Abstract
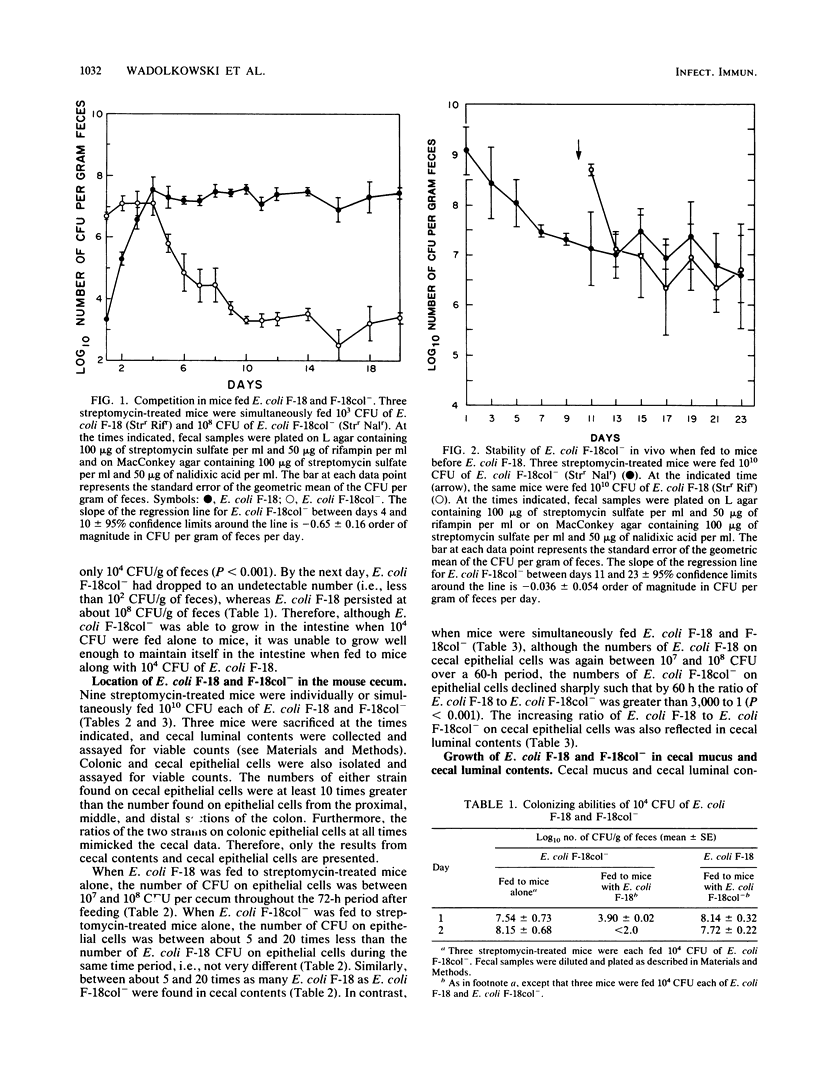
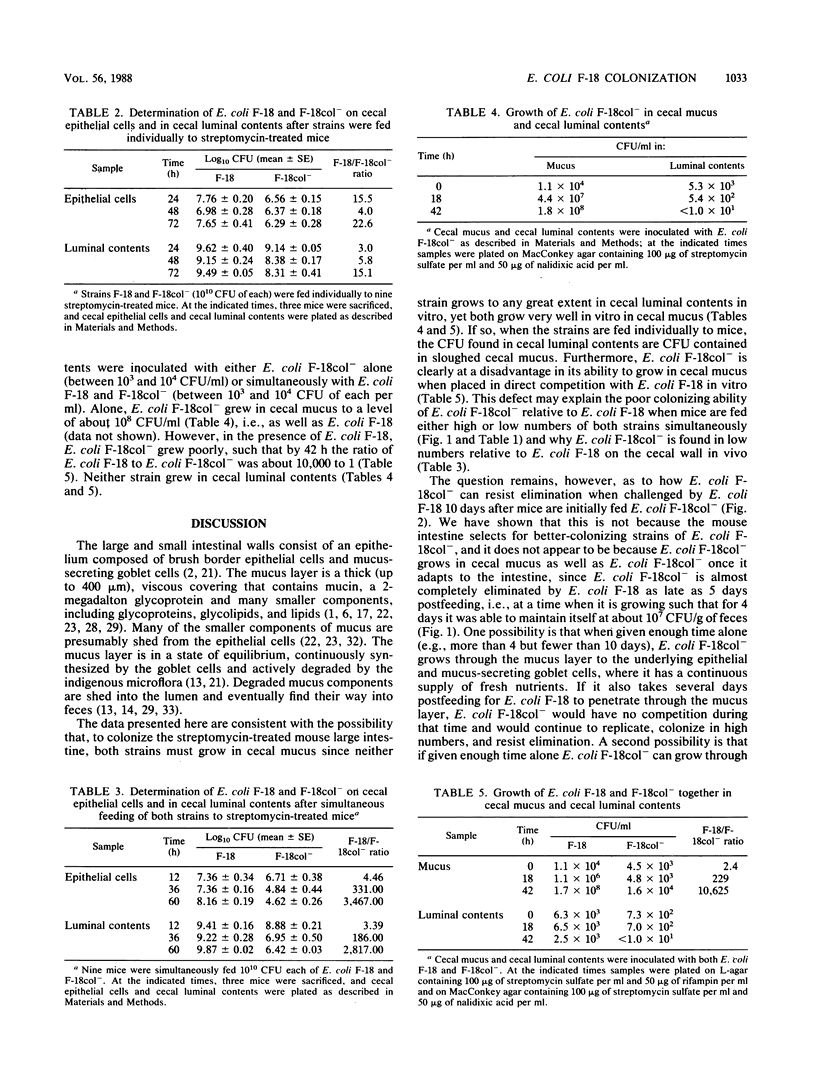
The relative colonizing abilities of Escherichia coli F-18, isolated from the feces of a healthy human, and E. coli F-18col-, a strain derived from it which does not make the E. coli F-18 colicin, were studied. In a previous report, it was shown that when each strain was fed individually to streptomycin-treated mice, at approximately 10(10) CFU per mouse, each colonized the large intestine at between 10(7) and 10(8) CFU/g of feces indefinitely. However, when simultaneously fed to mice, although E. coli F-18 colonized at about 10(8) CFU/g of feces, E. coli F-18col- dropped to a level of 10(3) CFU/g of feces within 3 to 5 days. In the present investigation, we show that when given enough time to establish a state of colonization, E. coli F-18col- persists in feces in high numbers despite subsequent challenge by E. coli F-18. Therefore, a major defect in the ability of E. coli F-18col- to colonize in the presence of E. coli F-18 appears to be in initiating that state. In addition, when mucus was scraped from the cecal wall and, without further treatment, was inoculated with E. coli F-18 or F-18col-, both strains grew well. However, when cecal mucus was inoculated with both strains simultaneously, E. coli F-18 grew far more rapidly than E. coli F-18col-. Moreover, neither strain grew in cecal luminal contents. Together, these data suggest the possibility that both E. coli F-18 and F-18col- must grow in mucus to colonize the streptomycin-treated mouse large intestine, that E. coli F-18col- is eliminated by E. coli F-18 because it does not grow in mucus as well as E. coli F-18, and that E. coli F-18col- can resist elimination by E. coli F-18 if it is allowed enough time to establish itself within the mucus layer.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. II. FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR ITS LOSS FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:817–828. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Rossoll R., Cabelli V. J., Yang S. L., Laux D. C. Relationship between the mouse colonizing ability of a human fecal Escherichia coli strain and its ability to bind a specific mouse colonic mucous gel protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.62-69.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corliss T. L., Cohen P. S., Cabelli V. J. R-Plasmid Transfer to and from Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Human Fecal Samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):959–966. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.959-966.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. (1-14C)glucosamine incorporation by subcellular fractions of small intestinal mucosa. Identification by precursor labeling of three functionally distinct glycoprotein classes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3584–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Brickner H., Botney M., Cleven D., Aranki A. Mechanisms that control bacterial populations in continuous-flow culture models of mouse large intestinal flora. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.676-685.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Brickner H., Fekete J., Vickerman M. M., Carey K. E. Survival and implantation of Escherichia coli in the intestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):686–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.686-703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Mechanisms of association of bacteria with mucosal surfaces. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:36–55. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Stauffer E., Cleven D., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Continuous-flow cultures as in vitro models of the ecology of large intestinal flora. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):666–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.666-675.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley C. L., Neumann C. S., Richmond M. H. Adhesion of commensal bacteria to the large intestine wall in humans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):128–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.128-132.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Zamcheck N. Bacterial degradation of gastrointestinal mucins. I. Comparison of mucus constituents in the stools of germ-free and conventional rats. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikari N. S., Kenton D. M., Young V. M. Interaction in the germfree mouse intestine of colicinogenic and colicin-sensitive microorganisms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Apr;130(4):1280–1284. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Schmidt G., Blumenstock E., Vosbeck K. Escherichia coli adhesion to Saccharomyces cerevisiae and mammalian cells: role of piliation and surface hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):484–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.484-489.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhal M. L., Cohen P. S., Laux D. C. Altered colonizing ability for mouse large intestine of a surface mutant of a human faecal isolate of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1549–1558. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhal M. L., Laux D. C., Cohen P. S. Relative colonizing abilities of human fecal and K 12 strains of Escherichia coli in the large intestines of streptomycin-treated mice. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;1(3):186–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02019621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S., Allen T. D. Ultrastructure of cell loss in intestinal mucosa. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Aug;60(2):272–277. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)80071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUASTLER H., SHERMAN F. G. Cell population kinetics in the intestinal epithelium of the mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Jun;17(3):420–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que J. U., Casey S. W., Hentges D. J. Factors responsible for increased susceptibility of mice to intestinal colonization after treatment with streptomycin. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):116–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.116-123.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubulis A., Rubert M., Faloon W. W. Cholesterol lowering, fecal bile acid, and sterol changes during neomycin and colchicine. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Sep;23(9):1251–1259. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.9.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany A., Yano S., Slomiany B. L., Glass G. B. Lipid composition of the gastric mucous barrier in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti J. R., Salyers A. A., Bullard W. S., Wilkins D. Breakdown of mucin and plant polysaccharides in the human colon. Can J Biochem. 1977 Nov;55(11):1190–1196. doi: 10.1139/o77-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadolkowski E. A., Laux D. C., Cohen P. S. Colonization of the streptomycin-treated mouse large intestine by a human fecal Escherichia coli strain: role of adhesion to mucosal receptors. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1036-1043.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold J. K., Khan R., Midtvedt T. Intestinal glycoproteins of germfree rats. Chemical composition of intestinal and fecal mucus from germfree rats fed a chemically defined diet. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(4):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



