Abstract
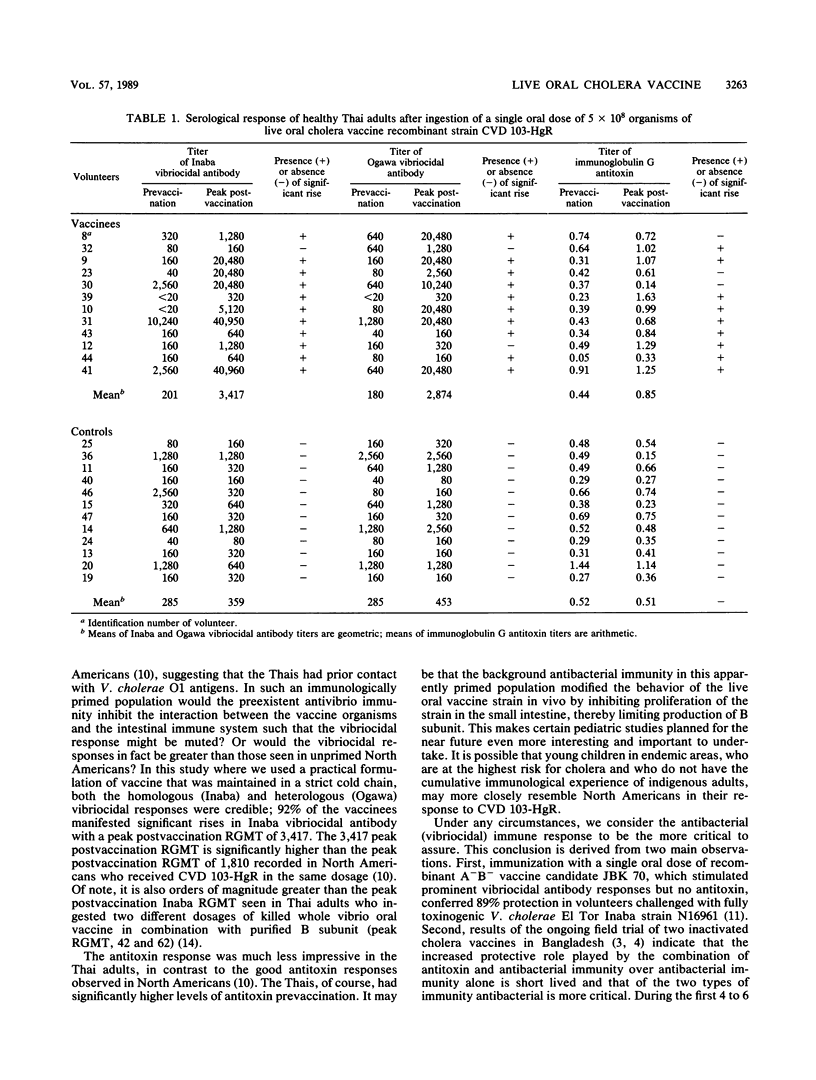
A single dose (5 x 10(8) organisms) of attenuated A- B+ Vibrio cholerae classical Inaba recombinant vaccine strain CVD 103-HgR or placebo was administered to 24 healthy young Thai adults in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of safety and immunogenicity. None of the volunteers experienced untoward reactions. The vaccine strain was recovered from 2 of 12 vaccines. The vibriocidal antibody response (the best immunological correlate of protection) was good: 11 of 12 vaccinees (92%) manifested significant serotype-homologous Inaba antibody rises with a peak reciprocal geometric mean titer (RGMT) postvaccination of 3,417; 9 of 12 exhibited significant serotype-heterologous Ogawa antibody rises (prevaccination RGMT, 180; peak RGMT, 2,874). Nine of 12 vaccinees had significant rises in serum antitoxin. None of the controls exhibited rises in vibriocidal or antitoxic antibody. This preliminary study further confirms the safety and immunogenicity of CVD 103-HgR live oral cholera vaccine and paves the way for larger community studies of this candidate cholera vaccine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Young C. R., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Protective efficacy in humans of killed whole-vibrio oral cholera vaccine with and without the B subunit of cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1116–1120. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1116-1120.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Snyder M. J., Wenzel R. P., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. I. Clinical, serologic, and bacteriologic responses to a known inoculum. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Harris J. R., Sack D. A., Chakraborty J., Ahmed F., Stanton B. F., Khan M. U., Kay B. A., Huda N., Khan M. R. Field trial of oral cholera vaccines in Bangladesh: results of one year of follow-up. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):60–69. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Harris J. R., Chakraborty J., Khan M. R., Stanton B. F., Kay B. A., Khan M. U., Yunus M., Atkinson W. Field trial of oral cholera vaccines in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1986 Jul 19;2(8499):124–127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements M. L., Levine M. M., Young C. R., Black R. E., Lim Y. L., Robins-Browne R. M., Craig J. P. Magnitude, kinetics, and duration of vibriocidal antibody responses in North Americans after ingestion of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):465–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Lanata C., Sears S., Honda T., Young C. R., Finkelstein R. A. Evaluation in humans of attenuated Vibrio cholerae El Tor Ogawa strain Texas Star-SR as a live oral vaccine. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.515-522.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Ketley J., Losonsky G., Tacket C. O., Tall B., Cryz S. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of recombinant live oral cholera vaccines, CVD 103 and CVD 103-HgR. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):467–470. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Craig J. P., Hoover D., Bergquist E. J., Waterman D., Holley H. P., Hornick R. B., Pierce N. P., Libonati J. P. Immunity of cholera in man: relative role of antibacterial versus antitoxic immunity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Young C. R., Black R. E., Takeda Y., Finkelstein R. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure antibodies to purified heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine strains of Escherichia coli and to cholera toxin: application in serodiagnosis and seroepidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):174–179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.174-179.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migasena S., Desakorn V., Suntharasamai P., Pitisuttitham P., Prayurahong B., Supanaranond W., Black R. E. Immunogenicity of two formulations of oral cholera vaccine comprised of killed whole vibrios and the B subunit of cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):117–120. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.117-120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Benenson A. S., Barui R. A serological survey for cholear antibodies in rural east Pakistan. 1. The distribution of antibody in the control population of a cholera-vaccine field-trial area and the relation of antibody titre to the pattern of endemic cholera. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(3):327–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Chen M. E., Holmes R. K., Kaper J., Levine M. M. Environmental and human isolates of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus produce a Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga)-like cytotoxin. Lancet. 1984 Jan 14;1(8368):77–78. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennels M. B., Levine M. M., Daya V., Angle P., Young C. Selective vs. nonselective media and direct plating vs. enrichment technique in isolation of Vibrio cholerae: recommendations for clinical laboratories. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):328–331. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Jertborn M., Gothefors L., Karim A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J. Mucosal antitoxic and antibacterial immunity after cholera disease and after immunization with a combined B subunit-whole cell vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):884–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



