Abstract
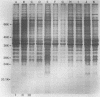
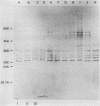
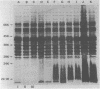
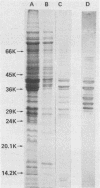
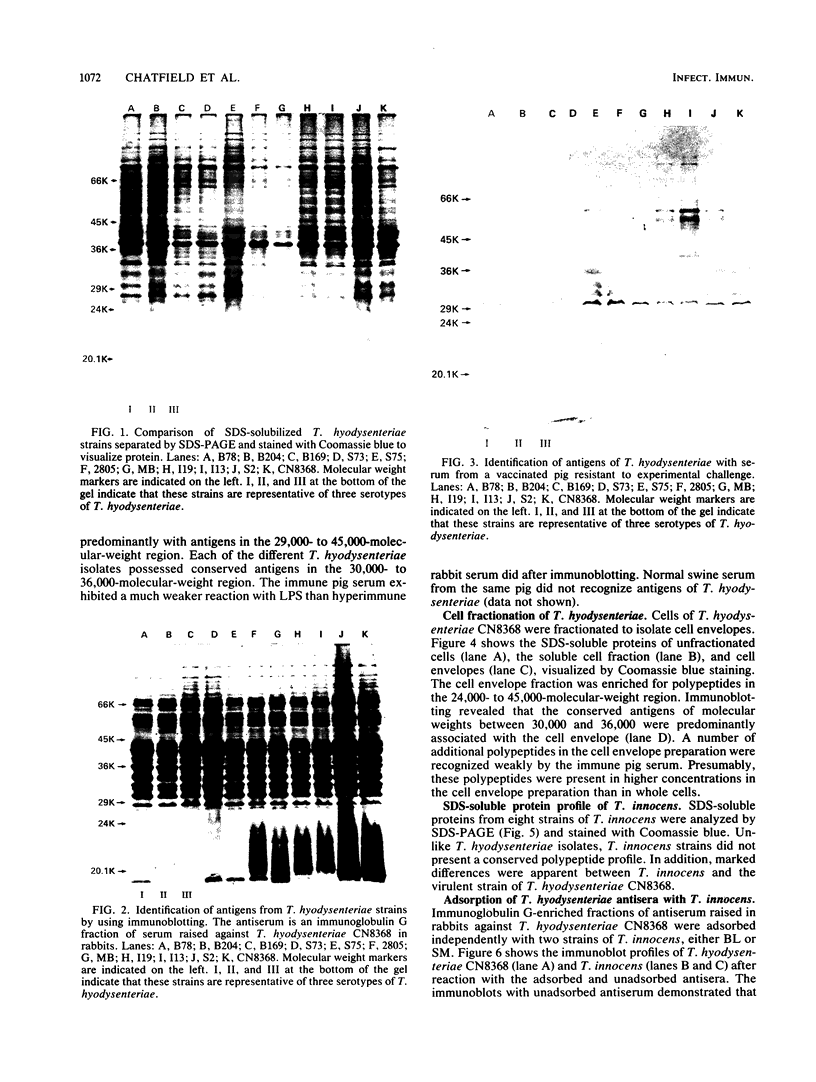
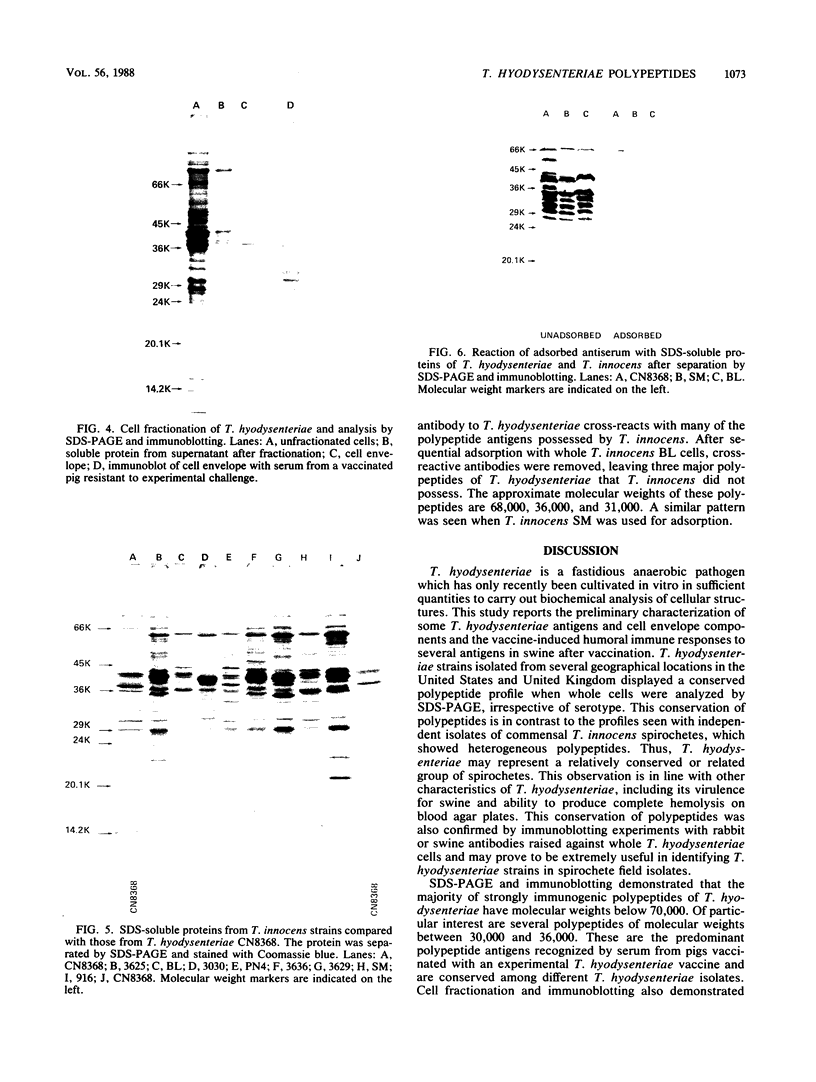
Eleven strains of Treponema hyodysenteriae isolated from pigs with swine dysentery were examined by using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. T. hyodysenteriae strains formed a homogeneous group with respect to sodium dodecyl sulfate-soluble proteins. However, immunoblotting with antiserum from rabbits immunized with T. hyodysenteriae CN8368 revealed heterogeneity among the lipopolysaccharide complexes of different strains. Polypeptides of molecular weights between 30,000 and 36,000 were the predominant T. hyodysenteriae polypeptides detected by porcine immune serum. In contrast, Treponema innocens did not form a homogeneous group with respect to sodium dodecyl sulfate-soluble proteins. Adsorption studies and immunoblotting identified polypeptide antigens present on cells of T. hyodysenteriae which were not detected on cells of T. innocens. These unique antigens may play a role in the virulence of T. hyodysenteriae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander T. J., Taylor D. J. The clinical signs, diagnosis and control of swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1969 Jul 19;85(3):59–63. doi: 10.1136/vr.85.3.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum D. H., Joens L. A. Serotypes of beta-hemolytic Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):792–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.792-796.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie D. S., Ripley P. H., Walker P. D. Swine dysentery: protection against experimental challenge following single dose parenteral immunisation with inactivated Treponema hyodysenteriae. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):217–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. J., Alexander T. J., Lysons R. J. Diagnosis of swine dysentery: spirochaetes which may be confused with Treponema hyodysenteriae. Vet Rec. 1976 Dec 18;99(25-26):498–500. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.25-26.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Olander H. J., Kanitz D. L., Qureshi S. A study of swine dysentery by immunofluorescence and histology. Vet Pathol. 1977 Sep;14(5):490–507. doi: 10.1177/030098587701400509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Olander H. J., Williams C. B. Swine dysentery: pathogenicity of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):971–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., DeYoung D. W., Glock R. D., Mapother M. E., Cramer J. D., Wilcox H. E., 3rd Passive protection of segmented swine colonic loops against swine dysentery. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2369–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Harris D. L., Baum D. H. Immunity to Swine dysentery in recovered pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Oct;40(10):1352–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Marquez R. B. Molecular characterization of proteins from porcine spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):893–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.893-896.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Nord N. A., Kinyon J. M., Egan I. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Treponema hyodysenteriae antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):249–252. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.249-252.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Whipp S. C., Glock R. D., Neussen M. E. Serotype-specific protection against Treponema hyodysenteriae infection in ligated colonic loops of pigs recovered from swine dysentery. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):460–462. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.460-462.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinyon J. M., Harris D. L., Glock R. D. Enteropathogenicity of various isolates of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.638-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapother M. E., Joens L. A. New serotypes of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):161–164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.161-164.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuessen M. E., Birmingham J. R., Joens L. A. Biological activity of a lipopolysaccharide extracted from Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):138–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.138-142.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuessen M. E., Joens L. A., Glock R. D. Involvement of lipopolysaccharide in the pathogenicity of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):997–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. D. Clinical and pathological observations on the experimental passage of swine dysentery. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Campbell W. H. Adaptation of the dye-binding protein assay to microtiter plates. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Alexander T. J. The production of dysentery in swine by feeding cultures containing a spirochaete. Br Vet J. 1971 Nov;127(11):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]