Abstract
Medulloblastoma (MB) can arise in the cerebellum due to genetic activation of the Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway. During normal cerebellum development, Shh spurs the proliferation of granule neuron precursors (GNPs), the precursor cells of MB. Mutations in the Shh receptor gene, patched1 (ptc1+/-), lead to increased MB incidence in humans and mice. MB tumorigenesis in mice heterozygous for ptc1+/- shows distinct steps of progression. Most ptc1+/- mice form clusters of pre-neoplastic cells on the surface of the mature cerebellum that actively transcribe Shh target genes. In ∼15% of mice, these pre-neoplastic cells will become fast-growing, lethal tumors. It was previously shown (1) that the loss of function of insulin-like growth factor 2 (igf2) suppresses MB formation in ptc1+/- mice. We found that igf2 is not expressed in preneoplastic lesions but is induced as these lesions progress to more advanced MB tumors. Igf2 is not required for formation of pre-neoplastic lesions, but is necessary for progression to advanced tumors. Exogenous Igf2 protein promoted proliferation of MB precursor cells (GNPs) and a MB cell line, PZp53MED. Blocking igf2 signaling inhibited growth of PZp53MED cells, implicating igf2 as a potential clinical target.
Keywords: hedgehog, igf2, medulloblastoma, patched, math1
INTRODUCTION
Mutations in the Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway that cause constitutive Shh target gene transcription are associated with the formation of many human tumors. Medulloblastoma (MB), the most common malignant brain tumor in children, can arise when such mutations occur in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors (GNPs) (2). Loss of function of the PATCHED1 (PTCH, ptc1 in mice) tumor suppressor gene, which occurs in sporadic and hereditary MB, is the most common of these mutations (3, 4). PTCH encodes a 12-transmembrane receptor (Ptc1) for Shh. In the absence of Shh signal, Ptc1 inhibits the downstream transducers of the Shh pathway, preventing activation of target gene transcription by Gli transcription factors. Shh activates target gene transcription by binding to and inhibiting Ptc1. Shh and Ptc1 are therefore antagonists. Ptc1 and gli1 are Shh target genes. Induction of ptc1 and gli1 by Shh creates a negative feedback loop (through Ptc1) that restrains ongoing Shh signaling and a positive feedback loop (through Gli1) that acts as an amplifier of the initial Shh signal. The balance between negatively-acting Ptc1 and positively-acting Gli proteins determines the functional state of Shh pathway activity (5, 6, 7, 8).
In the developing cerebellum, Shh signal produced by Purkinje neurons stimulates proliferation of GNPs in the external germinal layer (EGL) on the surface of the cerebellum (9, 10, 11). Shh target genes, such as N-myc and cyclin-D1 become active and promote cell cycle entry (12, 13, 14). In mice, expansion of GNPs ceases within three weeks after birth, as GNPs migrate to the internal granule cell layer and differentiate to form mature granule neurons (Fig. 1A). By the end of this period, the EGL has disappeared.
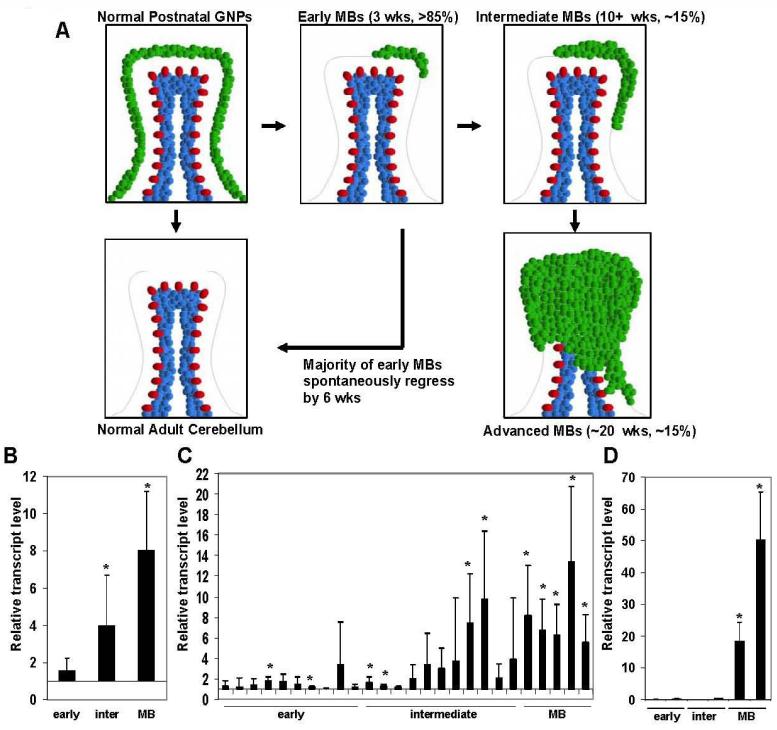
Figure 1.
Igf2 transcription increases at a late stage of MB tumorigenesis. (A) Multiple stages of MB tumorigenesis in the ptc1+/- mouse. GNPs (green) in the normal developing postnatal cerebellum proliferate in response to Shh produced by underlying Purkinje cell neurons (red). Throughout the first 3 weeks of postnatal life, GNPs stop responding to Shh, differentiate, and migrate into the internal granule cell layer to become mature granule neurons (blue). GNPs express Math1, while mature granule neurons do not. From 3 weeks of age to adulthood, no GNPs remain in the normal cerebellum, and Math1 expression is lost. However, in the majority of ptc1+/- mice (>85%) at 3 weeks of age, small clusters of Math1-expressing GNP-like cells persist as early, pre-neoplastic MB lesions. The majority of these lesions regress spontaneously by 6 weeks of age. A subset of these lesions (∼15% of total) progress to form more aggressive-appearing intermediate, asymptomatic MBs by 10 weeks and eventually advanced, symptomatic MBs by ∼20 weeks of age. (B) Pooled averages of igf2 transcript levels by microarray analysis of pre-neoplastic early MBs (early), intermediate MBs (inter), and advanced MBs (MB). Values are relative to normal P7 GNPs. Note that igf2 transcript levels are not increased until late in tumorigenesis. Asterisk denotes p<0.01. (C) Fold-enrichment of igf2 transcript in individual MB lesions relative to normal GNPs. Each measurement is the average of five different igf2 probes. Asterisk denotes p<0.05. (D) Quantification of igf2 transcript levels by quantitiative real-time PCR from individual early MBs (early), intermediate MBs (inter), and advanced MBs (MB). Values are relative to normal P7 GNPs. Asterisk denotes p<0.01. In (B-D) error bars denote standard deviation. P values were calculated using student’s T-test relative to normal P7 GNP controls.
Mice heterozygous for ptc1 spontaneously form MB and rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a tumor derived from muscle (15, 16). These tumors exhibit constitutive Shh target gene expression due to reduced Ptc1 activity. Small molecule Shh pathway inhibitors can reduce tumor formation in ptc1+/- mouse models of MB (17, 18), demonstrating the dependence of MB cells on Shh target gene expression. Therefore, knowledge of critical Shh target genes or genes that cooperate with the Shh pathway to promote tumorigenesis has potential clinical importance as a step toward identifying drug targets.
Insulin-like growth factor 2 (igf2) is expressed at high levels compared to normal tissue in both MB and RMS in ptc1+/- mice (16) and in humans (19, 20, 21, 22). Hahn et al demonstrated that igf2 is critical for the formation of both MB and RMS in ptc1+/- mice. When ptc1+/- mice are crossed into an igf2-deficient background, they no longer form MB or RMS like their igf2-wild-type littermates (1). Igf2 has also been shown to synergize with the Shh pathway to promote MB, as retroviral transfer of Shh and Igf2 expression constructs into postnatal cerebella causes a higher incidence of MB formation than delivery of a Shh expression construct alone (23). Igf2 protein can stimulate proliferation of cultured MB cell lines and their precursor cells, GNPs, suggesting a mechanistic basis for the role of igf2 in MB tumorigenesis (24).
Important questions remain about the involvement of igf2 in MB. The mechanism of increased igf2 expression in MB and RMS from ptc1+/- mice is not clear. Two independent analyses of igf2 expression from maternal and paternal alleles showed that increased igf2 levels do not result from loss of imprinting in MB or RMS or from gene amplification (1, 24). Rather, increased igf2 RNA levels appeared to be induced at a purely transcriptional level. Hahn et al. proposed that igf2 might be a Shh target gene, over-expressed in ptc1+/- tumors due to constitutive Shh pathway target gene transcription. In support of this hypothesis, the authors showed that compared to ptc1+/+ embryonic day 8.5 (E8.5) embryos, igf2 transcript levels were higher in ptc1+/- embryos and highest in ptc1-/- embryos (1). C3H/10T1/2 cells transfected with the Shh pathway-activating transcription factor Gli1 have increased igf2 RNA levels after 72 hours (25). However, cultured GNPs treated with Shh do not have increased igf2 RNA levels at the 6 hour time point tested (24). Therefore, it remains unclear whether constitutive Shh pathway transcriptional activity causes the increased levels of igf2 transcript found in MB.
It is also not clear what role igf2 plays in MB tumorigenesis. Igf2 could contribute to tumor initiation, either as a critical Shh target gene or an independently regulated gene. Alternatively, igf2 could cooperate with the Shh pathway to cause tumor progression at a specific stage of tumorigenesis.
Here, we evaluate igf2 expression at multiple stages of MB tumorigenesis. We also test the requirement for igf2 during early and late stages of tumorigenesis. We show that igf2 is not required for tumor initiation but is required for progression to advanced MB lesions. Modulation of igf2 signaling can regulate proliferation of MB cells in vitro, suggesting that igf2 is important not just for tumor progression but also for tumor maintenance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mouse strains
Igf2 knockout mice were kindly provided by Dr. Argiris Efstratiadis. Since igf2 is an imprinted gene for which only the paternal gene is expressed, male mice heterozygous for igf2 were mated with ptc1+/- mice (108B2) (15) with or without the Math1-gfp transgene. Math1-gfp mice were kindly provided by Dr. Jane Johnson. Offspring heterozygous for the igf2 knockout allele by PCR, using primers specific for wild-type and mutant igf2 alleles were effectively igf2 null. Offspring homozygous for the wild-type igf2 allele were considered wild-type.
Math1-gfp ptc1+/- igf2- mice and igf2+ littermates were sacrificed at 3 weeks to evaluate for early MB formation. Cerebella were visualized under a fluorescent dissecting microscope for development of GFP-positive lesions. Adult ptc1+/- igf2- and ptc1+/- igf2+ littermates were assessed for MB formation at 20-24 weeks by visual inspection of cerebella and X-gal staining, as previously described (15).
Microarray analysis
Early and intermediate MB cells were isolated from cerebella of math1-gfp ptc1+/- mice at 3-6 weeks or 10-20 weeks, respectively. Tumors were identified by inspection of cerebella for GFP fluorescence. Tumors were dissected and GFP-expressing cells were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Advanced MBs were isolated from symptomatic ptc1+/- mice and tumor cells were purified as previously described (11). RNA was isolated using Trizol reagent (GIBCO). RNA was amplified using Riboamp kit (Arcturus). Probe was reverse transcribed in the presence of aminoallyl-dUTP (Sigma) and subsequently labeled with Cy3 or Cy5 dye (Amersham). Probe made from tumor cell RNA was hybridized to cDNA microarrays produced by the Stanford Microarray Facility. Cy3-labeled tumor cell probes were hybridized against Cy5-labeled probe made from RNA isolated from high-level GFP-expressing GNPs isolated by FACS from the outer EGL of math1-gfp mice. Igf2 transcript level values are displayed relative to outer EGL GNPs. Average values of five independent probes were determined, per experiment.
Quantitative real time RT-PCR
Igf2 and gli1 transcript levels were measured by real-time PCR using RNA isolated with Trizol reagent (GIBCO). Gene expression assays for mouse igf2, gli1, and pgk1 and gapdh were purchased from Applied Biosystems. Igf2 and gli1 transcript levels were normalized to gapdh transcript levels in tumor cell, fibroblast, and PZp53MED cell experiments and to pgk1 transcript levels in GNP cell experiments.
P7 GNPs were isolated and cultured with or without 3μg/mL Shh for 48h as previously described (11). PZp53MED cells, ptc1+/- fibroblasts, or ptc1+/+ fibroblasts were cultured to confluence in DMEM + 0.5% FBS in the presence or absence of 10μM cyclopamine. RNA from ptc1+/+ fibroblasts transfected with CMV promoter-driven GFP, Gli1, and Gli2 expression constructs was kindly provided by Dr. Anna Penn.
In situ hybridization studies
35S-UTP-labeled probes were made by in vitro transcription, with T3 or T7 RNA polymerase, of linearized plasmids purchased from ATCC. Probes were diluted to 5×106 cpm/mL final concentration in buffer containing E. coli tRNA and DTT. Frozen tissue was embedded in OCT and cut to 15 μm sections on glass slides. Sections were dried and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and dehydrated through ethanol. Prior to hybridization, sections were treated with Proteinase K, acetylated with acetic anhydride, and dehydrated through ethanol. Hybridization was performed at 60-65°C overnight. Sections were RNAse-treated and washed with increasing stringencies of SSC with DTT. Slides were dehydrated, dipped in photographic emulsion, incubated for 4-14 days, developed, and counterstained with cresyl violet.
Cell survival assays
P7 GNPs were cultured in Neurobasal medium (GIBCO) with or without B27 supplement for 48h. Igf2 protein (R&D systems) was added to a final concentration of 250ng/mL. Cell titer was determined with CellTiter96 assay (Promega).
Cell proliferation assays
Proliferation of PZp53MED cells in the presence of anti-Igf1R (Anti-IR3, Calbiochem) blocking antibody was assayed by seeding cells at 1-2×103 cells/well of a 96-well plate in DMEM+0.5% FBS. Antibody or Igf2 protein was diluted in DMEM+0.5% FBS and added to cells 3h after seeding. Cells were cultured for 48h, and cell titer was determined by CellTiter96 assay.
For sIgf2R experiments, PZp53MED cells were seeded at 6×103 cells/well on coverslips in 24-well plates. The next day, cells were co-transfected in triplicate with 0.5μg pEYFP-N3 and 1μg of either pEFBOS-sIgf2R (kindly provided by Dr. Bass Hasan) or, as a control, 1μg of pECFP-N2. 24h post-transfection, cells were switched to DMEM+0.5% FBS and cultured for an additional 36h. BrdU was added for the final 6h. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and DNAse-treated as above. Cells were stained with rat anti-BrdU antibody (Abcam) at 1:50 dilution. The next day, anti-BrdU staining was detected with TRITC-conjugated anti-rat secondary antibody. Percentage of YFP-positive cells that were also BrdU-positive was calculated for each sample.
Immunoblotting and Immunoprecipitation
Cells were grown to confluence in 10-cm plates and then serum starved for 48h in DMEM+0.5%FBS. Then, cells were treated with 1 μg/mL or 10 μg/mL anti-Igf1R antibody (Calbiochem) and/or 250 ng/mL Igf2 protein (R&D systems), as described above, for 30 minutes. Protein extracts were prepared in RIPA buffer containing 50mM Tris, 1% NP-40, 0.25% DOC, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 1mM PMSF, protease inhibitors (Roche), and phosphatase inhibitors (Calbiochem). Protein samples (30 μg per sample) were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad), and then immunoblotted with the following antibodies: anti-Igf1Rβ (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-phospho-Akt (ser473) (Cell Signaling), anti-Akt (Cell Signaling), and anti-β-Tubulin (Covance). For determination of Igf1R phosphorylation, 200 μg protein extracts were incubated overnight at 4°C with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (Upstate) bound to protein G beads (Invitrogen). The immunoprecipitates were washed extensively, eluted in SDS sample buffer, and subjected to western blotting analysis using an anti-Igf1Rβ antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology).
RESULTS
Igf2 transcription increases at a late stage of MB tumorigenesis
To observe developing MBs, we crossed ptc1+/- mice with mice expressing GFP from a Math1 enhancer that is specifically expressed in immature GNPs (26). Math1 is a critical regulator of GNP development that is required for the formation of GNPs (27). Since Math1 expression is preserved throughout MB tumorigenesis (28,29), tumor cells from multiple stages of MB progression could be readily detected and isolated by virtue of their GFP expression. RNA from these cells was analyzed using cDNA microarrays to identify changes in gene expression that occur at each stage of MB tumorigenesis. We collected three tumor cell populations for this analysis (Fig. 1A): (1) pre-neoplastic “early” MB lesions that are present in >80% of 3 week old mice, the majority of which regress by 6 weeks, (2) intermediate, asymptomatic MB lesions that are present in ∼15% of 10 week old mice, the majority of which appear to progress to advanced MBs, and (3) advanced, symptomatic MB that occur in ∼15% of mice, with peak incidence at ∼20 weeks of age. For comparison, we used RNA from a purified population of GNPs, the precursor cells of MB, isolated from the EGL of normal post-natal day 7 (P7) cerebella.
We found that igf2 transcript levels are not significantly increased in early MB lesions relative to normal GNPs. Igf2 transcript levels are significantly increased only in intermediate MBs and are even higher in advanced MBs (Fig. 1B). Only 20% of individually tested early MBs have significantly increased levels relative to normal GNPs, compared to 36% of intermediate and 100% of advanced MBs (Fig. 1C). To confirm these microarray results, igf2 transcript levels from individual early, intermediate, and advanced MBs were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Advanced MB samples showed a statistically significant increase (∼20 to 50-fold) in igf2 transcript levels (Fig. 1D). Igf2 transcript levels were not statistically increased in any of the early or intermediate MBs tested. Increased igf2 transcription appears to be a late event in MB tumorigenesis and is correlated with the critical transition from early and intermediate to advanced MBs.
In situ hybridization of early and advanced MB with a probe specific for igf2 showed absent or low levels of igf2 transcript in early MB, but very high levels of transcript in advanced MBs (Fig. 2A, 2B). These data are consistent with our microarray data, confirming that increased igf2 transcription is a late event in MB tumorigenesis. High levels of igf2 transcript were also detected in the meninges of normal cerebella and cerebella containing tumors (Fig. 2A, 2B, arrows; Fig. 2C).
Figure 2.
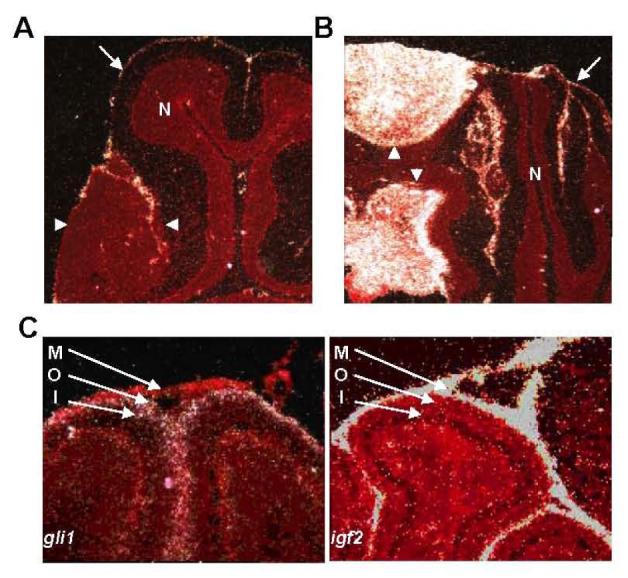
Expression of igf2 in developing cerebella and MB. (A, B) In situ hybridization studies of early MB (A) and advanced MB (B) using a probe specific to igf2. Signal from hybridized probe appears white. Tissue is counterstained in red. In each panel, tumor is outlined by arrowheads. Igf2 transcript is not seen in early MB (A), but is seen at high levels in the advanced MB (B). Igf2 transcript is not seen in normal cerebellum (N), but is observed in the meninges (arrows) surrounding the cerebellum. (C) In situ hybridization studies of P7 cerebella using probes specific to igf2 or gli1. Igf2 transcript is observed in the meninges (M), but not in the outer (O) or inner (I) EGL. Conversely, the Shh target transcript gli1 is absent from the meninges, but is seen in the outer, but not inner EGL.
Igf2 transcription can be regulated by the Shh pathway
The temporal pattern of igf2 expression during MB tumorigenesis raises the question of how the induction of igf2 expression is regulated. The expression pattern of igf2 is different from what is expected and observed for most Shh target genes. Shh target genes like ptc1 and gli1 are typically expressed at high levels in GNPs of the outer EGL, which proliferate in response to Shh produced by Purkinje neurons. In situ hybridization studies of developing P7 cerebella show high levels of igf2 transcript in the meninges and low levels in the EGL (Fig. 2C). Conversely, gli1, a Shh target gene in all tissues, is absent from the meninges, but abundantly transcribed in the outer EGL. We conclude that igf2 transcript is minimally produced in areas of Shh target gene transcription in the developing cerebellum.
To further investigate the relationship between Shh pathway activity and igf2 transcription, we examined the effect on igf2 transcript levels of activating or inhibiting the Shh pathway in cultured GNPs and MB cells. Shh-treatment of primary GNP cultures does not increase igf2 transcript levels after 6 hours (24). However, treatment of GNPs with Shh for 24 hours increased igf2 transcription relative to untreated controls (Fig. 3A). Similarly, treatment of PZp53MED cells, a MB cell line derived from a ptc1+/- p53-/- mouse MB, with the Shh pathway inhibitor, cyclopamine (CPN) reduced igf2 transcript levels relative to untreated controls (Fig. 3B). These results show that activation or inhibition of Shh target gene transcription can influence igf2 mRNA levels in cultured MB cells and their precursors.
Figure 3.
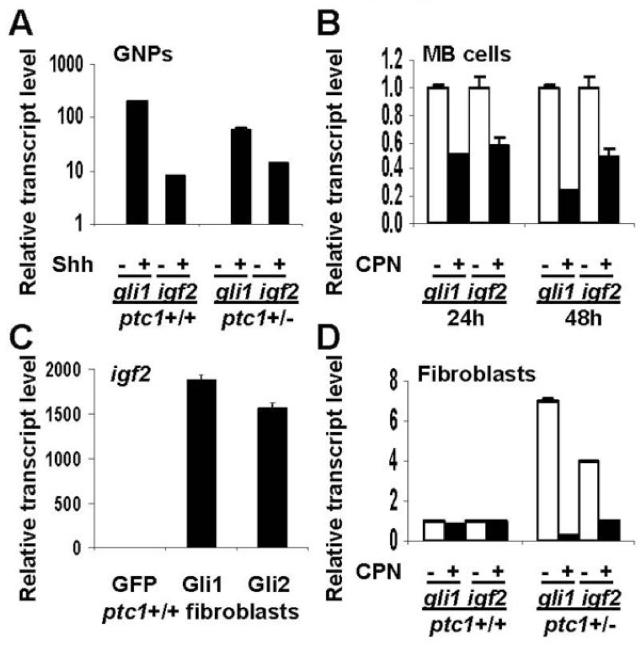
Igf2 transcription can be regulated by the Shh pathway. (A) Levels of gli1 and igf2 transcript are increased in ptc1+/+ or ptc1+/- P7 GNPs treated with Shh (3μg/mL) for 48h. (B) PZp53MED cells (MB cells) show decreased levels of gli1 and igf2 transcript when treated with the Shh pathway inhibitor cyclopamine (CPN) for 24 or 48h. (C) ptc1+/+ fibroblasts transfected with CMV promoter-driven Gli1 or Gli2 expression constructs showed increased levels of igf2 transcript after 24h compared with cells transfected with a GFP control. (D) ptc1+/- fibroblasts have increased levels of gli1 and igf2 transcript at baseline. In CPN-treated ptc1+/- fibroblasts, levels of both transcripts are reduced to levels comparable to those seen in ptc1+/+ fibroblasts. Error bars represent standard deviation.
Igf2 also behaves as a Shh-responsive gene in fibroblasts derived from ptc1+/+ or ptc1+/- embryos. When ptc1+/+ fibroblasts are transfected with Shh target gene-activating transcription factors gli1 or gli2, igf2 transcription is induced more than 1500-fold (Fig. 3C). Ptc1+/- embryos have reduced Ptc1 function and exhibit increased transcription of Shh target genes compared to ptc1+/+ embryos (15). Fibroblasts derived from ptc1+/- embryos have a 4-fold higher basal level of igf2 transcription than ptc1+/+ embryonic fibroblasts (Fig. 3D). Cyclopamine treatment does not change igf2 transcript levels in ptc1+/+ fibroblasts, but decreases igf2 transcript levels in ptc1+/- fibroblasts to levels similar to those seen in ptc1+/+ fibroblasts.
In summary, regulation of igf2 by the Shh pathway is complex. Although igf2 is a Shh-responsive gene in some cell types, it appears that igf2 is refractory to induction by Shh in the developing cerebellum and in early MBs that express other Shh target genes.
Igf2 is required for MB tumor progression, but not tumor initiation
Hahn et al demonstrated that igf2 is required for formation of advanced MBs in ptc1+/- mice (1), but which stage of tumorigenesis requires igf2 is unknown. Because igf2 transcription is induced during the transition between early and advanced MBs, we tested whether igf2 is required for early MB formation. The low level of igf2 expression in early MBs suggests that early MB formation would not require igf2 to be active within the pre-tumor cells. However, it is still possible that igf2 might play a role in early MB tumor initiation, since paracrine Igf2 signal produced in the neighboring meninges could stimulate GNPs or MB cells during early tumorigenesis. In this way, early lesions might be dependent on igf2, despite their lack of igf2 expression. Late in tumorigenesis, when lesions become too large to subsist on meningeal Igf2 alone, Igf2 produced by the tumor cells themselves may supplement the meningeal source through autocrine signaling.
To distinguish between these possibilities, we crossed Math1-gfp ptc1+/- females with igf2+/- males and analyzed Math1-gfp ptc1+/- offspring that were igf2+/- or igf2+/+. Because igf2 is an imprinted gene, only the paternal allele is expressed, and igf2+/- offspring are effectively igf2 null. We analyzed igf2+/- and igf2+/+ mice for early MB lesions and for MB formation. Consistent with previously reported results (1), no advanced MBs were observed in igf2 null offspring, while advanced MBs formed as expected in their igf2 wild-type littermates (Table 1). In contrast, formation of early MB lesions occurred even in the absence of igf2. All igf2 wild-type and null offspring developed clusters of pre-neoplastic cells by three weeks of age. These results suggest that igf2 plays a critical role exclusively in the progression to advanced MBs.
Table 1.
Early MB formation persists in Math1-gfp ptc1+/- igf2- mice. 100% of ptc1+/- igf2+ and ptc1+/- igf2- mice sacrificed at 3 weeks of age had early MB lesions. However, while ptc1+/- igf2+ mice developed advanced MBs, no MBs were observed in ptc1+/- igf2- mice (p<0.05).
| ptc1+/- igf2+ | ptc1+/- igf2- | |
|---|---|---|
| Early MBs | 3/3 | 3/3 |
| Advanced MBs | 5/18 | 0/12 |
Inhibition of igf2 signaling reduces proliferation of MB cells
Igf2 could act at a specific point in the tumor progression decision or as an ongoing promoter of growth. We tested whether igf2 plays a role in maintaining the growth of fully developed MB cells. Proliferative and survival-promoting signals are important for maintaining tumor growth. It was shown previously that Igf2 protein can induce proliferation in GNPs (24). Similarly, we find that Igf2 increases the fraction of proliferating GNPs three-fold (Fig 4A). We also show that Igf2 promotes cell survival of cultured GNPs. If GNPs are cultured in minimal media, the majority undergo apoptosis. GNPs cultured in minimal media with Igf2 alone show enhanced survival similar to GNPs grown in fully supplemented media (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
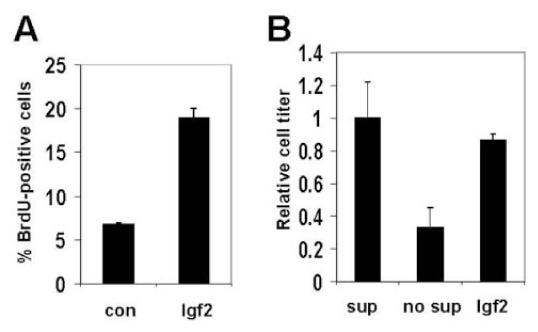
Igf2 promotes GNP proliferation and survival. (A) The percentage of GNPs which are proliferating (measured by BrdU staining) is increased when cells are cultured in the presence of Igf2 versus control for 48h. (B) Igf2 increases GNP survival under conditions which normally lead to apoptosis. If P7 GNPs are cultured in media without supplement (no sup) for 48h, a majority undergo apoptosis compared to those cultured in supplemented media (sup). When Igf2 is added to unsupplemented media, GNP survival is restored. Error bars represent standard deviation.
We tested the effects of augmenting or inhibiting igf2 signaling on cell proliferation of the MB cell line, PZp53MED. Addition of exogenous Igf2 increased proliferation of MB cells in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 5A).
Figure 5.
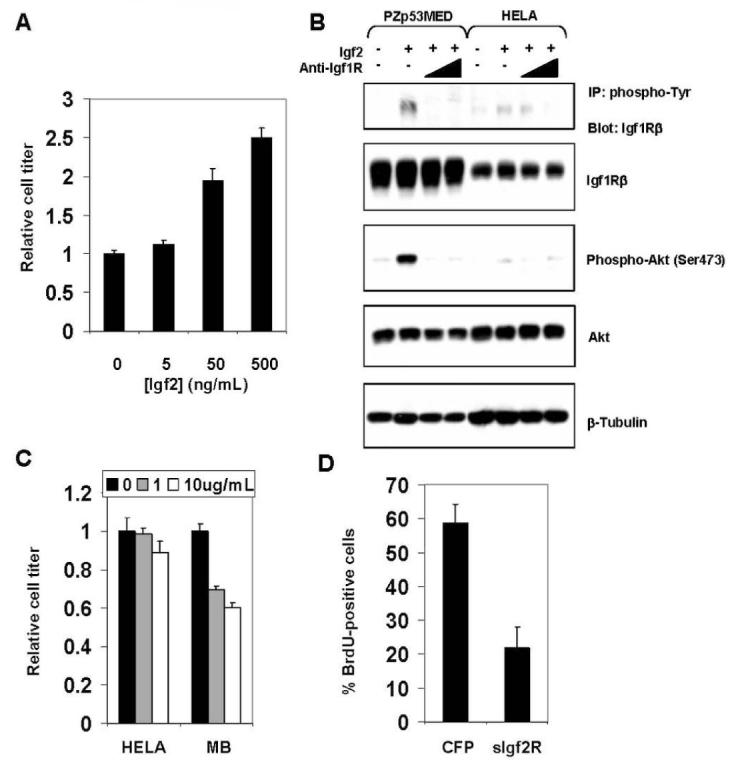
Inhibition of Igf2 signaling reduces MB cell proliferation. (A) Proliferation of PZp53MED cells is increased in a dose-dependent manner by exogenous Igf2 protein. Cell titer was measured after 48h in culture. (B) Levels of Igf1R and Akt phosphorylation in PZp53MED and HELA cell controls treated for 30 min with Igf2 with or without increasing concentrations of an antibody that blocks the Igf1R (anti-Igf1R, 1μg/mL, 10μg/mL). Levels of Igf1R and Akt phosphorylation increase dramatically in PZp53MED cells and only minimally in HELA cells when treated with Igf2 protein. Co-treatment with anti-Igf1R antibody reduced Igf1R and Akt phosphorylation to levels equal or below baseline in PZp53MED cells. Phospho-Igf1R was detected by immunoprecipitation with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody and immunoblotting with anti-Igf1Rβ antibody. (C) Anti-Igf1R antibody inhibits MB cell, but not control cell (HELA), proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Antibody was added for 48h at the specified concentrations, and cell titer was determined. (D) PZp53MED cells were co-transfected with YFP and either a CFP control or sIgf2R. Cells were assessed for BrdU staining after 36h (BrdU was added for the final 6h). The percentage of YFP-positive cells that were also BrdU-positive was calculated for each sample. Error bars represent standard deviation.
Igf2 ligand acts through the Igf1 receptor (Igf1R), which also can serve as a receptor for Igf1 and Insulin. We used an Igf1R-blocking antibody to inhibit the autocrine activity of endogenously produced Igf2. PZp53MED cells derived from a medulloblastoma have low basal levels of Igf1R phosphorylation and phosphorylation of Igf pathway target Akt (Fig. 5B). Phosphorylation of Igf1R and Akt increased dramatically when treated with exogenous Igf2 protein. In contrast, only a minimal increase in phosphorylation was observed in Igf2-treated HELA cell controls. When cells were treated with anti-Igf1R antibody and Igf2, levels of Igf1R and Akt phosphorylation are reduced to levels equal to or below baseline. Treatment of PZp53MED cells with anti-Igf1R antibody can therefore block the effects of even superphysiologic levels of Igf2.
When PZp53MED cells or HELA cell controls were cultured in the presence of anti-Igf1R antibody, PZp53MED cells showed a ∼40% decrease in cell number relative to untreated PZp53MED cells after 48 hours (Fig. 5C). There was no significant difference in cell number between treated and untreated HELA cells.
Blocking Igf1R can potentially also block the effects of Igf1 and Insulin. To more specifically block the effects of MB cell-produced Igf2, we used a soluble Igf2-Receptor (sIgf2R) construct that has been used previously to block the effects of Igf2 on cells or in vivo tissues (30,31). When sIgf2R is expressed, it is secreted from the cell where it binds and sequesters the Igf2 ligand, blocking its effect. Since sIgf2R specifically binds Igf2, it does not interfere with the actions of insulin, Igf1 or Igf1R. When PZp53MED cells were transfected with sIgf2R, they showed a ∼60% reduction in proliferation, measured by BrdU-incorporation, relative to CFP-transfected cells (Fig. 5D). These results indicate that Igf2 is specifically required for MB cell proliferation. In summary we observe that activation or inhibition of Igf2 signaling can promote or prevent MB cell growth, respectively.
DISCUSSION
The mechanism of igf2 induction in MB
Here we present evidence that igf2 is a Shh-responsive gene in cultured GNPs, MB cells, and fibroblasts. It might seem that igf2 is expressed at high levels in MBs because these tumors have increased Shh target gene transcription. However, increased igf2 transcription is not seen until late stages of MB tumorigenesis, even though constitutive Shh target gene transcription begins at early stages. Furthermore, increased igf2 transcription is not seen in developing GNPs of the outer EGL in vivo (Fig. 2B), which respond to Shh signal and express Shh target genes (11). Previous studies have indicated that neither genomic imprinting nor gene amplification are the causes of increased igf2 expression (1, 24). Rather, increased igf2 transcription appears to be due purely to transcriptional regulation.
One explanation for why igf2 transcription might be induced by Shh in cultured GNPs, but not in GNPs or early tumor cells in vivo is that the level of Shh pathway activation achieved in culture may be higher than in vivo. The concentration of Shh protein used in our cultured assays causes maximal activation of Shh target gene transcription (11). If igf2 transcription requires very high levels of Shh pathway activity, then perhaps this threshold activity is not achieved until late in tumorigenesis. Alternatively, the presence of some activating factor in the culture media, or the absence of some inhibitory factor that is present in the intact developing cerebellum may account for the differences in the response of GNPs to Shh in vitro versus in vivo. For example, restrictive chromatin structure or the presence of repressive transcription factors in cells in vivo may not be reproduced when these cells are cultured in vitro.
Another explanation for the pattern of igf2 regulation could be that Shh target gene transcription alone cannot account for increased igf2 transcription in MB. Shh target gene transcription likely plays a role in increased igf2 transcription, since igf2 transcript levels are decreased in cultured MB cells treated with the Shh pathway inhibitor cyclopamine, albeit only 2-fold. Another regulator may cooperate with the Shh pathway to induce igf2 transcription.
What might be responsible for the dramatic increase in igf2 transcription that occurs late in MB tumorigenesis? Increased igf2 expression due to altered transcriptional regulation in human tumors is a common finding, and perhaps such a mechanism cooperates with the Shh pathway to cause increased igf2 transcript levels in MB. Igf2 expression is induced by over-expression of the early growth response gene 1 (EGR1) protein in prostate cancer (32). Igf2 expression may be induced due to mutation of its flanking regulatory sequences. Changes in the 3′ untranslated region of igf2 are associated with 100 to 1000-fold increases in igf2 transcript levels in colorectal cancer (33). Altered methylation of the igf2 promoter causes increased igf2 transcription in hepatoblastoma (34).
PTEN activity can modulate igf2 expression in hepatoma (35). Increased PTEN activity leads to decreased igf2 transcription, and decreased PTEN activity causes increased igf2 transcription. Since igf2 signaling antagonizes PTEN activity by activating PI3-K (36), increases in Igf2 production may induce progressively increased autotranscription in feed-forward fashion. This hypothesis could explain why Hartmann et al did not see induction of igf2 transcription in GNPs treated with Shh alone for 6 hours, but did see low-level induction of igf2 transcription in GNPs treated with Shh and Igf2 (24). Shh target gene transcription and Igf2 production, first from the meninges and later from tumor cells themselves, may cooperate to induce igf2 transcription during MB tumorigenesis. A better understanding of the mechanism of increased igf2 expression in MB could yield opportunities to reverse this induction and inhibit the oncogenic effects of Igf2.
Temporal requirement for igf2 in late tumorigenesis
Our results suggest that induction of igf2 transcription is a late event in MB tumorigenesis that occurs as the pre-neoplastic cells of early MBs acquire a malignant phenotype. The requirement for Igf2 activity arises in late tumorigenesis, as early MB lesion formation occurs in the absence of igf2. These data do not preclude that igf2 may contribute to early tumorigenesis, as high levels of igf2 transcription are observed in the overlying meninges. However, the indispensable role for igf2 in MB formation occurs only in the late malignant conversion of MB and not during tumor initiation. This hypothesis is consistent with the observation that activation of Igf2 signaling alone in the developing cerebellum by retroviral transfer of igf2 is not sufficient to initiate MB formation (23).
This temporal pattern suggests a cooperation of autocrine Igf2 and other Shh target genes in MB tumorigenesis. Recent data have supported a cooperative hypothesis for these pathways. If Shh and Igf2 are introduced into neural progenitors by retroviral delivery, the frequency of MB formation is three-fold greater than with delivery of Shh alone (23). The Shh and Igf2 pathways converge to trigger the production of high levels of N-myc protein. The Shh pathway stimulates transcription of N-myc, while the Igf pathway leads to stabilization of N-myc protein through Akt-mediated effects on GSK-3β (13, 14, 37). Consistent with this hypothesis, retroviral delivery of stabilized N-myc along with Shh also causes a three-fold increase in MB frequency compared to Shh alone (38).
Igf2 might also cooperate with the Shh pathway in MB tumorigenesis by activating cell survival pathways. We show that Igf2 can promote GNP survival under conditions that normally lead to apoptosis. Similarly, the Igf family members, insulin and Igf1, can promote survival in cultured GNPs, likely through activation of the protooncogene Akt (39).
Igf2 may cooperate with Shh to promote transcription of Shh target genes. Transcription of the Shh target genes, gli1 and cyclinD1, is significantly increased in GNPs co-treated with Shh and Igf2 compared to Shh alone (24). Igf2 could increase levels of Shh target transcripts, including, as proposed earlier, igf2 itself, to promote tumor formation.
A model for medulloblastoma tumorigenesis
Based on our findings, we propose the following model of MB tumorigenesis. Normal GNPs in ptc1+/- mice accumulate one or more mutations that result in constitutive Shh target gene expression. The mutation could inactivate the remaining copy of ptc1, perhaps by methylation (17), or affect some other component. Cells with active Shh targets would proliferate and would resist cues to arrest and differentiate, leading to formation of early MBs. Most of these lesions resolve or remain as benign lesions that are noted in most asymptomatic adult ptc1+/- mice. In an ill-fated subset of these mice, the pre-MB cells would undergo additional changes, the most critical being those that cause increased transcription of igf2. Increased autocrine Igf2 production would allow persistence of these lesions and their conversion to a malignant phenotype. Such a further transformation would be consistent with the effects of Igf2 on cell survival and growth. These lesions then progress to form the advanced MB seen in ∼15% of ptc1+/- mice.
Given the apparent requirement of igf2 for progression to advanced MB, it is notable that when igf2 expression is analyzed in independent early MBs (Fig 1C), a significant increase in igf2 transcript is observed in ∼20% of lesions. This frequency is similar to the ∼15% of mice that form advanced MB, suggesting that those early MBs that have induced igf2 transcription comprise the subset of lesions that will progress to advanced MB. Failure to induce igf2 transcription would cause these lesions to regress or remain benign. In summary, Igf2 may be an important malignancy-associated factor required for the progression to advanced MB, making it an attractive therapeutic target.
Igf2 as a therapeutic target in MB
Strategies for blocking Igf2 signaling for the treatment of human tumors, such as MB, might include inhibition of Igf1R with small molecule inhibitors or receptor-blocking antibodies. Blocking Igf1R offers the advantage of preventing signaling by both Igf1 and Igf2, which stimulate the same signaling cascades. Whether Igf1 contributes to ptc1+/- MB formation is unclear. Increased igf1 expression is noted sporadically in ptc1+/- MBs (data not shown), but at levels much lower than those of igf2. We do not observe substitution for Igf2 by Igf1 in igf2-deficient ptc1+/- mice.
Our work demonstrates the promise of specific targeting of the Igf2 ligand. We used a soluble Igf2R to inhibit MB cell proliferation, which presumably worked by sequestering Igf2. Recently, this same protein, produced from a transgene, was shown to inhibit tumor formation in a mouse model of intestinal adenoma associated with high Igf2 levels (31). Neutralizing antibodies specific to Igf2 could also achieve this end. Finally, manipulation of Igf-binding proteins (IgfBPs) could block signaling by Igf ligands. For instance, IgfBP-3 can bind to and regulate the mitogenic activities of Igfs and inhibit their antiapoptotic effects (40).
Our data show a critical role for Igf2 in the progression and continued growth of MB in ptc1+/- mice. In human MB, dysregulation of the Shh pathway, often through loss of PTCH, is associated with a specific desmoplastic MB histology. Compared to classic medulloblastoma, desmoplastic MBs have a distinct gene expression profile that includes increased expression of igf2 and Shh target genes (41). It is possible that Igf2 could hold similar importance in this class of human MB and that Igf2-directed therapies could provide clinical benefit.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Drs. Argiris Efstratiadis and Jane Johnson for providing mouse strains, Dr. Susan McConnell for an in situ hybridization protocol, Dr. Bass Hasan for the sIgf2R plasmid, Dr. Anna Penn for RNA from Gli1- and Gli2-transfected fibroblasts, Natalia Snarskaya for assistance with microarray and RT-PCR experiments, and Hermie Manuel for assistance with mouse husbandry. This research was supported by National Cancer Institute grant #RO1 CA 088060. R.B.C. and M.T.B. were supported by the Stanford Medical Scientist Training Program NIH training grant. T.R. was supported by a Damon Runyan postdoctoral fellowship. M.T.B. was also supported by a National Science Foundation graduate research fellowship. E.Y.L. was supported by the National Institutes of Health under Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (5F32CA117775-03) from the NCI. M.P.S. is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
REFERENCES
- 1.Hahn H, Wojnowski L, Specht K, et al. Patched target Igf2 is indispensable for the formation of medulloblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:28341–4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C000352200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goussia AC, Bruner JM, Kyritsis AP, Agnantis NJ, Fuller GN. Cytogenetic and molecular genetic abnormalities in primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, et al. Sporadic medulloblstomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res. 1997;57:842–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, et al. Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science. 1996;272:1668–71. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5268.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ingham PW, Taylor AM, Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signaling. Nature. 1991;353:184–7. doi: 10.1038/353184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goodrich LV, Johnson RL, Milenkovic L, McMahon JA, Scott MP. Conservation of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway from flies to mice: induction of a mouse patched gene by Hedgehog. Genes Dev. 1996;10:301–12. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marigo V, Johnson RL, Vortkamp A, Tabin CJ. Sonic hedgehog differentially regulates expression of GLI and GLI3 during limb development. Dev Biol. 1996;180:273–83. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Altaba A Ruiz I. Gli proteins encode context-dependent positive and negative functions: implications for development and disease. Development. 1999;126:3205–16. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.14.3205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dahmane N, Altaba A Ruiz I. Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development. 1999;126:3089–100. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.14.3089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wallace VA. Purkinje-cell-derived Sonic hedgehog regulates granule neuron precursor cell proliferation in the developing mouse cerebellum. Curr Biol. 1999;9:445–8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP. Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog. Neuron. 1999;22:103–14. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80682-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kenney AM, Rowitch DH. Sonic hedgehog promotes G(1) cyclin expression and sustained cell cycle progression in mammalian neuronal precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:9055–67. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.23.9055-9067.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH. Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development. 2003;130:15–28. doi: 10.1242/dev.00182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Oliver TG, Grasfeder LL, Carroll AL, et al. Transcriptional profiling of the Sonic hedgehog response: a critical role for N-myc in proliferation of neuronal precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:7331–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0832317100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP. Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science. 1997;277:1109–13. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5329.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hahn H, Wojnowski L, Zimmer AM, Hall J, Miller G, Zimmer A. Rhabdomyosarcomas and radiation hypersensitivity in a mouse model of Gorlin syndrome. Nat Med. 1998;4:619–22. doi: 10.1038/nm0598-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, et al. Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science. 2002;297:1559–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1073733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Romer JT, Kimura H, Magdaleno S, et al. Suppression of the Shh pathway using a small molecule inhibitor eliminates medulloblastoma in Ptc1(+/-)p53(-/-) mice. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:229–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.van Doorn J, Gilhuis HJ, Koster JG, et al. Differential patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II mRNA expression in medulloblastoma. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2004;30:503–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2004.00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chopra A, Brown KM, Rood BR, Packer RJ, MacDonald TJ. The use of gene expression analysis to gain insights into signaling mechanisms of metastatic medulloblastoma. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2003;39:68–74. doi: 10.1159/000071317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Albrecht S, Waha A, Koch A, Kraus JA, Goodyer CG, Pietsch T. Variable imprinting of H19 and IGF2 in fetal cerebellum and medulloblastoma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996;55:1270–76. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199612000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhan S, Shapiro D, Zhan S, et al. Concordant loss of imprinting of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene promoters in cancer. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27983–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.47.27983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rao G, Pedone CA, Valle LD, Reiss K, Holland EC, Fults DW. Sonic hedgehog and insulin-like growth factor signaling synergize to induce medulloblastoma formation from nestin-expressing neural progenitors in mice. Oncogene. 2004;23:6156–62. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hartmann W, Koch A, Brune H, et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor II is involved in the proliferation control of medulloblastoma and its cerebellar precursor cells. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1153–62. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62335-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ingram WJ, Wicking CA, Grimmond SM, Forrest AR, Wainwright BJ. Novel genes regulated by Sonic Hedgehog in pluripotent mesenchymal cells. Oncogene. 2002;21:8196–205. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lumpkin EA, Collisson T, Parab P, et al. Math1-driven GFP expression in the developing nervous system of transgenic mice. Gene Expr Patterns. 2003;3:389–395. doi: 10.1016/s1567-133x(03)00089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jensen P, Smeyne R, Goldowitz D. Analysis of cerebellar development in math1 null embryos and chimeras. J. Neurosci. 2004;24:2202–2211. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3427-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee Y, Miller HL, Jensen P, et al. A molecular fingerprint for medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5428–5437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oliver TG, Read TA, Kessler JD, et al. Loss of patched and disruption of granule cell development in a pre-neoplastic stage of medulloblastoma. Development. 2005;132:2425–39. doi: 10.1242/dev.01793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zaina S, Newton RV, Paul MR, Graham CF. Local reduction in organ size in transgenic mice expressing a soluble Insulin-like Growth Factor II/Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor. Endocrinology. 1998;139:3886–95. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.9.6200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Harper J, Burns JL, Foulstone EJ, Pignatelli M, Zaina S, Hassan AB. Soluble IGF2 receptor rescues Apc(Min/+) intestinal adenoma progression induced by Igf2 loss of imprinting. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1940–8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Svaren J, Ehrig T, Abdulkadir SA, Ehrengruber MU, Watson MA, Milbrandt J. EGR1 target genes in prostate carcinoma cells identified by microarray analysis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:38524–31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005220200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hodzic D, Frey B, Marechal D, Scarcez T, Grooteclaes M, Winkler R. Cloning of breakpoints in and downstream the IGF2 gene that are associated with overexpression of IGF2 transcripts in colorectal tumours. Oncogene. 1999;18:4710–7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li X, Kogner P, Sandstedt B, Haas OA, Ekstrom TJ. Promoter-specific methylation and expression alterations of igf2 and h19 are involved in human hepatoblastoma. Int J Cancer. 1998;75:176–80. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19980119)75:2<176::aid-ijc2>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kang-Park S, Lee YI, Lee YI. PTEN modulates insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)-mediated signaling; the protein phosphatase activity of PTEN downregulates IGF-II expression in hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2003;545:203–8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yao R, Cooper GM. Growth factor-dependent survival of rodent fibroblasts requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase but is independent of pp70S6K activity. Oncogene. 1996;13:343–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kenney AM, Widlund HR, Rowitch DH. Hedgehog and PI-3 Kinase signaling converge on Nmyc1 to promote cell cycle progression in cerebellar neuronal precursors. Development. 2004;131:217–28. doi: 10.1242/dev.00891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Browd SR, Kenney AM, Gottfried ON, et al. N-myc can substitute for Insulin-like Growth Factor signaling in a mouse model of Sonic Hedgehog-induced medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2666–72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al. Regulation of neuronal survival by the serinethreonine protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;275:661–5. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5300.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nickerson T, Huynh H, Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 induces apoptosis in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;237:690–3. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature. 2002;415:436–42. doi: 10.1038/415436a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]