Abstract
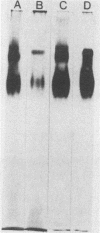
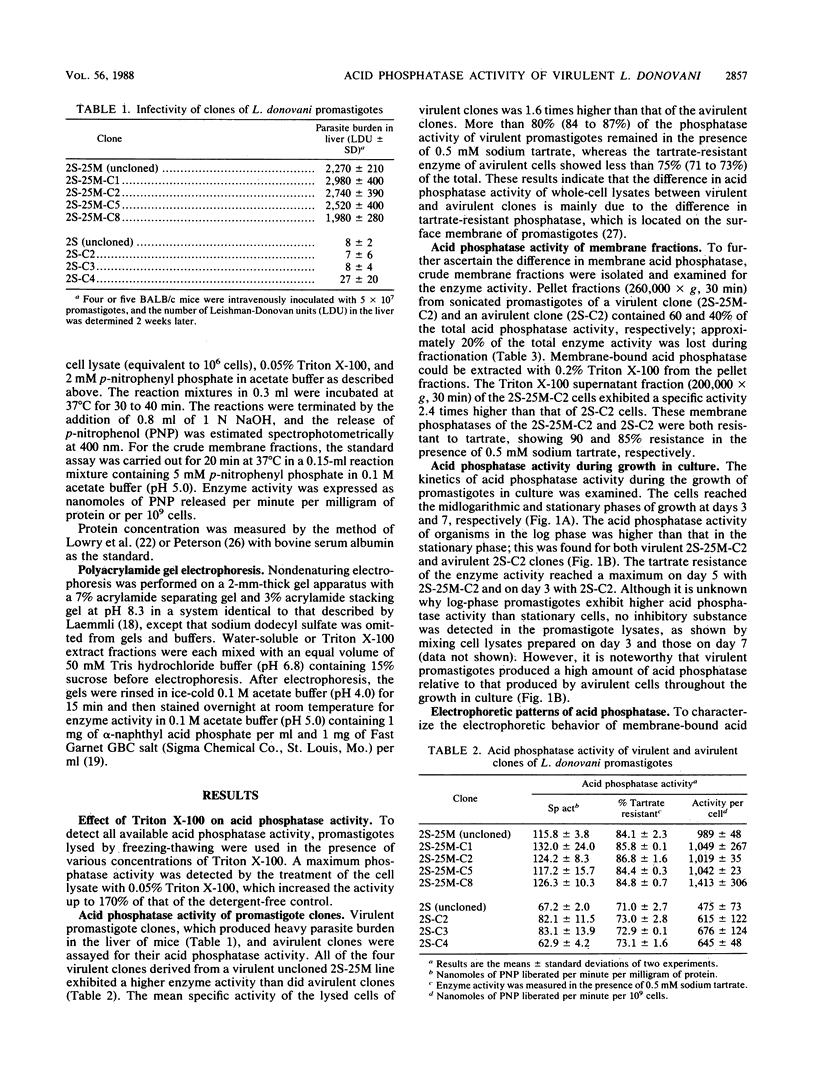
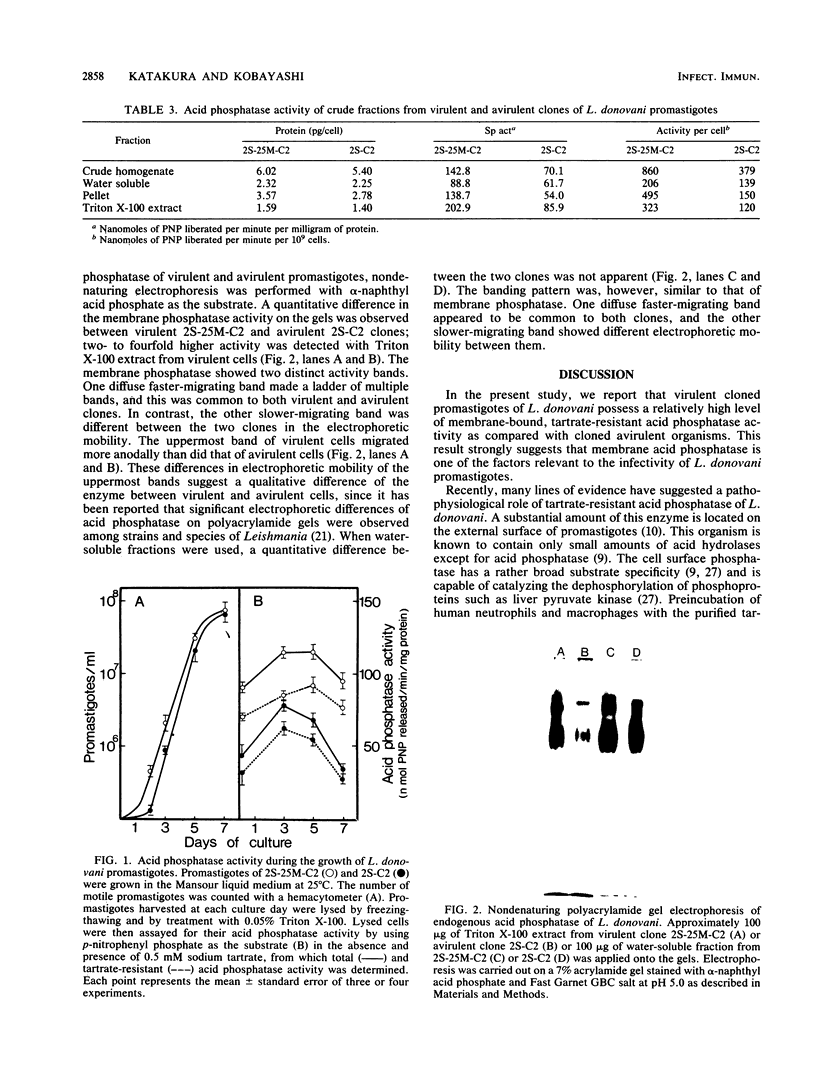
Virulent and avirulent clones of Leishmania donovani promastigotes were examined for their acid phosphatase activity. The acid phosphatase activity of whole-cell lysates of virulent clones was 1.5 to 2.0 times higher than that of avirulent clones. Pellet fractions (260,000 x g, 30 min) from sonicated promastigotes of a virulent clone and an avirulent clone contained 60 and 40% of the total enzyme activity, respectively. Membrane-bound acid phosphatase was extracted with Triton X-100 from the pellet. This membrane-bound phosphatase activity was 2.4-fold higher in virulent organisms than in avirulent organisms. The membrane acid phosphatase exhibited two distinct bands on polyacrylamide gels stained for enzyme activity. One diffuse, faster-migrating band showed identical electrophoretic mobility in both virulent and avirulent clones, although a higher enzymatic activity was observed with the extract from virulent cells. In contrast, a slower-migrating band was different between the two clones in the mobility. These results suggest that membrane-bound acid phosphatase was quantitatively and qualitatively different between virulent and avirulent promastigotes of L. donovani. In addition, virulent cells produced a relatively high level of acid phosphatase throughout the growth in culture.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouvier J., Etges R., Bordier C. Identification of the promastigote surface protease in seven species of Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Kirkley J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. I. the variable course of Leishmania donovani infections in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri G., Chang K. P. Acid protease activity of a major surface membrane glycoprotein (gp63) from Leishmania mexicana promastigotes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 1;27(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawidowicz K., Hernandez A. G., Infante R. B., Convit J. The surface membrane of Leishmania. I. The effects of lectins on different stages of Leishmania braziliensis. J Parasitol. 1975 Oct;61(5):950–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Herman R. Characterization of populations of promastigotes of Leishmania donovani. J Protozool. 1981 Aug;28(3):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb02863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimzadeh A., Jones T. C. A comparative study of different Leishmania tropica isolates from Iran: correlation between infectivity and cytochemical properties. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):694–702. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etges R., Bouvier J., Bordier C. The major surface protein of Leishmania promastigotes is a protease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9098–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini M. S. Effects of promastigote growth phase, frequency of subculture, and host age on promastigote-initiated infections with Leishmania donovani in the golden hamster. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):521–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Czuczman M. S., Diven W. F., Berens R. L., Pope M. T., Katsoulis D. E. Partial purification and characterization of particulate acid phosphatase of Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;72(4):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani: surface membrane acid phosphatase activity of promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Aug;52(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Hocking R. E., Mitchell G. F., Spithill T. W. Isolation and characterization of infective and non-infective clones of Leishmania tropica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Feb;7(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. F., Coombs G. H. Phosphomonoesterases of Leishmania mexicana mexicana and other flagellates. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Apr;23(3):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakura K., Kobayashi A. Enhancement of infectivity of Leishmania donovani promastigotes by serial mouse passages. J Parasitol. 1985 Jun;71(3):393–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kink J. A., Chang K. P. N-glycosylation as a biochemical basis for virulence in Leishmania mexicana amazonensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kink J. A., Chang K. P. Tunicamycin-resistant Leishmania mexicana amazonensis: expression of virulence associated with an increased activity of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase and amplification of its presumptive gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1253–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kweider M., Lemesre J. L., Darcy F., Kusnierz J. P., Capron A., Santoro F. Infectivity of Leishmania braziliensis promastigotes is dependent on the increasing expression of a 65,000-dalton surface antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Yam L. T., Lam K. W. Studies of acid phosphatase isoenzymes in human leukocytes demonstration of isoenzyme cell specificity. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Dec;18(12):901–910. doi: 10.1177/18.12.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovelace J. K., Dwyer D. M., Gottlieb M. Purification and characterization of the extracellular acid phosphatase of Leishmania donovani. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Sep;20(3):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovelace J. K., Gottlieb M. Comparison of extracellular acid phosphatases from various isolates of Leishmania. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Nov;35(6):1121–1128. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour N. S., Hady J., McConnell E. A modified liquid medium for Leishmania. J Parasitol. 1973 Dec;59(6):1088–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagakura K., Tachibana H., Kaneda Y. Alteration of the cell surface acid phosphatase concomitant with the morphological transformation in Trypanosoma cruzi. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1985;81(4):815–817. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(85)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Das S., Campbell P. I., LaRocca G. M., Pope M. T., Glew R. H. Characterization of Leishmania donovani acid phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Glew R. H., Kuhns D. B., Basford R. E., Waggoner A. S., Ernst L. A., Pope M. Leishmania donovani: surface membrane acid phosphatase blocks neutrophil oxidative metabolite production. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Dec;60(3):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO K., SUTER E. LYSOSOMAL ACID HYDROLASES IN MICE INFECTED WITH BCG. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:727–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Hieny S., Sher A. Identification of cell surface carbohydrate and antigenic changes between noninfective and infective developmental stages of Leishmania major promastigotes. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Perkins P. V. Development of infective stage Leishmania promastigotes within phlebotomine sand flies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):456–459. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Perkins P. V. Identification of an infective stage of Leishmania promastigotes. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.6701528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. K., Das S., Glew R. H., Gottlieb M. Resistance of leishmanial phosphatases to inactivation by oxygen metabolites. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):329–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.329-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]