Abstract
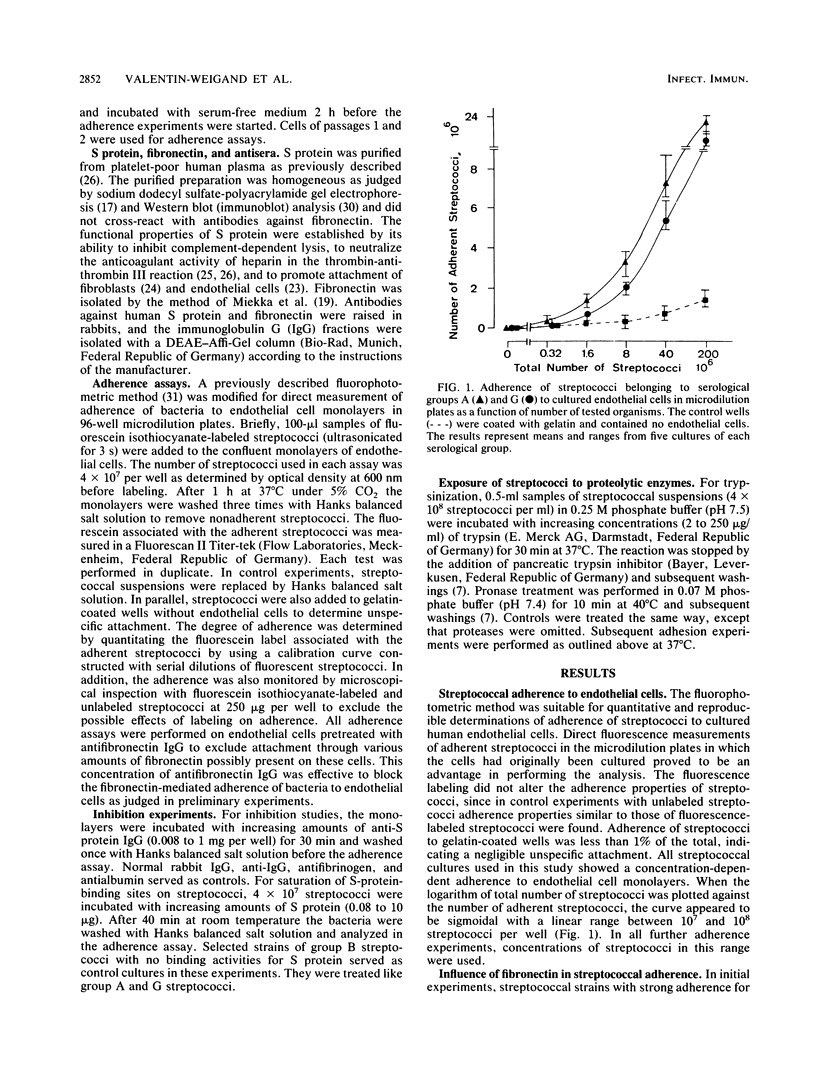
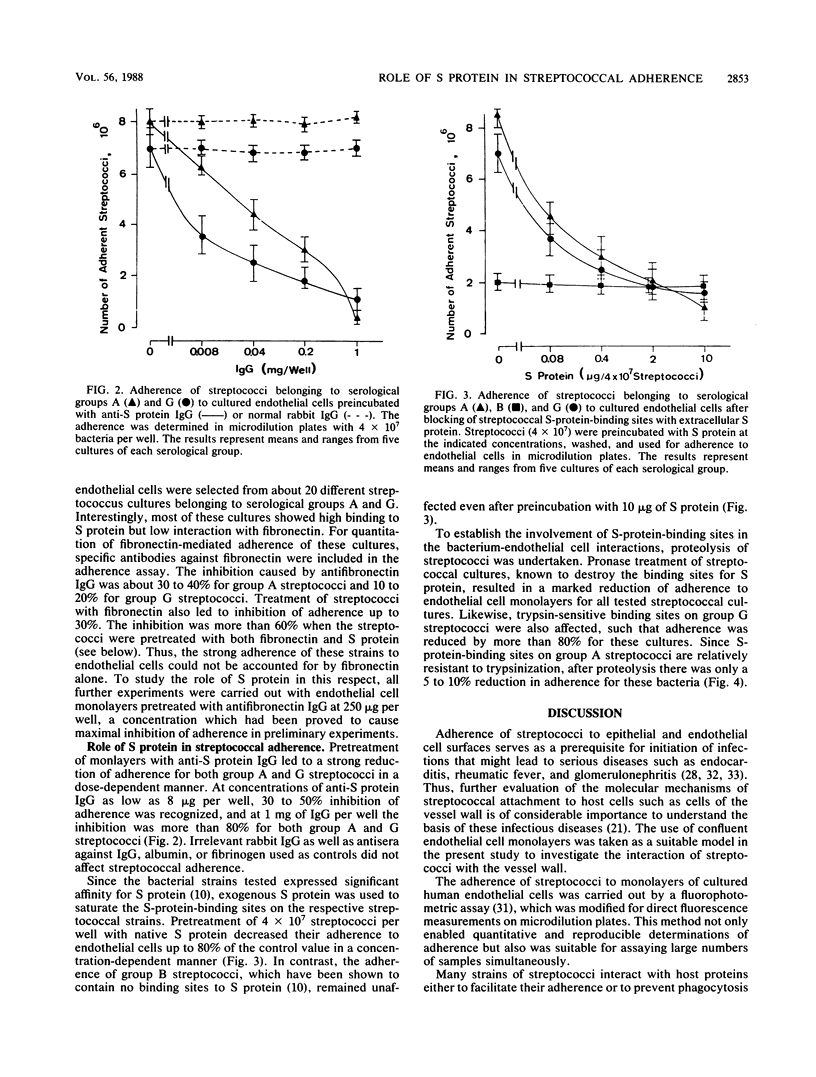
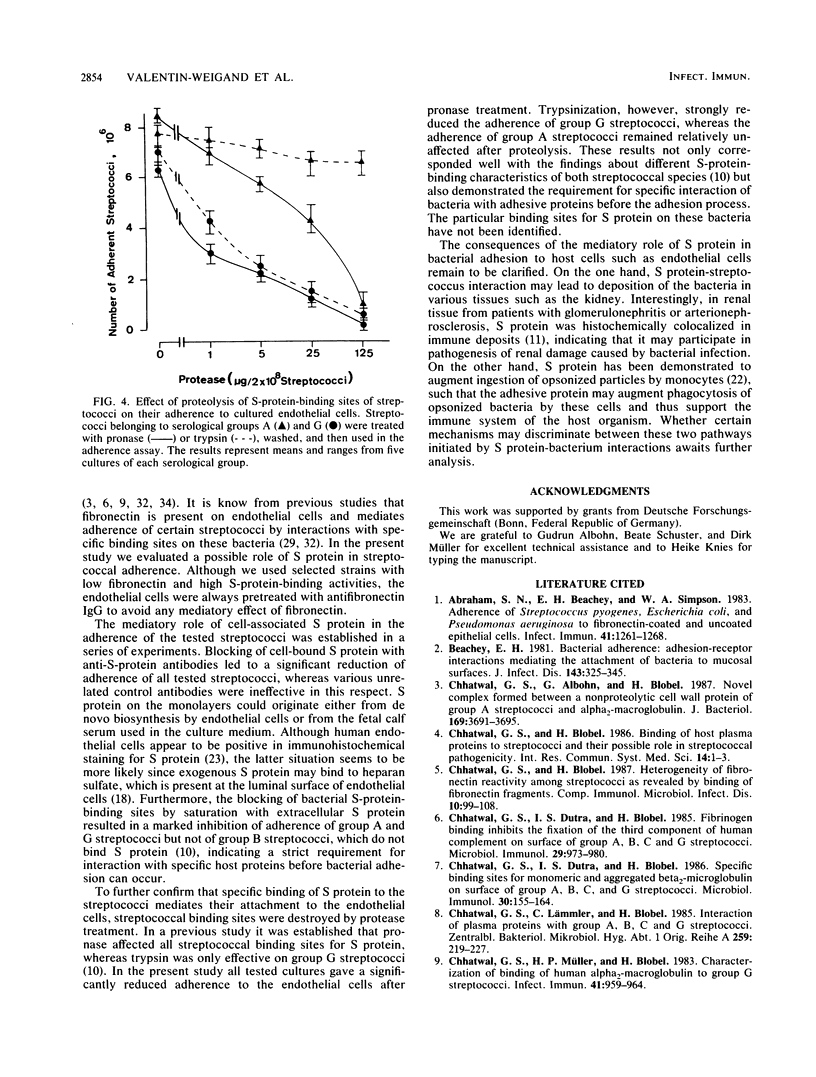
The role of S protein in the adherence of group A and G streptococci to human umbilical vein endothelial cells cultivated in 96-well microdilution plates was studied by utilizing fluorescein-labeled streptococci. The assay proved suitable for quantitative determination of bacterial adherence to cultured endothelial cells for all tested strains of streptococci. Only bacterial strains with significant S protein binding but weak fibronectin binding were included in these studies. Fibronectin-mediated adherence to endothelial cells of these streptococci was less than 25% of total and could be blocked by antifibronectin immunoglobulin G. Further treatment of endothelial cell monolayers with anti-S protein immunoglobulin G at concentrations up to 1 mg per well led to an almost complete inhibition of adherence for all tested streptococcal cultures, indicating significant contribution of S protein in the streptococcus-endothelial cell interaction. Blocking of S-protein-binding sites on streptococci by preincubation with exogeneous S protein at a concentration of 10 micrograms per 4 x 10(7) streptococci led to about 75% reduction of S-protein-mediated adherence to endothelial cells. Trypsin pretreatment of group G streptococci and pronase pretreatment of group A and G streptococci, modifications known to destroy the bacterial binding sites of S protein, also inhibited the capacity of the streptococci for S-protein-mediated adherence to endothelial cells by 75 to 80%. These results indicate that S protein plays a mediatory role in adherence of streptococci to endothelial cells and that S-protein-specific binding sites on streptococci are involved in this interaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. Adherence of streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to fibronectin-coated and uncoated epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1261-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Albohn G., Blobel H. Novel complex formed between a nonproteolytic cell wall protein of group A streptococci and alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3691–3695. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3691-3695.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Blobel H. Heterogeneity of fibronectin reactivity among streptococci as revealed by binding of fibronectin fragments. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987;10(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(87)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Dutra I. S., Blobel H. Fibrinogen binding inhibits the fixation of the third component of human complement on surface of groups A, B, C, and G streptococci. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(10):973–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb02961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Dutra I. S., Blobel H. Specific binding sites for monomeric and aggregated beta 2-microglobulin on surface of groups A, B, C, and G streptococci. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(2):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Lämmler C., Blobel H. Interactions of plasma proteins with group A, B, C and G streptococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Apr;259(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Müller H. P., Blobel H. Characterization of binding of human alpha 2-macroglobulin to group G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.959-964.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Blobel H. Specific binding of the human S protein (vitronectin) to streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1878–1883. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1878-1883.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Podack E., Dalmasso A. P., Jennette J. C. Localization of S protein and its relationship to the membrane attack complex of complement in renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):182–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Engvall E., A'Hearn E., Barnes D., Pierschbacher M., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment on replicas of SDS polyacrylamide gels reveals two adhesive plasma proteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):20–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Mosher D. F. Synthesis of fibronectin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1779–1791. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miekka S. I., Ingham K. C., Menache D. Rapid methods for isolation of human plasma fibronectin. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. J., Frame R. N., Elstad M. R. Vitronectin (S protein) augments the functional activity of monocyte receptors for IgG and complement C3b. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):86–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Anders E., Grulich-Henn J., Müller-Berghaus G. Attachment of cultured human endothelial cells is promoted by specific association with S protein (vitronectin) as well as with the ternary S protein-thrombin-antithrombin III complex. Blood. 1988 Jun;71(6):1581–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Heimburger N., Anders E., Müller-Berghaus G. Physicochemical, immunochemical and functional comparison of human S-protein and vitronectin. Evidence for the identity of both plasma proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):951–956. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G. Neutralization and binding of heparin by S protein/vitronectin in the inhibition of factor Xa by antithrombin III. Involvement of an inducible heparin-binding domain of S protein/vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12247–12253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Wassmuth R., Müller-Berghaus G. Physicochemical characterization of human S-protein and its function in the blood coagulation system. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):349–355. doi: 10.1042/bj2310349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Weigand P., Chhatwal G. S., Blobel H. A simple method for quantitative determination of bacterial adherence to human and animal epithelial cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(10):1017–1023. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Lussenhop D., Peterson P. K., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B., Jacob H. S., Moldow C. F. Bacterial adherence to fibronectin and endothelial cells: a possible mechanism for bacterial tissue tropism. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jan;103(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Schlesinger J. J. Pathoanatomic, pathophysiologic and clinical correlations in endocarditis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 17;291(16):832–837. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410172911609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Antiopsonic activity of fibrinogen bound to M protein on the surface of group A streptococci. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1042–1045. doi: 10.1172/JCI110508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


