Abstract
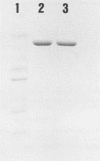
The gene encoding perfringolysin O, the thiol-activated hemolysin from Clostridium perfringens (ATCC 13124), was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. A gene library of C. perfringens chromosomal DNA was constructed in bacteriophage lambda EMBL3. A recombinant was identified that produced a hemolysin that was inhibited by cholesterol and was tentatively identified as perfringolysin O. Subcloning experiments localized the perfringolysin O gene (pfo) to a 1.8-kilobase region on the cloned chromosomal fragment. E. coli which carried a plasmid subclone of pfo (pRT1B) expressed perfringolysin O and secreted it into the periplasm. The amino-terminal sequence of the pfo gene product was identical with that determined for perfringolysin O purified from C. perfringens, indicating that E. coli correctly removed the signal peptide during secretion. Purification of the pfo product was accomplished by high-resolution gel filtration and anion-exchange chromatography. Analysis of the pfo product by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis showed that it comigrated with authentic perfringolysin O; both had an estimated molecular weight of 54,000. Two-dimensional tryptic peptide maps of the pfo product and of authentic perfringolysin O purified from C. perfringens were identical. The hemolytic activity of the pfo product was similar to that of authentic perfringolysin O; one hemolytic unit (HU) of the cloned gene product or authentic perfringolysin O corresponded to approximately 1 ng or a hemolytic activity of 10(6) HU per mg.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garnier T., Cole S. T. Characterization of a bacteriocinogenic plasmid from Clostridium perfringens and molecular genetic analysis of the bacteriocin-encoding gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1189-1196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the streptolysin O determinant from Streptococcus pyogenes: characterization of the cloned streptolysin O determinant and demonstration of the absence of substantial homology with determinants of other thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.804-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Mitsui N., Hase J. Clostridium perfringens exotoxins. II. Purification and some properties of theta-toxin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Oct;43(5):377–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOYES H. E., PRITCHARD W. L., BRINKLEY F. B., MENDELSON J. A. ANALYSES OF WOUND EXUDATES FOR CLOSTRIDIAL TOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:623–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.623-629.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Iwamoto M., Mitsui K., Kawasaki H., Ando S. Cold-labile hemolysin produced by limited proteolysis of theta-toxin from Clostridium perfringens. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6048–6053. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Berry A. M., Lock R. A., Hansman D., Manning P. A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Streptococcus pneumoniae gene encoding pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J. The identification and purification of multiple forms of theta-haemolysin (theta-toxin) of Clostridium perfringens type A. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):219–238. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Mitten J., Henry C. Effects of alpha and theta toxins from Clostridium perfringens on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):324–333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Iandolo J. J. Purification and partial characterization of a putative precursor to staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):900–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.900-907.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa Y., Ito A., Sato H. Theta-toxin of Clostridium perfringens. I. Purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 26;494(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]