Abstract
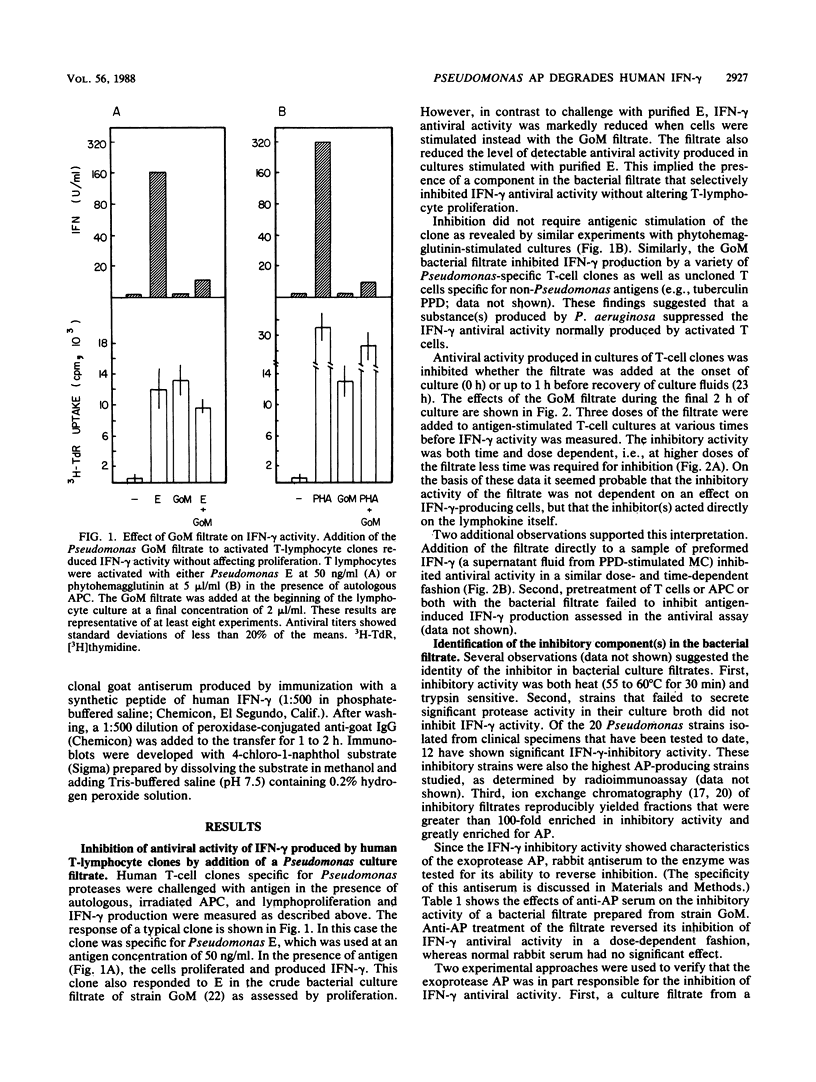
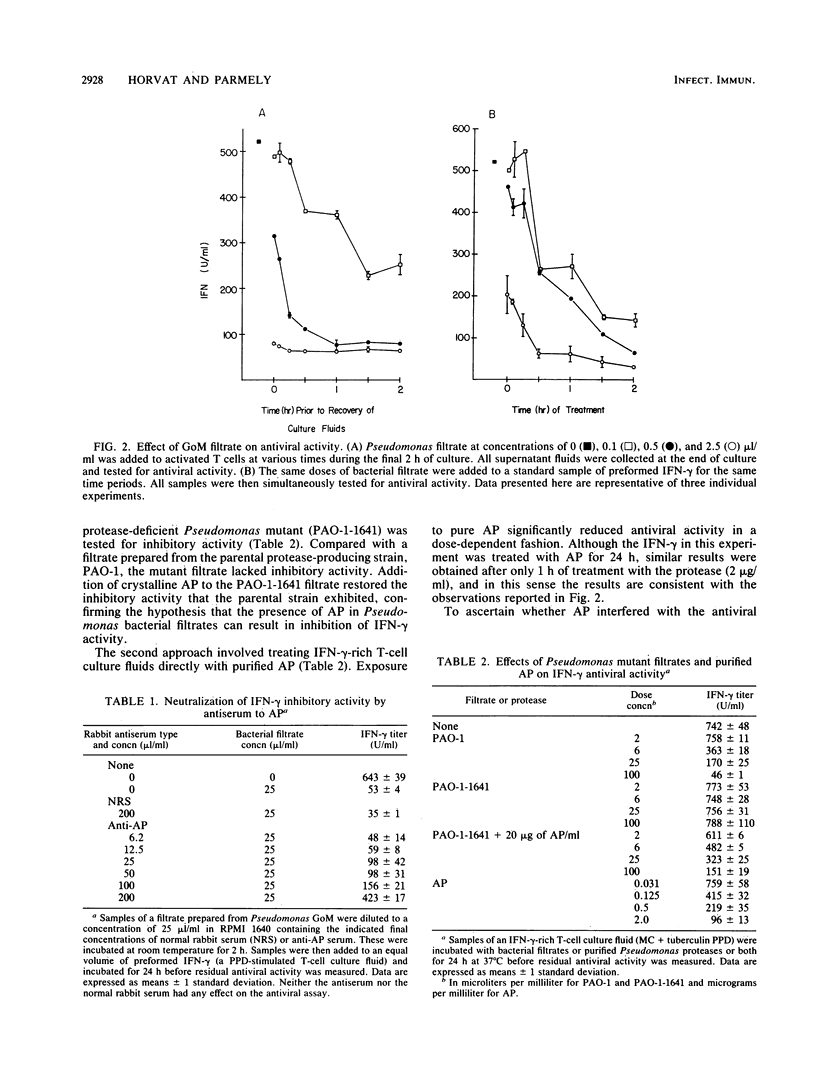
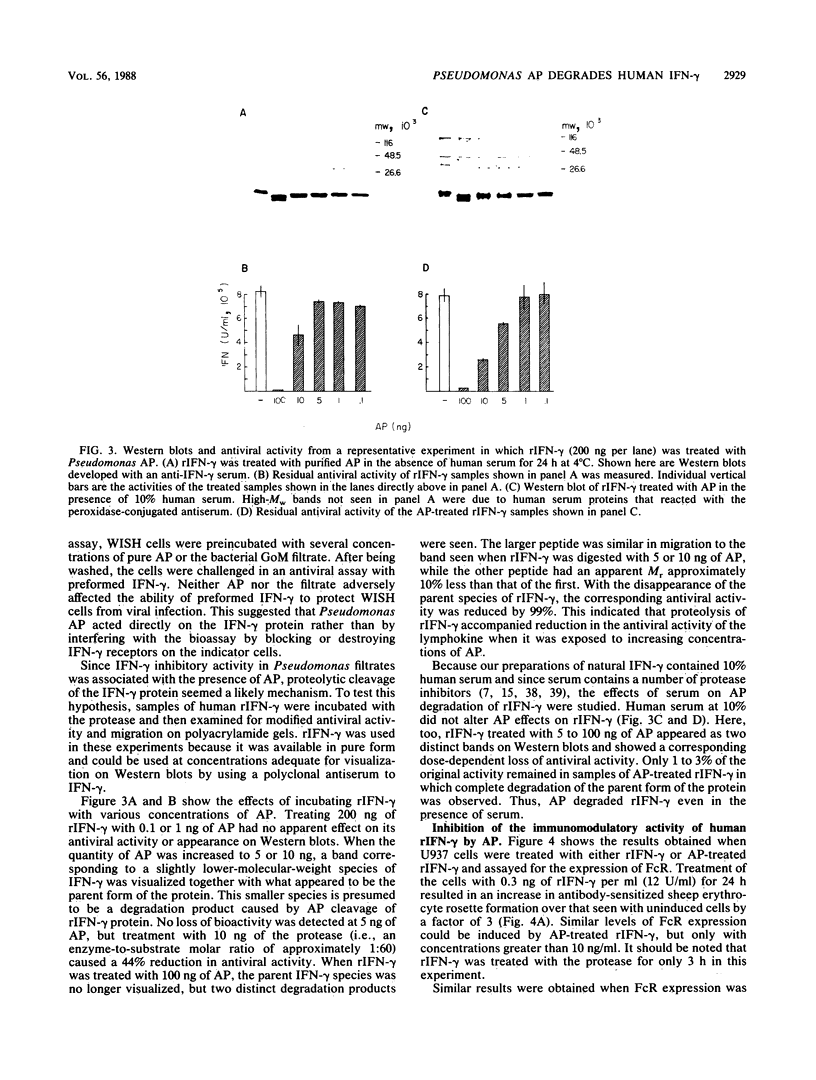
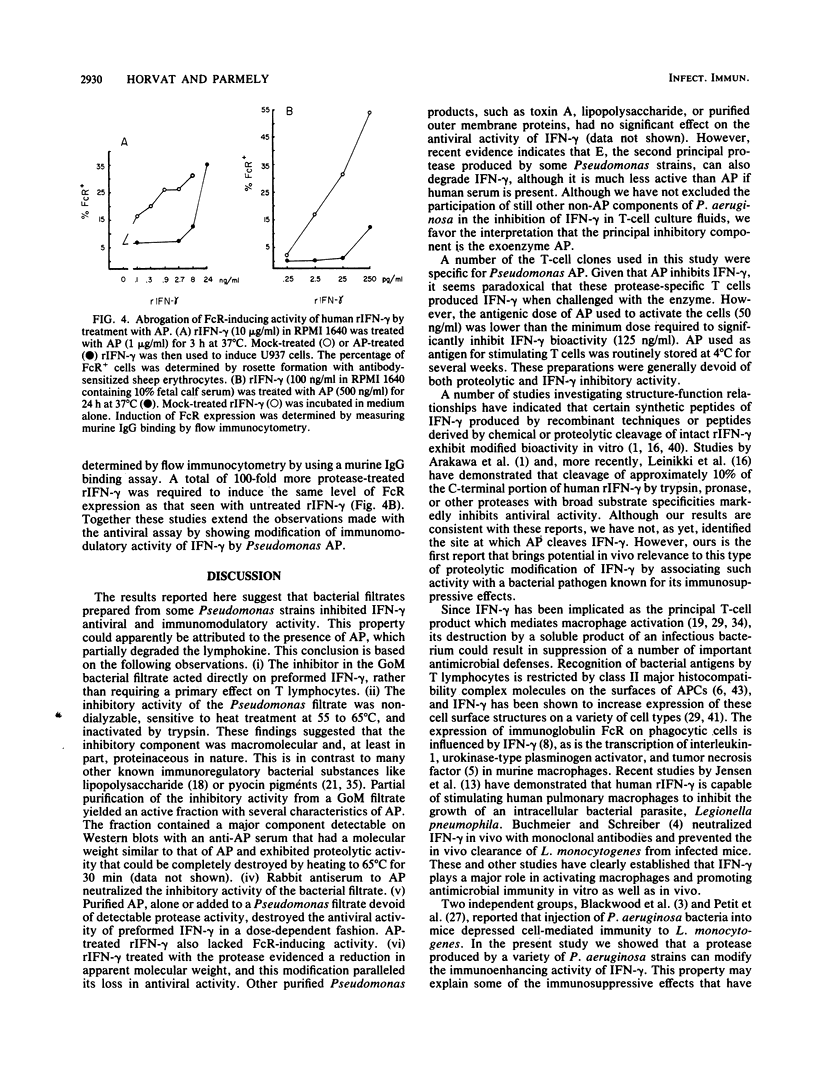
This study was performed to determine the effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production by antigen-stimulated human T-cell clones. Crude bacterial filtrates prepared from certain strains of P. aeruginosa inhibited IFN-gamma production by T cells and reduced the antiviral activity of preformed IFN-gamma. Bacterial filtrates prepared from mutant strains that did not produce the exoenzyme alkaline protease (AP) did not inhibit IFN-gamma activity. The inhibitory activity of bacterial filtrates was heat and trypsin sensitive and was neutralized by an antiserum to AP. Crystalline AP mimicked the effects of the bacterial filtrates, and an inactive filtrate from a protease-deficient mutant strain was reconstituted by the addition of AP. AP-treated recombinant IFN-gamma showed altered migration on Western blots (immunoblots) of polyacrylamide gels, and this modification correlated with a dose-dependent loss of antiviral activity. The ability of recombinant IFN-gamma to elevate the expression of Fc receptors on cells of the U-937 histiocytic cell line was also diminished by AP treatment. These results indicate that the Pseudomonas protease AP can inhibit the antiviral and immunomodulatory activities of IFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa T., Hsu Y. R., Parker C. G., Lai P. H. Role of polycationic C-terminal portion in the structure and activity of recombinant human interferon-gamma. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8534–8539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Ammons J. T., Kotzin B. L. Lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 1 inhibit interferon-gamma-induced Fc receptor expression on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1873–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Lin T., Rowe J. I. Suppression of the delayed-type hypersensitivity and cell-mediated immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):639–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.639-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Macrophage-T cell interactions involving Listeria monocytogenes--role of the H-2 gene complex. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2395–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioretti E., Angeletti M., Citro G., Barra D., Ascoli F. Kunitz-type inhibitors in human serum. Identification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3586–3589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck L. W., Morihara K., Abrahamson D. R. Degradation of soluble laminin and depletion of tissue-associated basement membrane laminin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase and alkaline protease. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):149–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.149-153.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. S., Misfeldt M. L. Variables which affect suppression of the immune response induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):96–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.96-100.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in a mouse eye model. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1058–1063. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1058-1063.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. A., Rose R. M., Wasserman A. S., Kalb T. H., Anton K., Remold H. G. In vitro activation of the antibacterial activity of human pulmonary macrophages by recombinant gamma interferon. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):574–577. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelder B., Rashidbaigi A., Pestka S. A sandwich radioimmunoassay for human IFN-gamma. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Gray L. D. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases and microscopic characterization of pseudomonal protease-induced rabbit corneal damage. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):630–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.630-648.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Calderon J., Luquette M. H., Schreiber R. D. Reduced receptor binding by a human interferon-gamma fragment lacking 11 carboxyl-terminal amino acids. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3360–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama S., Kojo H., Mine Y., Nishida M., Goto S., Kuwahara S. Inhibitory effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the phagacytic and killing activities of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes: purification and characterization of an inhibitor of polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):394–398. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.394-398.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutman J., Berger M., Chase P. A., Dearborn D. G., Miller K. M., Waller R. L., Sorensen R. U. Studies on the mechanism of T cell inhibition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa phenazine pigment pyocyanine. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3481–3487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Horvat R. T. Antigenic specificities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase defined by human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):988–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Horvat R. T., Iglewski B. H., Kanarek J., Furtado D., Van Enk R. The antigenicity of a pulmonary pathogen defined by monoclonal T cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;216B:1043–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Iglewski B. H., Horvat R. T. Identification of the principal T lymphocyte-stimulating antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1338–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K., Kharazmi A. Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):986–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.986-989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. C., Richard G., Albert B., Daguet G. L. Depression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa of two T-cell-mediated responses, anti-Listeria immunity and delayed-type hypersensitivity to sheep erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):900–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.900-908.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Markham R. B. Induction in mice of cell-mediated immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa by high molecular weight polysaccharide and vinblastine. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2121–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porwoll J. M., Gebel H. M., Rodey G. E., Markham R. B. In vitro response of human T cells to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):670–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.670-674.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powderly W. G., Pier G. B., Markham R. B. In vitro T cell-mediated killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. V. Generation of bactericidal T cells in nonresponder mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2272–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powderly W. G., Pier G. B., Markham R. B. T lymphocyte-mediated protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in granulocytopenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):375–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI112587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Hicks L. J., Celada A., Buchmeier N. A., Gray P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to murine gamma-interferon which differentially modulate macrophage activation and antiviral activity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1609–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Klinger J. D., Cash H. A., Chase P. A., Dearborn D. G. In vitro inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa phenazine pigments. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):321–330. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.321-330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Chase P., Polmar S. H. Defective cellular immunity to gram-negative bacteria in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):398–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.398-402.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Cellular immunity to bacteria: impairment of in vitro lymphocyte responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.735-740.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Stepanik T. M., Jones C. M., Lønblad P. B., Kristensen T., Wierzbicki D. M. Primary structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. I. Isolation of the 26 CNBr fragments, amino acid sequence of 13 small CNBr fragments, amino acid sequence of methionine-containing peptides, and alignment of all CNBr fragments. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8293–8303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Stepanik T. M., Kristensen T., Wierzbicki D. M., Jones C. M., Lønblad P. B., Magnusson S., Petersen T. E. Primary structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. V. The complete structure. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8318–8327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin L., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces enhanced expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on B lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Unanue E. R. The specific binding of Listeria monocytogenes-immune T lymphocytes to macrophages. I. Quantitation and role of H-2 gene products. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1143–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]