Abstract
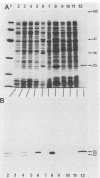
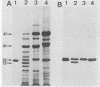
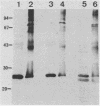
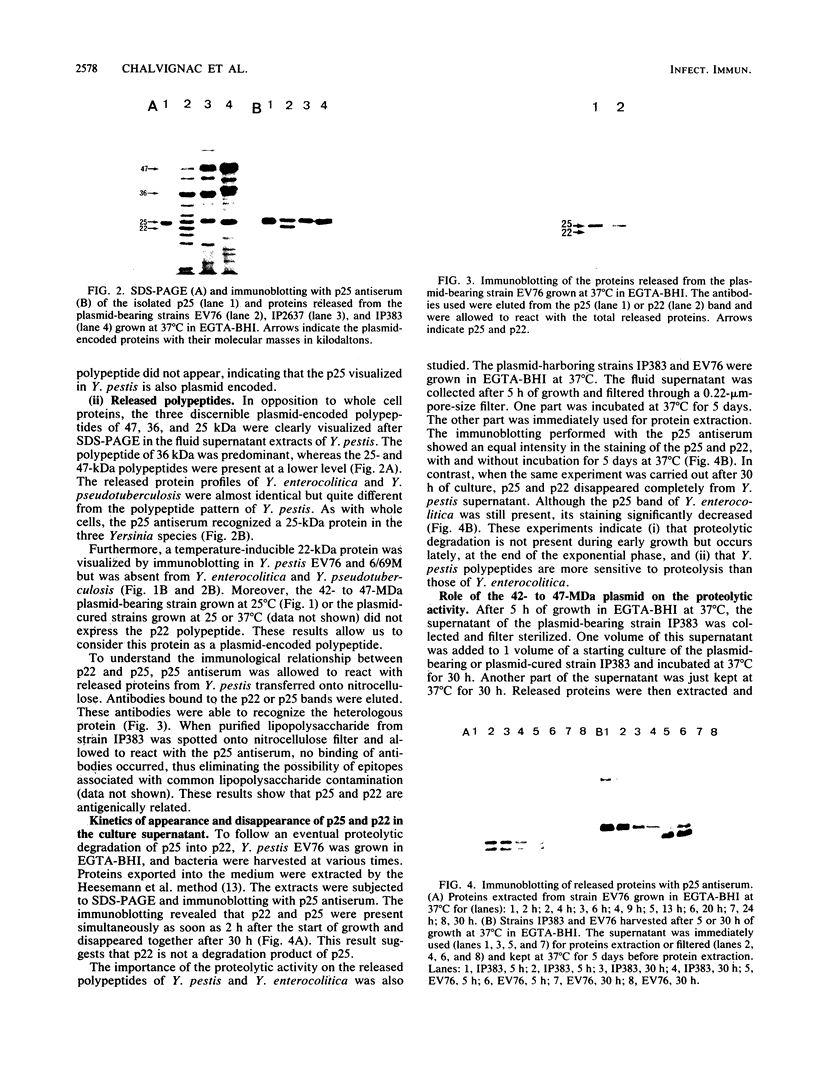
Antibodies raised against the 25-kilodalton (p25) plasmid-encoded polypeptide of Yersinia enterocolitica recognized the homologous protein in the three Yersinia species grown in vitro. This polypeptide was recovered from whole cells as well as from the fluid supernatant of bacteria grown at 37 degrees C in a Ca2+-deficient medium. Furthermore, a 22-kilodalton (p22) plasmid-encoded polypeptide immunologically related to p25 was found only in Y. pestis during early growth. After 30 h of culture, the Y. pestis p25 and p22 were completely degraded, whereas the intensity of the Y. enterocolitica p25 was decreased, but the protein was still detectable in the fluid supernatant. This proteolytic activity was independent of the presence of the virulence plasmid. Some disulfide bonds are probably involved in the quaternary structure of the p25 of the three pathogenic species and of the Y. pestis p22.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso J. M., Joseph-François A., Mazigh D., Bercovier H., Mollaret H. H. Résistance à la peste de souris expérimentalement infectées par Yersinia enterocolitica. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Aug-Sep;129B(2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Gurion R., Shafferman A. Essential virulence determinants of different Yersinia species are carried on a common plasmid. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. T., Doyle M. P. Identification of specific outer membrane polypeptides associated with virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):472–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.472-476.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Charnetzky W. T., Hurlbert R. F., Hancock R. E. Effects of growth temperature, 47-megadalton plasmid, and calcium deficiency on the outer membrane protein porin and lipopolysaccharide composition of Yersinia pestis EV76. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1092–1101. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1092-1101.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Gross U., Schmidt N., Laufs R. Immunochemical analysis of plasmid-encoded proteins released by enteropathogenic Yersinia sp. grown in calcium-deficient media. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):561–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.561-567.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Skarpeid H. J., Solberg R., Bergan T. Outer membrane proteins and plasmids in different Yersinia enterocolitica serogroups isolated from man and animals. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Feb;93(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Plasmid-mediated and temperature-regulated surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):921–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.921-930.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazza G., Karu A. E., Kingsbury D. T. Immune response to plasmid- and chromosome-encoded Yersinia antigens. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):676–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.676-685.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet M., Berche P., Mazigh D., Veron M. Protection against Yersinia infection induced by non-virulence-plasmid-encoded antigens. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Oct;20(2):225–231. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Localization in Yersinia pestis of peptides associated with virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.129-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence and immunity in yersiniae. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]