Abstract
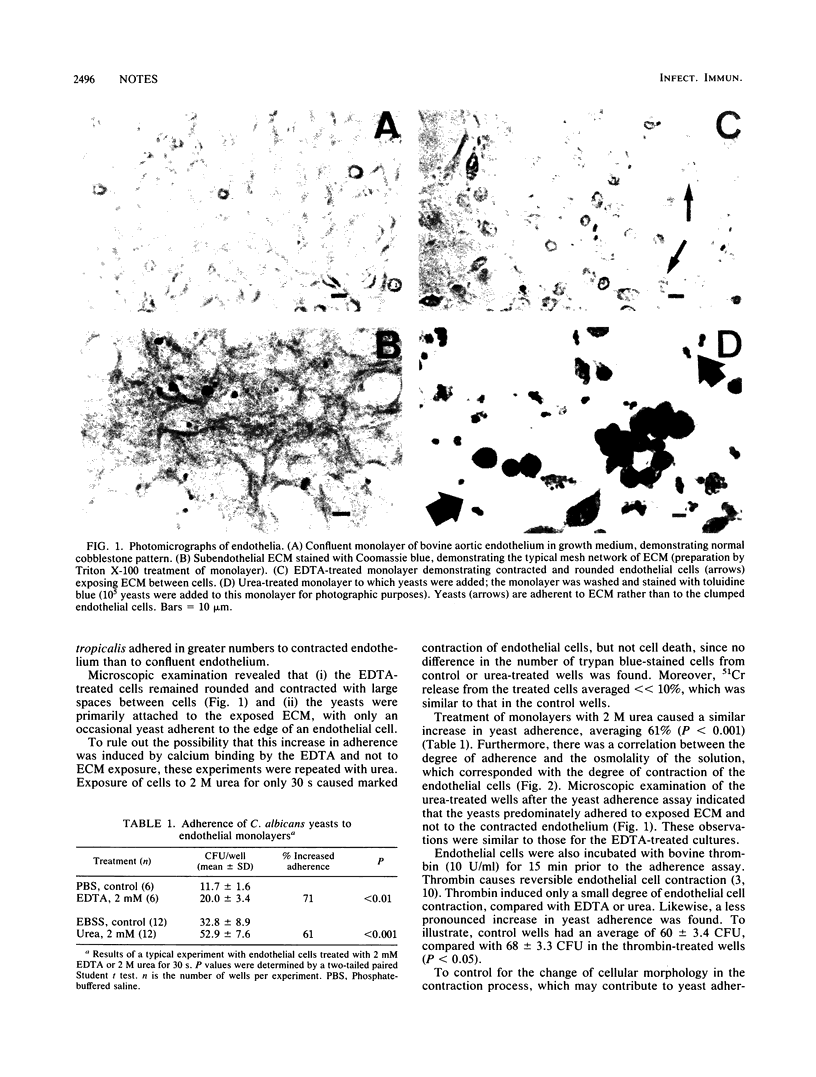
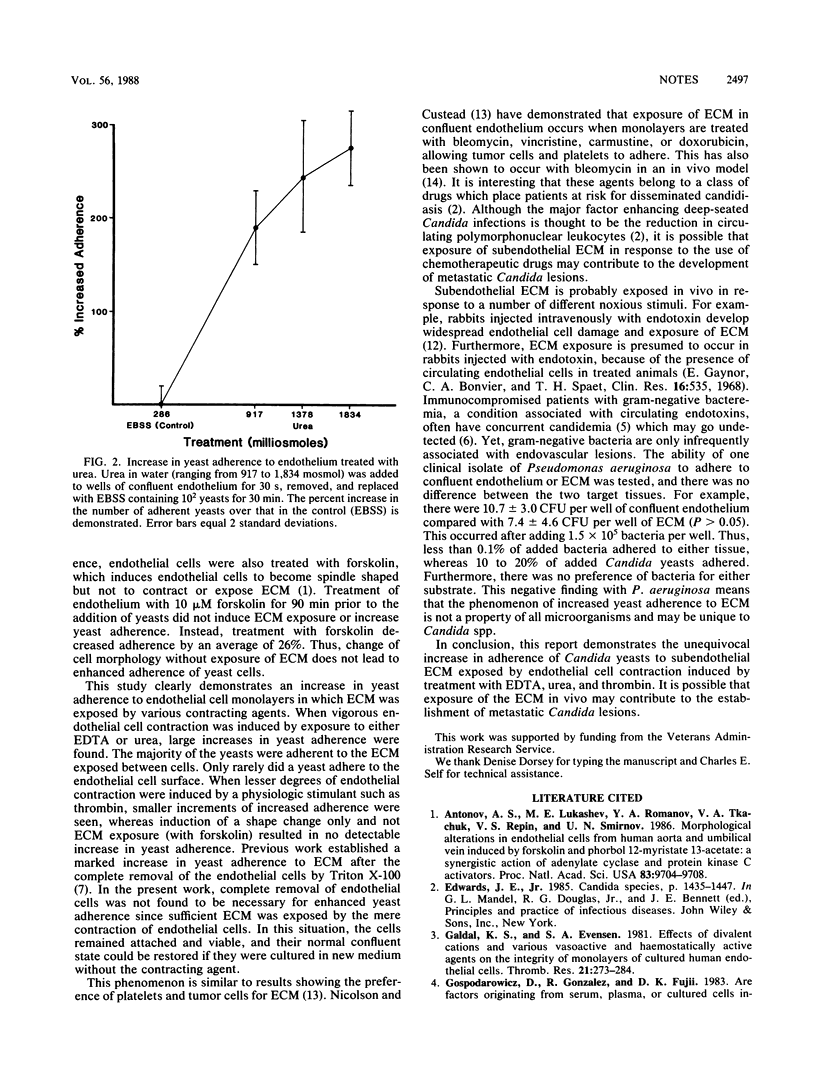
Bovine vascular endothelial cells treated with EDTA, urea, or thrombin underwent a marked, reversible contraction resulting in exposure of the subendothelial extracellular matrix (ECM). Candida yeasts adhered more to contracted monolayers than to confluent monolayers (P less than 0.01) by preferentially adhering to the ECM. Two strains of Candida albicans and one strain of Candida tropicalis bound avidly to exposed ECM, but Pseudomonas aeruginosa did not. However, treatment of endothelium with forskolin, which induces cell shape changes without exposure of the ECM, did not cause an increase in adherence.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonov A. S., Lukashev M. E., Romanov Y. A., Tkachuk V. A., Repin V. S., Smirnov V. N. Morphological alterations in endothelial cells from human aorta and umbilical vein induced by forskolin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate: a synergistic action of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C activators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9704–9708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A. Effects of divalent cations and various vasoactive and haemostatically active agents on the integrity of monolayers of cultured human endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1981 Feb 1;21(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. L., Myers J. P. Nosocomial fungemia in a large community teaching hospital. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Dec;147(12):2117–2120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockey L. J., Fujita N. K., Gibson T. R., Rotrosen D., Montgomerie J. Z., Edwards J. E., Jr Detection of fungemia obscured by concomitant bacteremia: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Drutz D. J., Harrison J. L., Huppert M. Adherence and penetration of vascular endothelium by Candida yeasts. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):374–384. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.374-384.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Gonzalez R., Nicolson G. L. Metastatic tumor cells adhere preferentially to the extracellular matrix underlying vascular endothelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1980 Nov 15;26(5):639–645. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata M., Dovnarsky D. K., Shin H. S. Thrombin-induced gap formation in confluent endothelial cell monolayers in vitro. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarak E. J., Howard B. V., Kefalides N. A. Properties of calf endothelial cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. M., Stewart G. J. The effects of endotoxin on vascular endothelium. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):833–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Custead S. E. Effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on platelet and metastatic tumor cell-endothelial cell interactions as a model for assessing vascular endothelial integrity. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr F. W., Adamson I. Y., Young L. Promotion of pulmonary metastasis in mice by bleomycin-induced endothelial injury. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]