Abstract
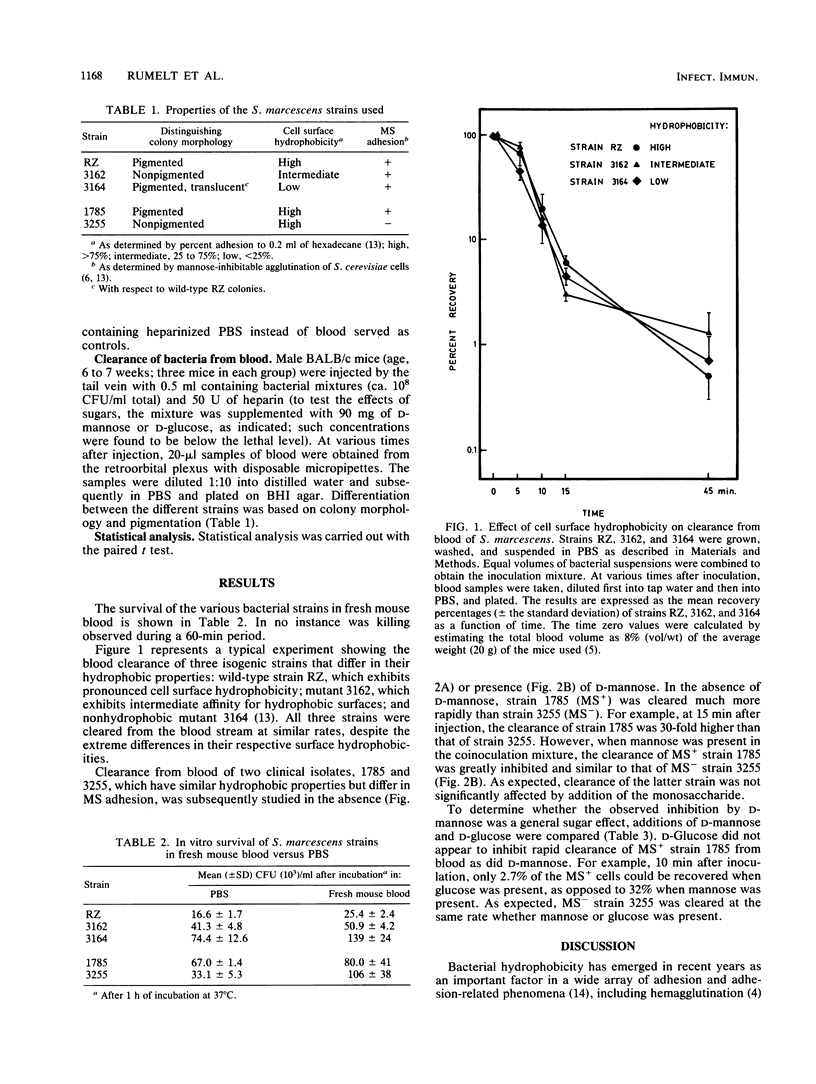
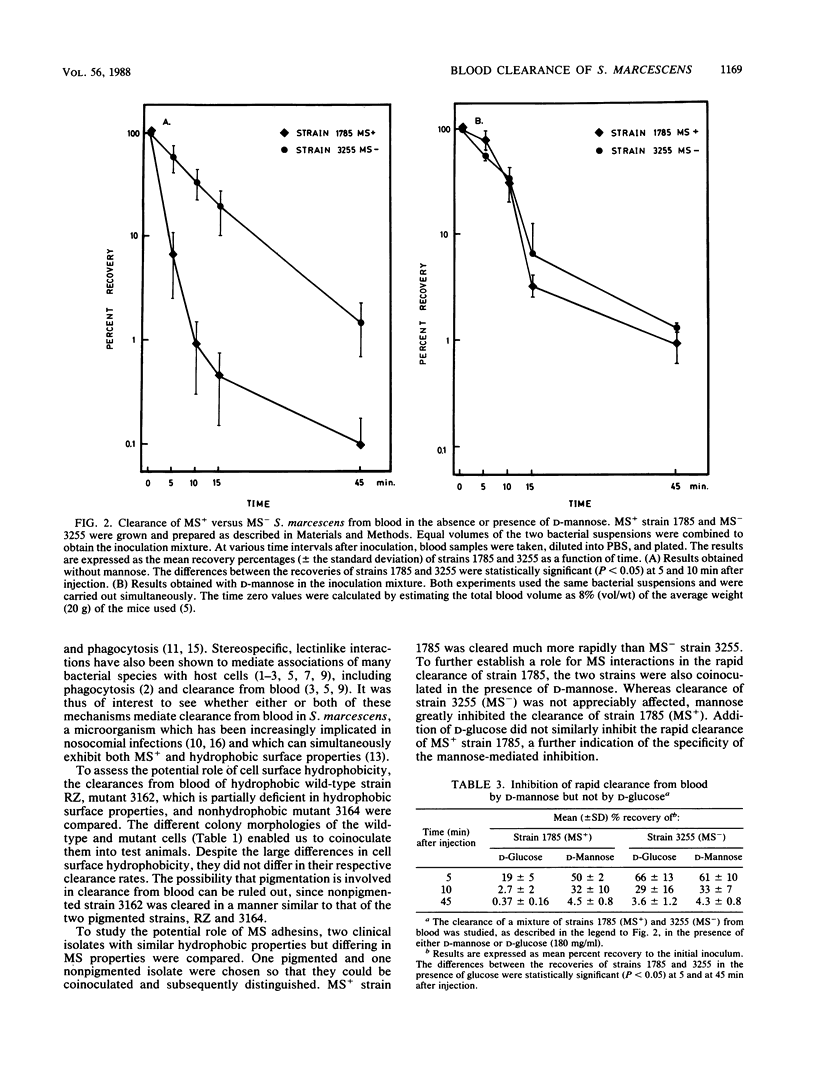
In the present study, we examined the potential roles of cell surface hydrophobicity and mannose-sensitive (MS) interactions in blood clearance of Serratia marcescens in mice. Hydrophobic strain RZ, partially hydrophobic mutant 3162, and nonhydrophobic mutant 3164 were coinoculated into BALB/c male mice, and blood samples were plated out at different time intervals; colonies of the three strains were distinguished by their different morphologies. All three strains were cleared from the blood stream at similar rates, despite their large relative differences in cell surface hydrophobicity. Clearance from blood was subsequently studied by coinoculating two clinical isolates which differ in their abilities to adhere via MS interactions. MS+ strain 1785 was cleared much more rapidly than MS- strain 3255; moreover, in the presence of D-mannose, clearance of strain 1785 was inhibited to a rate similar to that of MS- strain 3255. When D-glucose was substituted for D-mannose, inhibition was not observed. The results suggest that MS, rather than hydrophobic, interactions are primarily responsible for the rapid clearance of S. marcescens from blood observed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock E., Jann K. Adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli strains to phagocytes: differences between bacteria with mannose-sensitive pili and those with mannose-resistant pili. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):264–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.264-269.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Moon R. J. Hepatic clearance of Salmonella typhimurium in silica-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.1005-1012.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber N., Sharon N., Shohet D., Lam J. S., Doyle R. J. Contribution of hydrophobicity to hemagglutination reactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):336–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.336-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Moon R. J. Association of type 1 pili with the ability of livers to clear Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1168–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1168-1174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Altmann G., Eshdat Y. Screening of bacterial isolates for mannose-specific lectin activity by agglutination of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.328-331.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Hydrophobic interactions of group A streptococci with hexadecane droplets. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.139-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A., Ofek I. Inhibition of blood clearance and hepatic tissue binding of Escherichia coli by liver lectin-specific sugars and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):257–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.257-262.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Blumberger Y., Judes H., Bar-Ness R., Rubinstein E., Mazor Y. Cell surface hydrophobicity of pigmented and nonpigmented clinical Serratia marcescens strains. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):932–935. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.932-935.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. Isolation of pigmented and nonpigmented mutants of Serratia marcescens with reduced cell surface hydrophobicity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):480–482. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.480-482.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh J. D. Antibiotic resistance in Serratia marcescens. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Dec 3;287(6406):1651–1653. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6406.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Loh B. A., Cabral D. A., Salit I. E. Nonopsonic phagocytosis of nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human neutrophils and monocyte-derived macrophages is correlated with bacterial piliation and hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L. Serratia marcescens: historical perspective and clinical review. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 19;300(16):887–893. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904193001604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


