Abstract
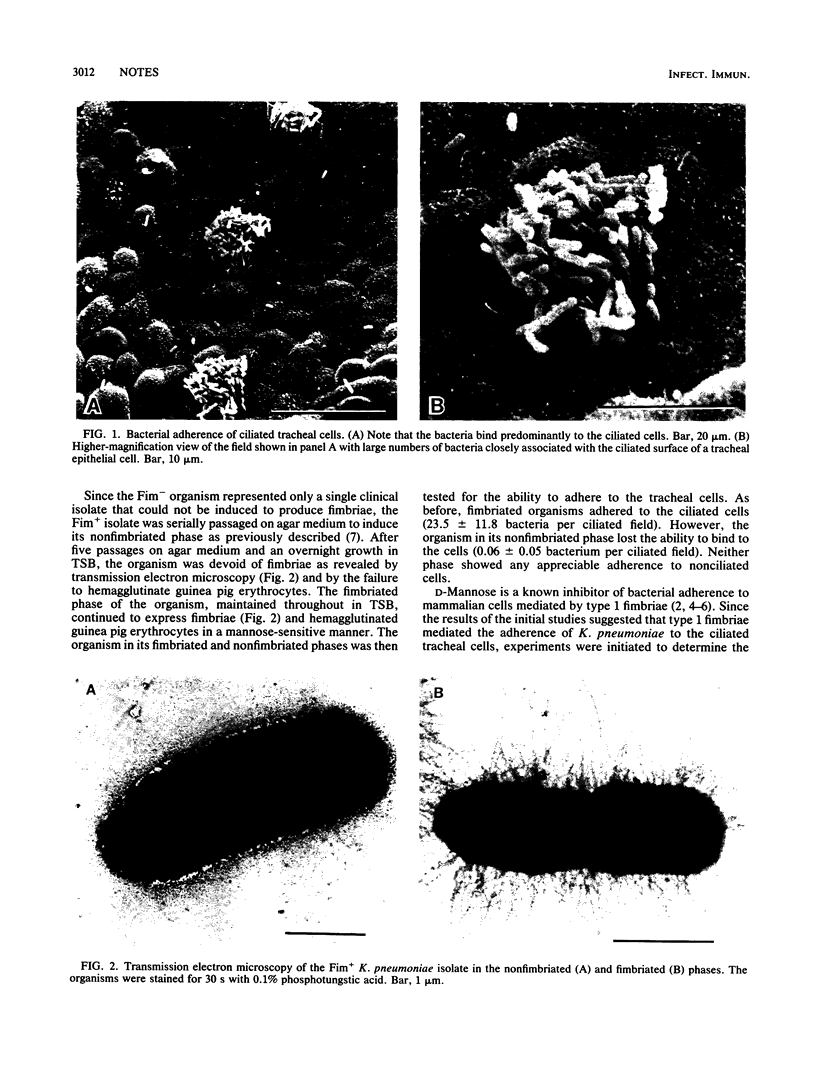
Clinical isolates of fimbriated and nonfimbriated Klebsiella pneumoniae were examined for the ability to adhere to hamster tracheal cells cultured in vitro. Fimbriated-phase K. pneumoniae adhered preferentially to ciliated cells, whereas nonfimbriated-phase organisms were not adherent. The adherence was inhibited by D-mannose but not D-glucose, suggesting that type 1 fimbriae serve as the adhesin in the attachment process.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collier A. M., Peterson L. P., Baseman J. B. Pathogenesis of infection with Bordetella pertussis in hamster tracheal organ culture. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S196–S203. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. Fimbriae and adhesive properties in Klebsiella strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:271–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Smith N. R., Todd T., Irvin R. T. Characterization of the binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1517-1522.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Avots-Avotins A. E., Davis C. P. Evidence for pili-mediated adherence of Klebsiella pneumoniae to rat bladder epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):729–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.729-737.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Davis C. P. Effect of piliation on Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in rat bladders. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):554–561. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.554-561.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Davis C. P. Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced experimental pyelitis: the effect of piliation on infectivity. J Urol. 1982 Jul;128(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52817-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin A. L., Todd T., Gurman G., Black D., Mankinen-Irvin P. M., Irvin R. T. Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to cilia of human tracheal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1523–1525. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1523-1525.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Woods D. E., Chaudhuri T. Association of respiratory tract colonization with adherence of gram-negative bacilli to epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):667–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus H., Baker N. R. Quantitation of adherence of mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to hamster tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):723–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.723-729.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller P. C., Partridge L. R., Cox R., Pellegrini V., Ritchie D. G. An in vitro system for the study of tracheal epithelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1987;19(6):783–791. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(87)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Scanning electron microscopic study of hamster tracheal organ cultures infected with Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):768–777. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pyle M. Adherence of mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to acid-injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.345-351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]