Abstract
Many studies have shown that lactoferrin and transferrin have antimicrobial activity against gram-negative bacteria, but a mechanism of action has not been defined. We hypothesized that the iron-binding proteins could affect the gram-negative outer membrane in a manner similar to that of the chelator EDTA. The ability of lactoferrin and transferrin to release radiolabeled lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from a UDP-galactose epimerase-deficient Escherichia coli mutant and from wild-type Salmonella typhimurium strains was tested. Initial studies in barbital-acetate buffer showed that EDTA and lactoferrin cause significant release of LPS from all three strains. Further studies found that LPS release was blocked by iron saturation of lactoferrin, occurred between pH 6 and 7.5, was comparable for bacterial concentrations from 10(4) to 10(7) CFU/ml, and increased with increasing lactoferrin concentrations. Studies using Hanks balanced salt solution lacking calcium and magnesium showed that transferrin also could cause LPS release. Additionally, both lactoferrin and transferrin increased the antibacterial effect of a subinhibitory concentration of rifampin, a drug excluded by the bacterial outer membrane. This work demonstrates that these iron-binding proteins damage the gram-negative outer membrane and alter bacterial outer membrane permeability.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A. Lactoferrin and transferrin: a comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Brewer M., Gauthier J. J. Bactericidal activity of human lactoferrin: sensitivity of a variety of microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):893–898. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.893-898.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., McGhee J. R. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.327545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Russell J. E., Champion W. J., Brewer M., Gauthier J. J. Bactericidal activity of human lactoferrin: differentiation from the stasis of iron deprivation. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):792–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.792-799.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Bagby G. C., Davis J. Calcium-dependent polymerization of lactoferrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. G., Schanbacher F. L., Ferguson L. C., Smith K. L. In vitro growth inhibition of mastitis-causing coliform bacteria by bovine apo-lactoferrin and reversal of inhibition by citrate and high concentrations of apo-lactoferin. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):911–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.911-918.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortner C. A., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Bactericidal effect of lactoferrin on Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):373–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.373-377.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S. Sensitization of E. coli to the serum bactericidal system and to lysozyme by ethyleneglycoltetraacetic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1431–1433. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
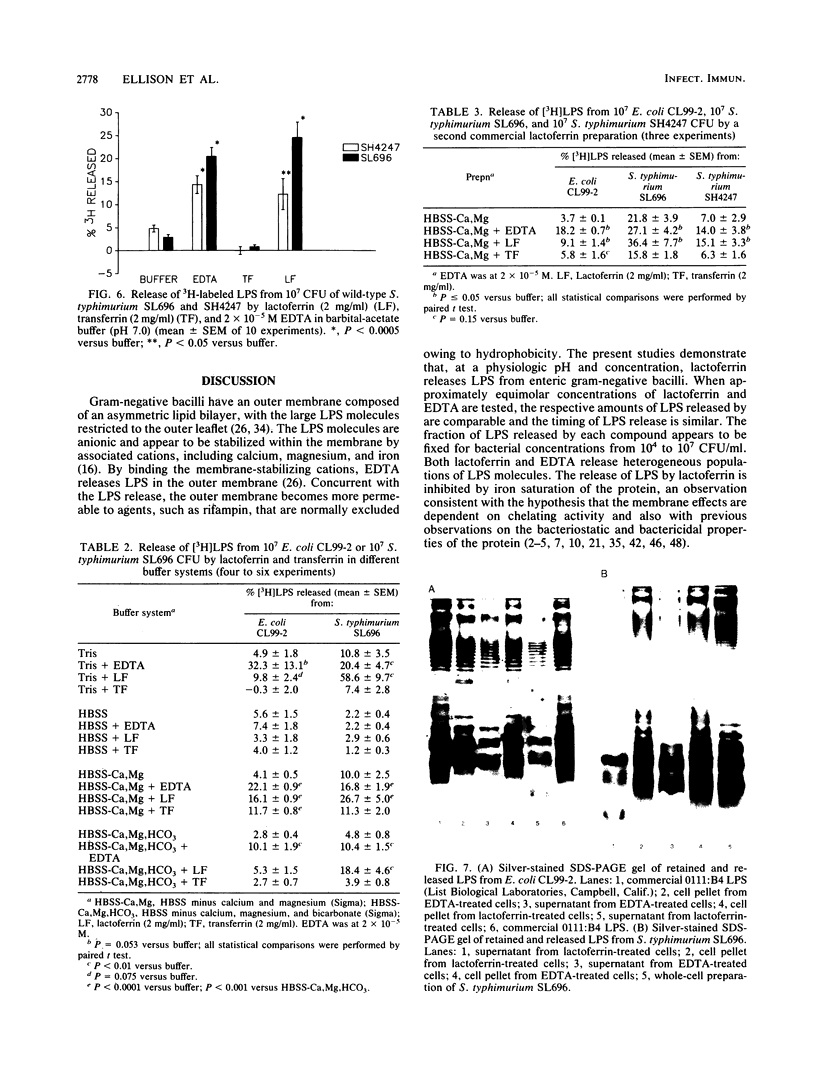
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J. Bacterial iron metabolism and immunity to Pasteurella septica and Escherichia coli. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):380–382. doi: 10.1038/224380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Leigh L. Iron-binding proteins in milk and resistance to Escherichia coli infection in infants. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):69–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Tonsager S., McGroarty E. J. Quantitation of metal cations bound to membranes and extracted lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Sciortino C. V., McIntosh M. A. Role of iron in microbe-host interactions. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S759–S777. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Joiner K., Leive L. Serum-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli O111 contain increased lipopolysaccharide, lack an O antigen-containing capsule, and cover more of their lipid A core with O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.877-882.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
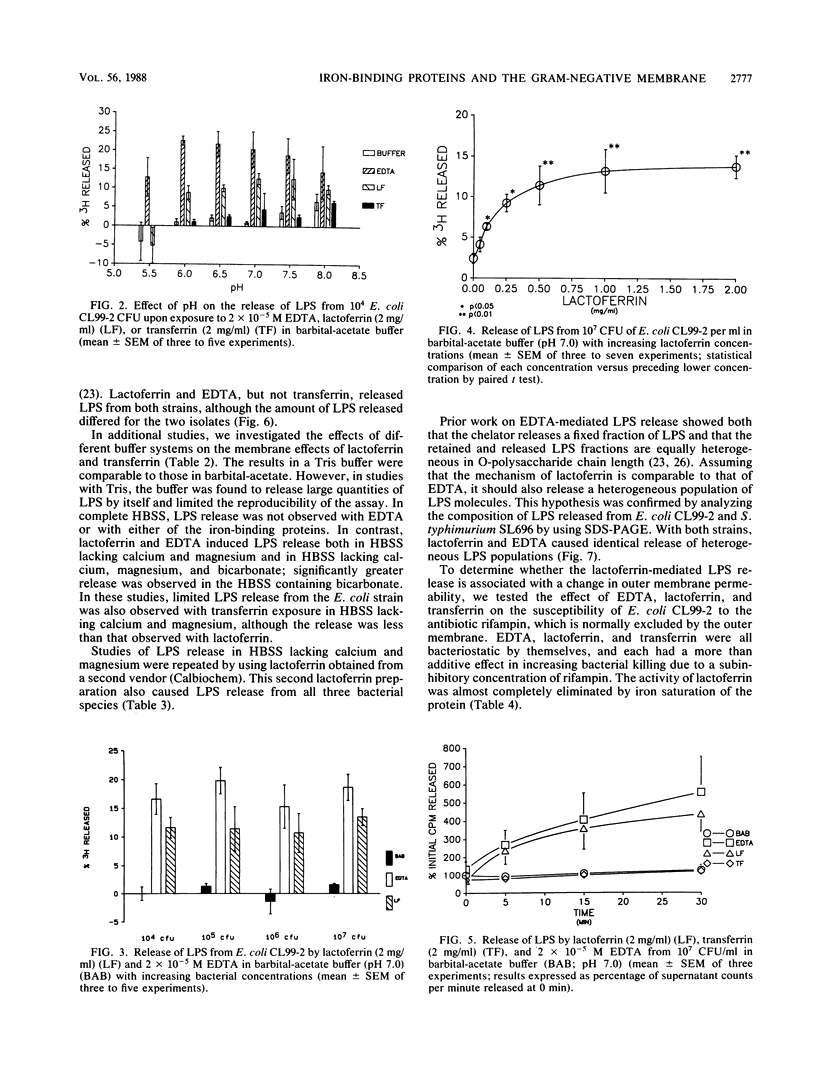
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E. Effect of pH and haem compounds on the killing of Pasteurella septica by specific antiserum. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jun;88(2):345–354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-2-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Humphreys J. Bacteriostatic effect of human milk and bovine colostrum on Escherichia coli: importance of bicarbonate. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):396–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.396-401.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J. Aberrant migration of lipopolysaccharide in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):685–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukari R., Helander I. M., Vaara M. Chain length heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharide released from Salmonella typhimurium by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or polycations. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):673–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R., Schmetz M., Berger M., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M., Leive L. A quantitative analysis of C3 binding to O-antigen capsule, lipopolysaccharide, and outer membrane protein of E. coli 0111B4. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):369–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGILVERY R. W., MOKRASCH L. C. Purification and properties of fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):909–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Prignot J. J., Wauters G. Immunohistochemical localization and bacteriostatic properties of an iron-binding protein from bronchial mucus. Thorax. 1966 Nov;21(6):538–544. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.6.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Schonne E. Lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein in neutrophilic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):643–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier J., Spik G. Comparative study of the iron-binding properties of human transferrins. I. Complete and sequential iron saturation and desaturation of the lactotransferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moguilevsky N., Retegui L. A., Masson P. L. Comparison of human lactoferrins from milk and neutrophilic leucocytes. Relative molecular mass, isoelectric point, iron-binding properties and uptake by the liver. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):353–359. doi: 10.1042/bj2290353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonnecke B. J., Smith K. L. Inhibition of mastitic bacteria by bovine milk apo-lactoferrin evaluated by in vitro microassay of bacterial growth. J Dairy Sci. 1984 Mar;67(3):606–613. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrod P., Williams R. P. Effects of iron and culture filtrates on killing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by normal human serum. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.918-924.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez Perez G. I., Blaser M. J. Lipopolysaccharide characteristics of pathogenic campylobacters. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.353-359.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihar O., Svorc J. The quantitative estimation of carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jun;13(6):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative bacteria by lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainard P. Bacteriostasis of Escherichia coli by bovine lactoferrin, transferrin and immunoglobulins (IgG1, IgG2, IgM) acting alone or in combination. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Feb;11(1-2):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T., Chart H. Interaction of lactoferrin and transferrins with the outer membrane of Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):891–898. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter B., Brock J. H., Steel E. D. Inhibition of Escherichia coli by bovine colostrum and post-colostral milk. II. The bacteriostatic effect of lactoferrin on a serum susceptible and serum resistant strain of E. coli. Immunology. 1975 Jan;28(1):83–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter B. The biological significance of lactoferrin. Int J Tissue React. 1983;5(1):87–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Pruul H. Sensitization of complement-resistant smooth gram-negative bacterial strains. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):365–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.365-372.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Synge C. Bacteriostatic effect of human milk on Escherichia coli: the role of IgA. Immunology. 1978 Jan;34(1):19–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Cheron A., Montreuil J., Dolby J. M. Bacteriostasis of a milk-sensitive strain of Escherichia coli by immunoglobulins and iron-binding proteins in association. Immunology. 1978 Oct;35(4):663–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens S., Dolby J. M., Montreuil J., Spik G. Differences in inhibition of the growth of commensal and enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli by lactotransferrin and secretory immunoglobulin A isolated from human milk. Immunology. 1980 Nov;41(3):597–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J., Norrell S., Harrington J. P. Kinetic effect of human lactoferrin on the growth of Escherichia coli 0111. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(10):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak L., Mandel I. D., Herrera M., Baurmash H. Changes in lactoferrin and other proteins in a case of chronic recurrent parotitis. J Oral Pathol. 1978 Apr;7(2):91–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1978.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. Increase in sensitivity to antibiotics and lysozyme on deletion of lipopolysaccharides in Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):453–454. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.453-454.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenovuo J., Lehtonen O. P., Aaltonen A. S., Vilja P., Tuohimaa P. Antimicrobial factors in whole saliva of human infants. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.49-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Duncan R. L., Jr, Morrison D. C. The interaction of Escherichia coli with normal human serum: the kinetics of serum-mediated lipopolysaccharide release and its dissociation from bacterial killing. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1329–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuwissen B., Masson P. L., Osinski P., Heremans J. F. Metal-combining properties of human lactoferrin. The possible involvement of tyrosyl residues in the binding sites. Spectrophotometric titration. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Viljanen P. Binding of polymyxin B nonapeptide to gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):548–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of bicarbonate in the binding of iron by transferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 18;322(2):231–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Muello K., Victor M., Elsbach P. The role of lipopolysaccharides in the action of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing neutrophil protein on the bacterial envelope. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3109–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]