Abstract
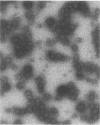
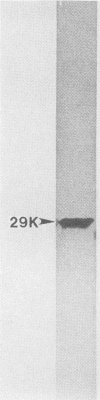
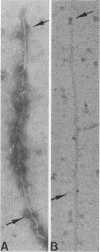
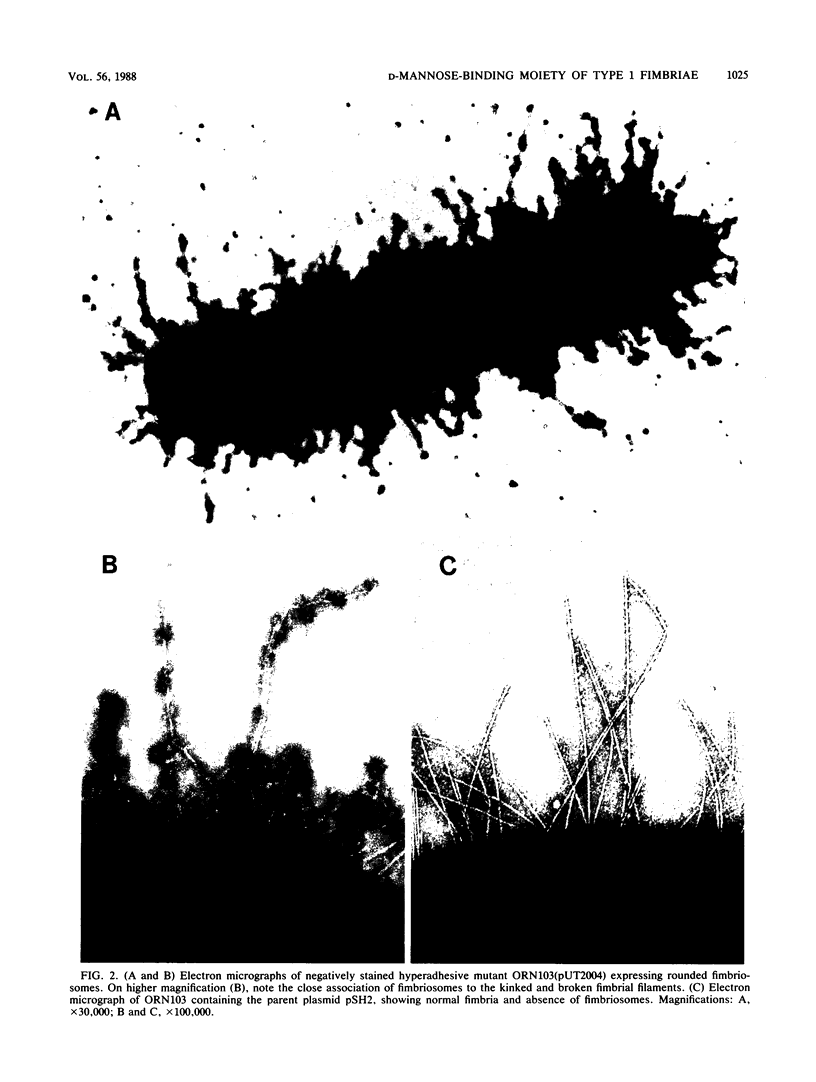
The relationships of the genes and gene-products mediating D-mannose-specific attachment of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli to eucaryotic cells were investigated by deletion mutation analysis of recombinant plasmid pSH2, which carries the genetic information for the synthesis and expression of functional type 1 fimbriae. Mutant pUT2004 was derived by a deletion remote from the structural gene encoding the 17-kilodalton (kDa) subunit protein of type 1 fimbriae. Phenotypically, the mutant demonstrated an eightfold-higher mannose-specific hemagglutination titer than the parent strain. On electron microscopy, the mutant strain expressed the same number of fimbriae as the parent strain. However, numerous 10-nm-diameter rounded structures (fimbriosomes) were observed both closely associated with fimbriae and in the culture medium. Fimbriosomes isolated from the medium agglutinated guinea pig erythrocytes in a mannose-sensitive manner. Dissociation of the fimbriosomes yielded a single 29-kDa protein, as demonstrated by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Antibodies raised against fimbriosomes reacted with a 29-kDa protein on immunoelectroblots of dissociated type 1 fimbriae and also blocked the adherence of other strains of type 1 fimbriated E. coli to eucaryotic cells. These findings suggest that the enhanced adhesive properties of the mutant pUT2004 strain are associated with overproduction of the 29-kDa FimH in the form of fimbriosomes which contain the determinant of the D-mannose-sensitive adhesion of type 1 fimbriae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Freitag C. S., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Babu J. P., Giampapa C. S., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Protection against Escherichia coli-induced urinary tract infections with hybridoma antibodies directed against type 1 fimbriae or complementary D-mannose receptors. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):625–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.625-628.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H. Assembly of a chemically synthesized peptide of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae into fimbria-like antigenic structures. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2460–2465. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2460-2465.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Goguen J. D., Sun D., Klemm P., Beachey E. H. Identification of two ancillary subunits of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae by using antibodies against synthetic oligopeptides of fim gene products. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5530–5536. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5530-5536.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Antiadhesive properties of a quaternary structure-specific hybridoma antibody against type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1114–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd D. C., Eisenstein B. I. Antigenic quantitation of type 1 fimbriae on the surface of Escherichia coli cells by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent inhibition assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):764–773. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.764-773.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayappa H. G., Goodnow R. A., Geary S. J. Role of Escherichia coli type 1 pilus in colonization of porcine ileum and its protective nature as a vaccine antigen in controlling colibacillosis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):350–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.350-354.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Christiansen G. Three fim genes required for the regulation of length and mediation of adhesion of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00328136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Jørgensen B. J., van Die I., de Ree H., Bergmans H. The fim genes responsible for synthesis of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli, cloning and genetic organization. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):410–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00330751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. The fimA gene encoding the type-1 fimbrial subunit of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence and primary structure of the protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Two regulatory fim genes, fimB and fimE, control the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lund B., Johansson L., Normark S. Localization of the receptor-binding protein adhesin at the tip of the bacterial pilus. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):84–87. doi: 10.1038/328084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for adherence of bacteria to animal cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.512-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of a gene product that regulates type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):61–66. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.61-66.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]