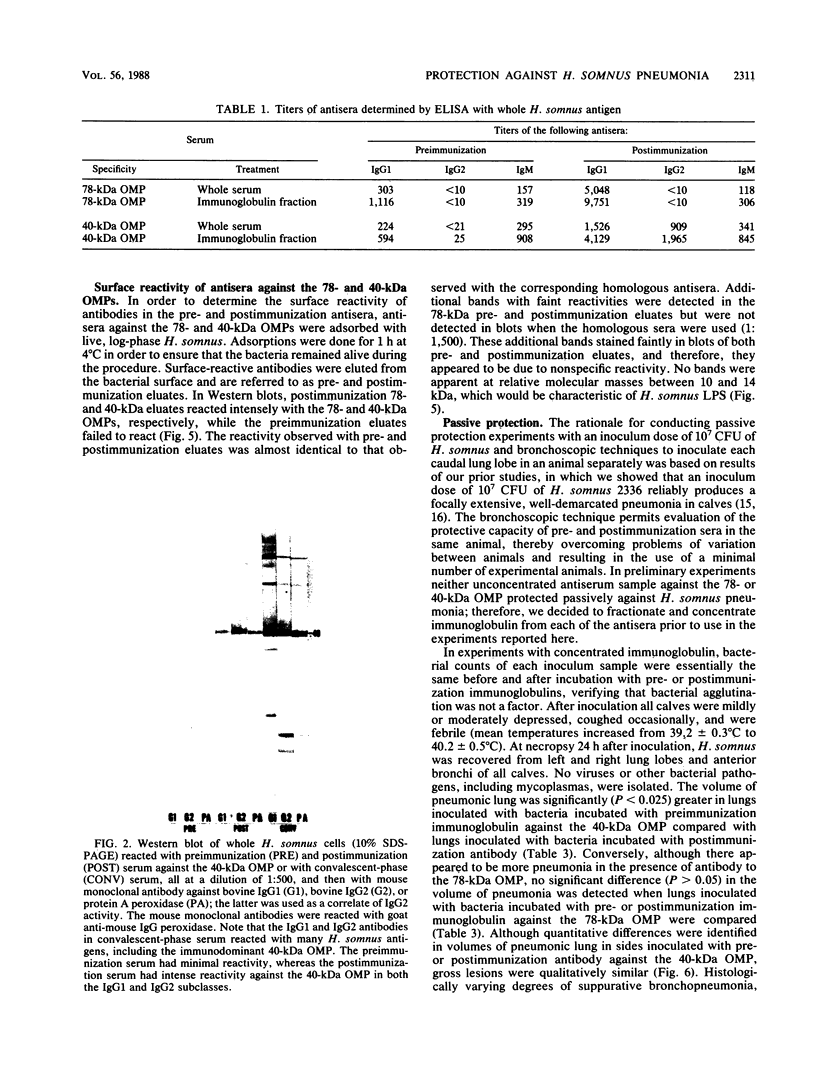
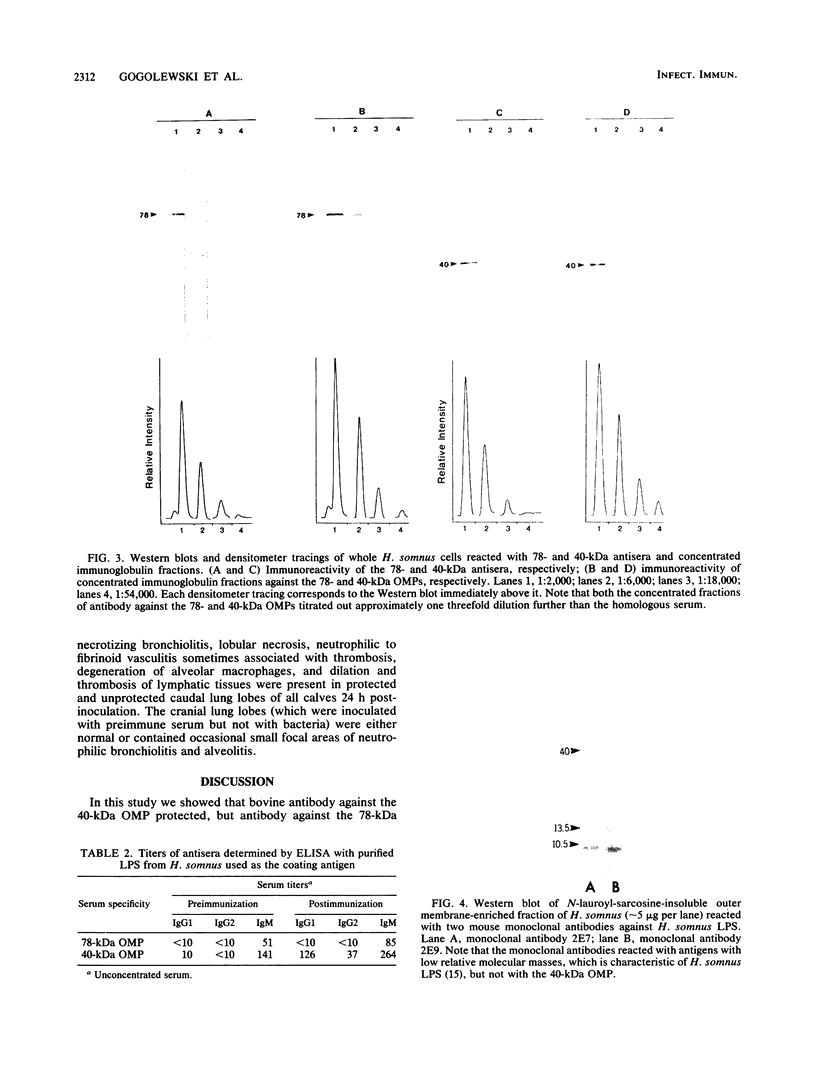
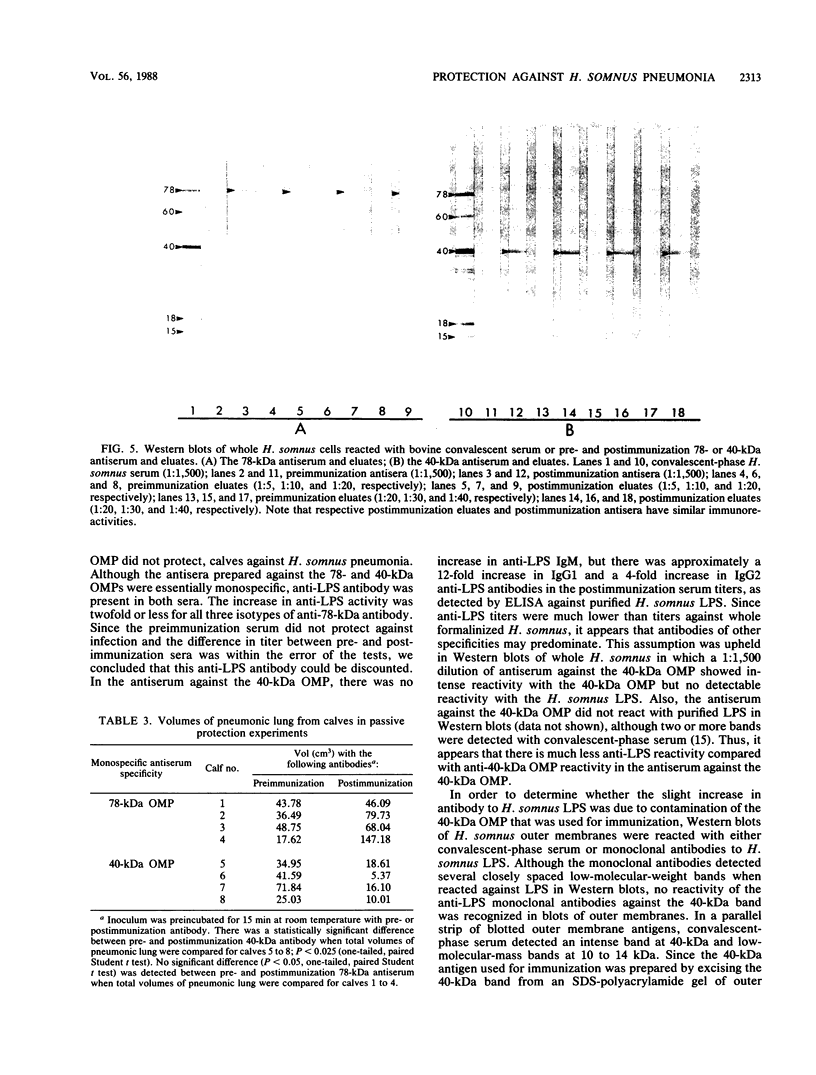
The ability of concentrated antibody against the 78- or 40-kilodalton (kDa) outer membrane protein (OMP) of Haemophilus somnus to passively protect calves against H. somnus-induced pneumonia was determined. The 78- and 40-kDa OMPs were evaluated in passive protection experiments, because results of previous studies demonstrated their (i) immunogenicity for cattle, (ii) intense reactivity with convalescent-phase sera which passively protected calves against experimental H. somnus pneumonia, (iii) surface location and accessibility to antibody, and (iv) conservation among a wide range of H. somnus isolates obtained from animals with different diseases and from different geographic locations. The specificity of the two antisera evaluated in this study was verified by (i) immunoblots in which reactivity against the 78- or 40-kDa OMP was present in postimmunization but not preimmunization serum and (ii) immunoblots in which affinity-purified, surface-reactive antibodies in each antisera were used, which demonstrated that essentially only antibody to the 78- or 40-kDa OMP was reactive with the surface of H. somnus. In enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, the antiserum against the 40-kDa OMP contained immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), IgG2, and IgM against H. somnus, while the antiserum against the 78-kDa OMP contained IgG1 and IgM but no IgG2 against H. somnus. The antiserum against the 40-kDa OMP contained IgG1 and IgG2 specific for the 40-kDa OMP, as determined by Western blot analysis. Slight reactivity against H. somnus lipopolysaccharide was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay but not by Western blot analysis. In passive protection experiments, preincubation of bacteria with antibody against the 40-kDa OMP protected calves (P less than 0.025) against H. somnus pneumonia, while antibody against the 78-kDa OMP failed to protect calves against H. somnus pneumonia. Determination of the potential protective capacity of the 78-kDa OMP awaits resolution of the role of anti-78-kDa IgG2 in protection against H. somnus pneumonia. The 40-kDa OMP is, however, a good candidate antigen for evaluation of protective ability against H. somnus pneumonia following active immunization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. J., Anderson T. D., Slife L. N., Stevenson G. W. Microscopic lesions associated with the isolation of Haemophilus somnus from pneumonic bovine lungs. Vet Pathol. 1985 Mar;22(2):131–136. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R., Douglas R. M., Schiffman G., Coetzee A. M., Koornhof H. J., Hayden-Smith S., Reid R. D. Prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia by vaccination. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1976;89:184–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Biological Activities of Rabbit Immunoglobulin M and Immunoglobulin G Antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):453–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.453-461.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandon M. R., Watson D. L., Lascelles A. K. The mechanism of transfer of immunoglobulin into mammary secretion of cows. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Dec;49(6):613–623. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chladek D. W. Bovine abortion associated with Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):1041–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Arthur J. E., Widders P. R., Smith J. W., Barbet A. F. Antigenic specificity of convalescent serum from cattle with haemophilus somnus-induced experimental abortion. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1381–1386. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1381-1386.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Blau K., Prieur D. J., Ward A. C. Serum susceptibility of Haemophilus somnus from bovine clinical cases and carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.192-198.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Watt B., Corbeil R. R., Betzen T. G., Brownson R. K., Morrill J. L. Immunoglobulin concentrations in serum and nasal secretions of calves at the onset of pneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Apr;45(4):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Widders P. R., Gogolewski R., Arthur J., Inzana T. J., Ward A. C. Haemophilus somnus: Bovine Reproductive and Respiratory Disease. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corboz L., Nicolet J. Infektionen mit sogenannten "Haemophilus somnus" beim Rind: Isolierung und Charakterisierung von Stämmen aus Respirations-und Geschlechtsorganen. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1975 Sep;117(9):493–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Wilkie B. N., Winter A. J. Natural and immune antibodies for Vibrio fetus in serum and secretions of cattle. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):728–733. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.728-733.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery D. L., Stewart D. J. Phagocytosis of Bacteroides nodosus by ovine peripheral blood leucocytes. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Apr;9(2):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Leathers C. W., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Experimental Haemophilus somnus pneumonia in calves and immunoperoxidase localization of bacteria. Vet Pathol. 1987 May;24(3):250–256. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Hansen E. J. Coprecipitation of lipopolysaccharide and the 39,000-molecular-weight major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b by lipopolysaccharide-directed monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):819–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.819-827.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. F., Williams J. M., Smith G. L. Field evaluation of Haemophilus somnus bacterin. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1977 Aug;72(8):1368–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Stephens L. R., Thorsen J. Occurrence of "Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):215–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Corbeil L. B. Development of a defined medium for Haemophilus somnus isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):366–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. W., Watson D. L. Cellular basis for differences in humoral immune responses of sheep immunized with living or killed Staphylococcus aureus vaccines. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1982 Dec;60(6):643–654. doi: 10.1038/icb.1982.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster M. J., McGillivery D. J., Patterson R. M., Irwin S. Pneumonia associated with Haemophilus somnus in a calf. Aust Vet J. 1984 Aug;61(8):269–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1984.tb15545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Ball D. R., Hoffmann E. M., Desjardin L. E., Boyle M. D. Production of Brucella abortus-specific protein A-reactive antibodies (IgG2) in infected and vaccinated cattle. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jun;12(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R. Protection of infant rats from Haemophilus influenzae type b infection by antiserum to purified outer membrane protein a. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2612-2618.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Acres S., Janzen E., Willson P., Allen B. A field trial of preshipment vaccination of calves. Can Vet J. 1984 Mar;25(3):145–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J. Biologic activities of bovine IgG subclasses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Small G. J., Lostrom M. E., Pier G. B. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibody therapy for experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.239-244.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Macleod N. S. The isolation of Haemophilus somnus following sudden deaths in suckler calves in Scotland. Vet Rec. 1977 Feb 12;100(7):126–127. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.7.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxén H., Nurminen M., Kuusi N., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Evidence for the importance of O antigen specific antibodies in mouse-protective Salmonella outer membrane protein (porin) antisera. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Isolation of Haemophilus somnus antigens and their use as vaccines for prevention of bovine thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Feb;45(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Evaluation of attenuated, live staphylococcal mastitis vaccine in lactating heifers. J Dairy Sci. 1984 Nov;67(11):2608–2613. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Immunologically-specific resistance to infection with particular reference to staphylococcal mastitis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:579–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widders P. R., Paisley L. G., Gogolewski R. P., Evermann J. F., Smith J. W., Corbeil L. B. Experimental abortion and the systemic immune response to "Haemophilus somnus" in cattle. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):555–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.555-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikse S. E. Feedlot cattle pneumonia. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1985 Jul;1(2):289–310. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)31328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]