Abstract
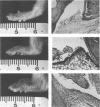
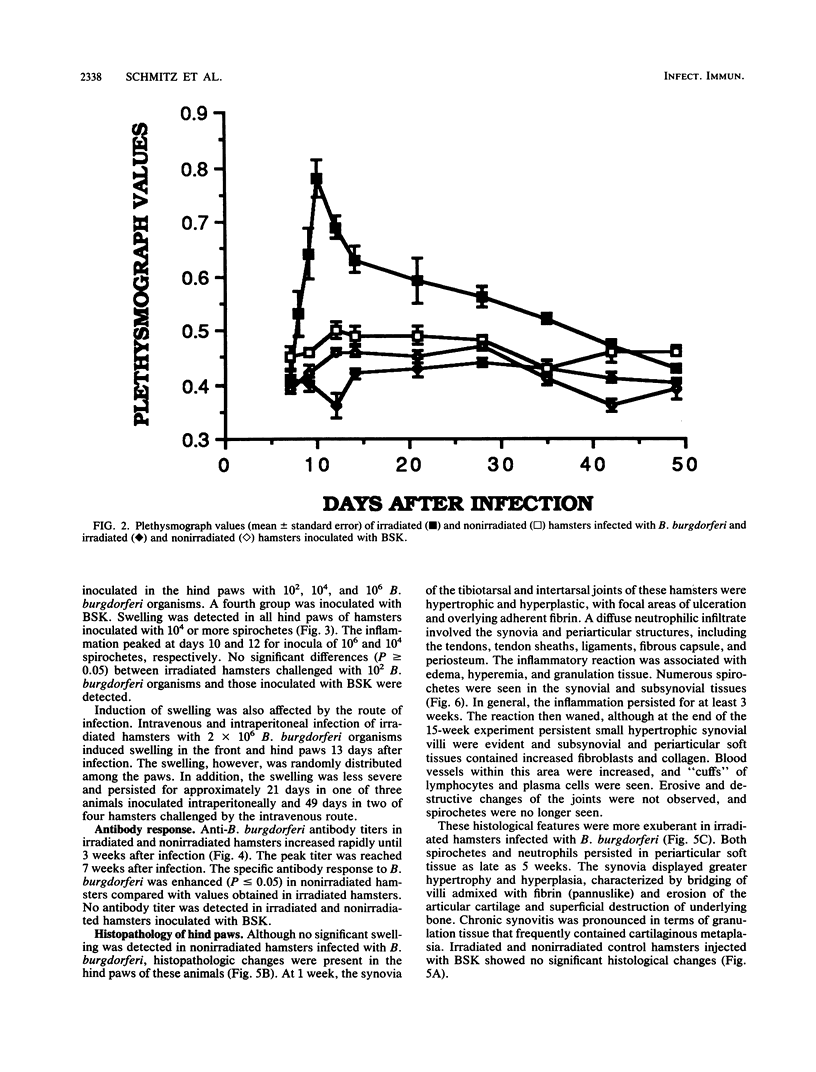
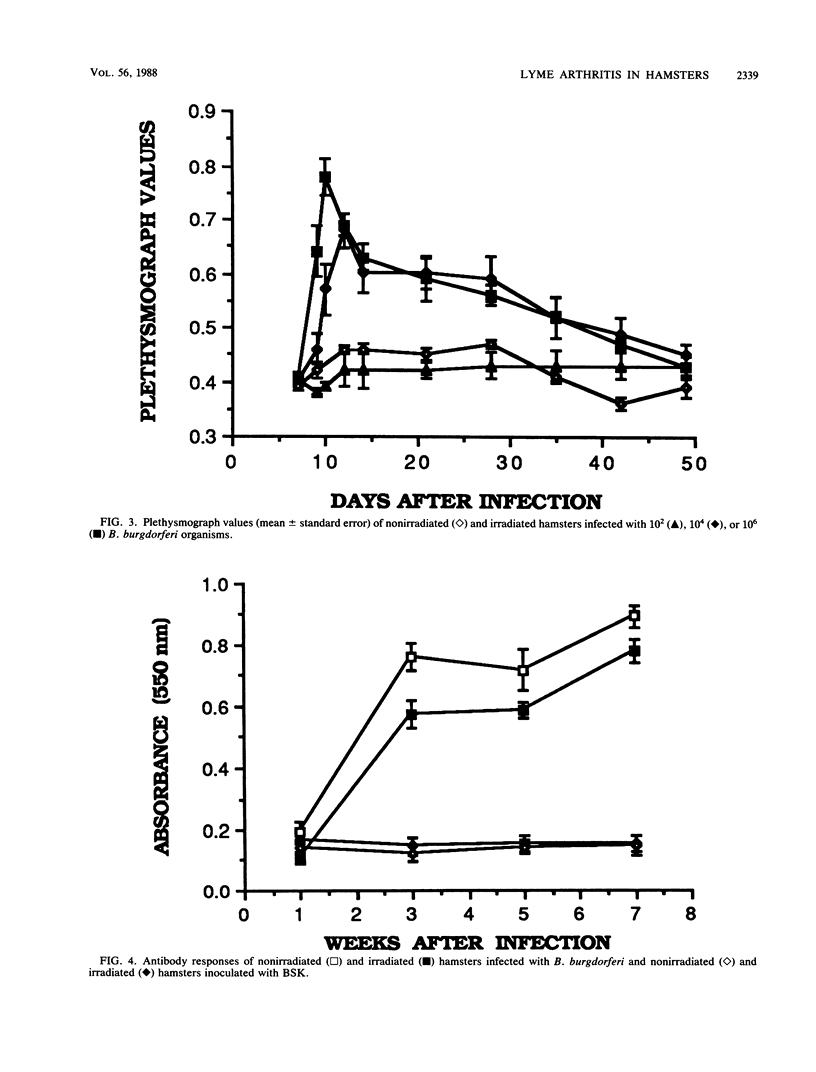
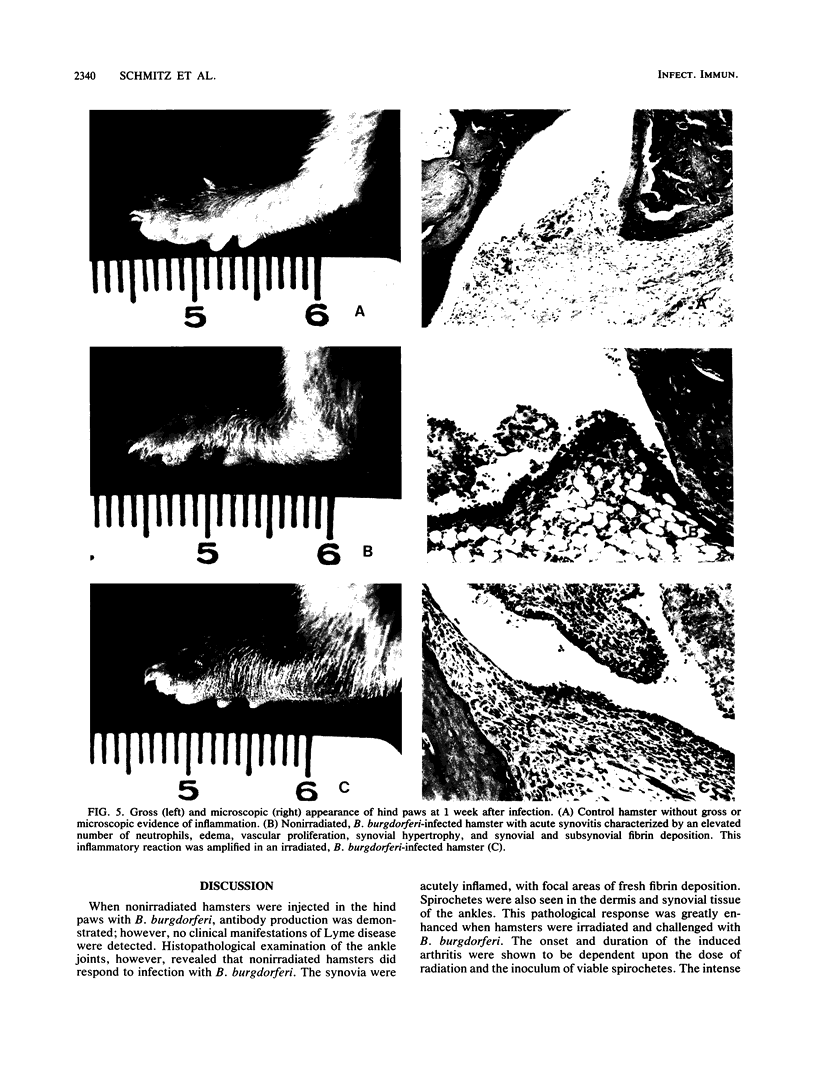
In studies of experimental Lyme disease, a major obstacle has been the unavailability of a suitable animal model. We found that irradiated LSH/Ss Lak hamsters developed arthritis after injection of Borrelia burgdorferi in the hind paws. When nonirradiated hamsters were injected in the hind paws with B. burgdorferi, acute transient synovitis was present. A diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate involved the synovia and periarticular structures. The inflammation was associated with edema, hyperemia, and granulation tissue. Numerous spirochetes were seen in the synovial and subsynovial tissues. The histopathologic changes were enhanced in irradiated hamsters. The onset and duration of the induced swelling were dependent on the dose of radiation and the inoculum of spirochetes. Inoculation of irradiated hamsters with Formalin-killed spirochetes or medium in which B. burgdorferi had grown for 7 days failed to induce swelling. This animal model should prove useful for studies of the immune response to B. burgdorferi and the pathogenesis of Lyme arthritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Duray P. H., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. Experimental Lyme arthritis in rats infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):842–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Gage K. L. Susceptibility of the hispid cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) to the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Nov;37(3):624–628. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. The New Zealand white rabbit: an experimental host for infecting ticks with Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):609–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Active immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):897–898. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.897-898.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, to four antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Passive immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):713–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.713-714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Steere A. C., Brownstein D. G. Infection in rabbits with the Lyme disease spirochete. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):613–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky W. L., Brown S. J., Askenase P. W. Ixodes dammini: induced skin lesions in guinea pigs and rabbits compared to erythema chronicum migrans in patients with lyme arthritis. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Jun;53(3):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L., Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Shope R. E., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Jul;58(4):281–294. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Batsford W. P., Weinberg M., Alexander J., Berger H. J., Wolfson S., Malawista S. E. Lyme carditis: cardiac abnormalities of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):8–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]