Abstract
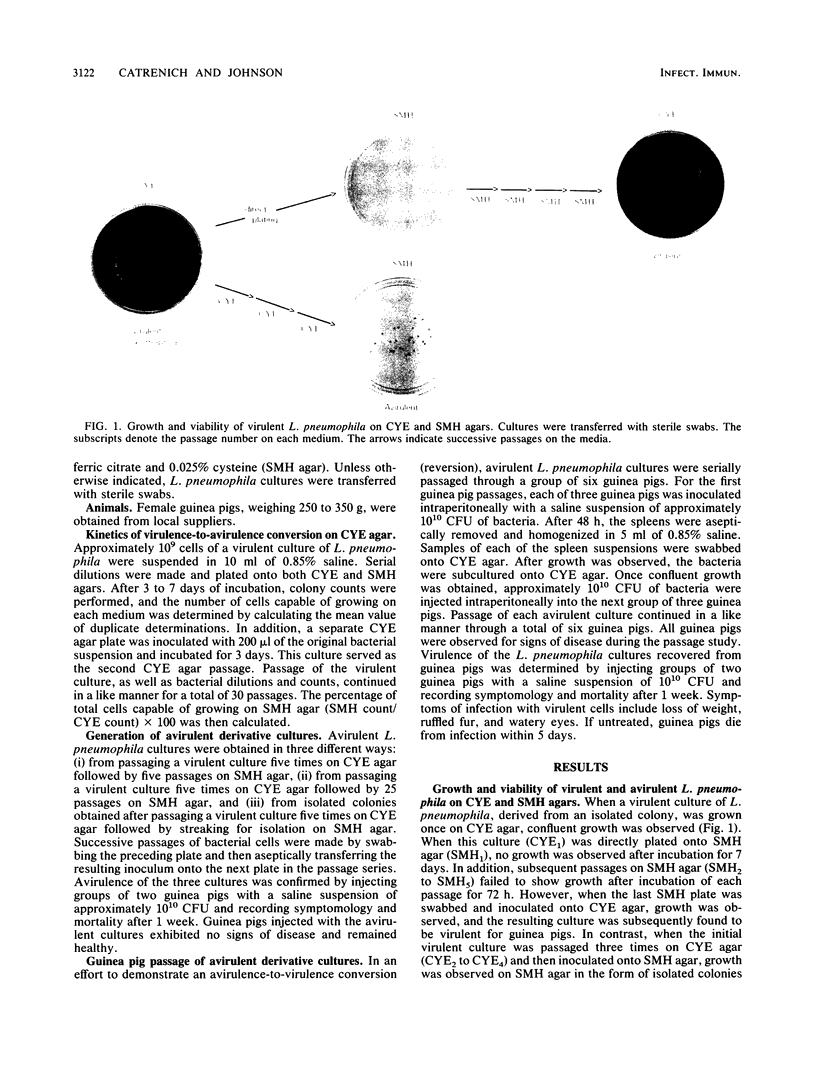
Previous investigations have shown that Legionella pneumophila converts from virulence to avirulence after passage on supplemented Mueller-Hinton (SMH) agar and may convert back to virulence after passage in guinea pigs. However, there is no additional information concerning the apparent interconversion of virulent and avirulent derivatives of L. pneumophila cultures. We investigated the stability of a parental virulent culture and its avirulent derivatives and the growth and viability of these cultures on charcoal-yeast extract (CYE) and SMH agars. Avirulent derivatives of a highly virulent L. pneumophila culture were obtained by passage of the virulent parent culture on SMH agar. The only time a virulent L. pneumophila culture was recoverable from an avirulent culture was when the avirulent culture was derived from a saline suspension of a virulent culture which had been passaged only five times on SMH agar. When an avirulent culture was derived from a virulent culture passaged 25 times on SMH agar or from an isolated colony which grew on a SMH agar plate, we were unable to recover a virulent culture after successive passage through guinea pigs. These results suggest that the conversion process which occurs between virulent and avirulent forms of L. pneumophila is a one-way phenomenon from virulence to avirulence and that stable avirulent derivatives can be isolated. Furthermore, our findings suggest that SMH agar acts as a selective medium for the growth of avirulent L. pneumophila, and growth on SMH agar may be a phenotypic marker for avirulence. Virulent cells, although unable to grow on SMH agar, may remain viable for several passages on SMH agar and propagate when inoculated into guinea pigs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTRIAN R. Morphologic variation in pneumococcus. I. An analysis of the bases for morphologic variation in pneumococcus and description of a hitherto undefined morphologic variant. J Exp Med. 1953 Jul;98(1):21–34. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W. Virulence conversion of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 by passage in guinea pigs and embryonated eggs. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):943–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.943-946.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Porter T. N., Schaeffer A. J., Duncan J. L. Role of type 1 pili and effects of phase variation on lower urinary tract infections produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):370–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.370-377.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maayan M. C., Ofek I., Medalia O., Aronson M. Population shift in mannose-specific fimbriated phase of Klebsiella pneumoniae during experimental urinary tract infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):785–789. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.785-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C. Virulent to avirulent conversion of Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila)--its effect on isolation techniques. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):707–711. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




