Abstract
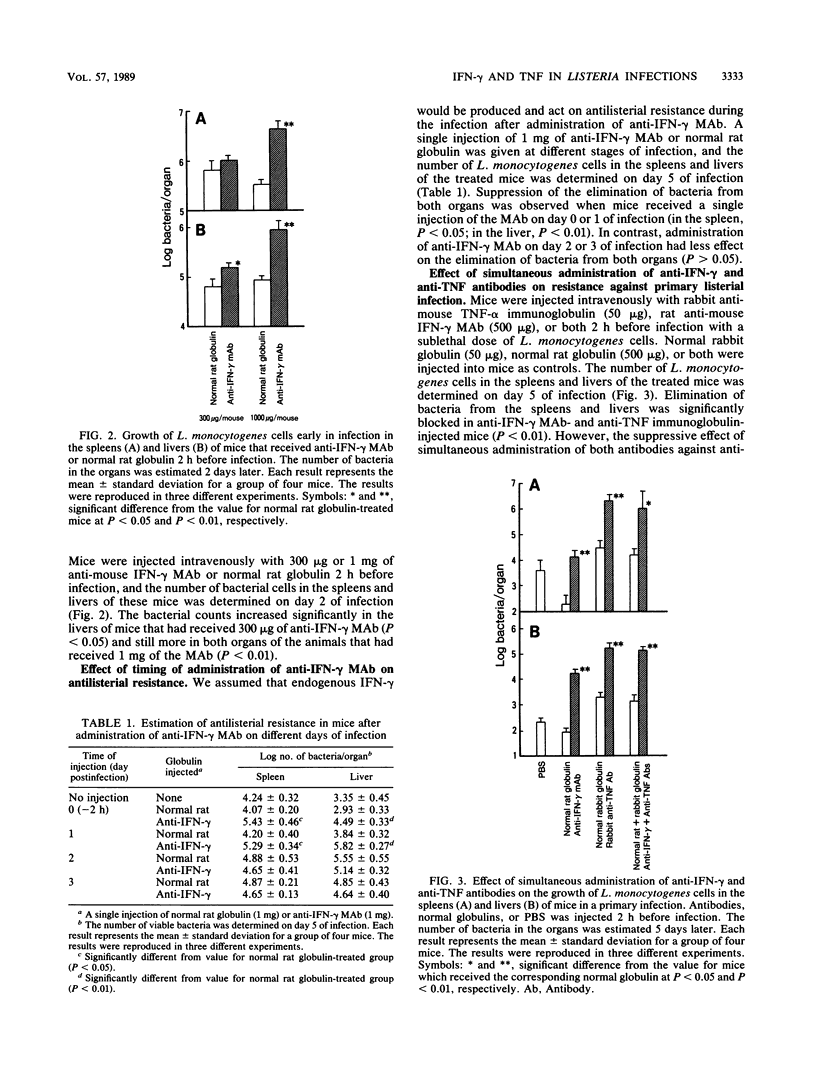
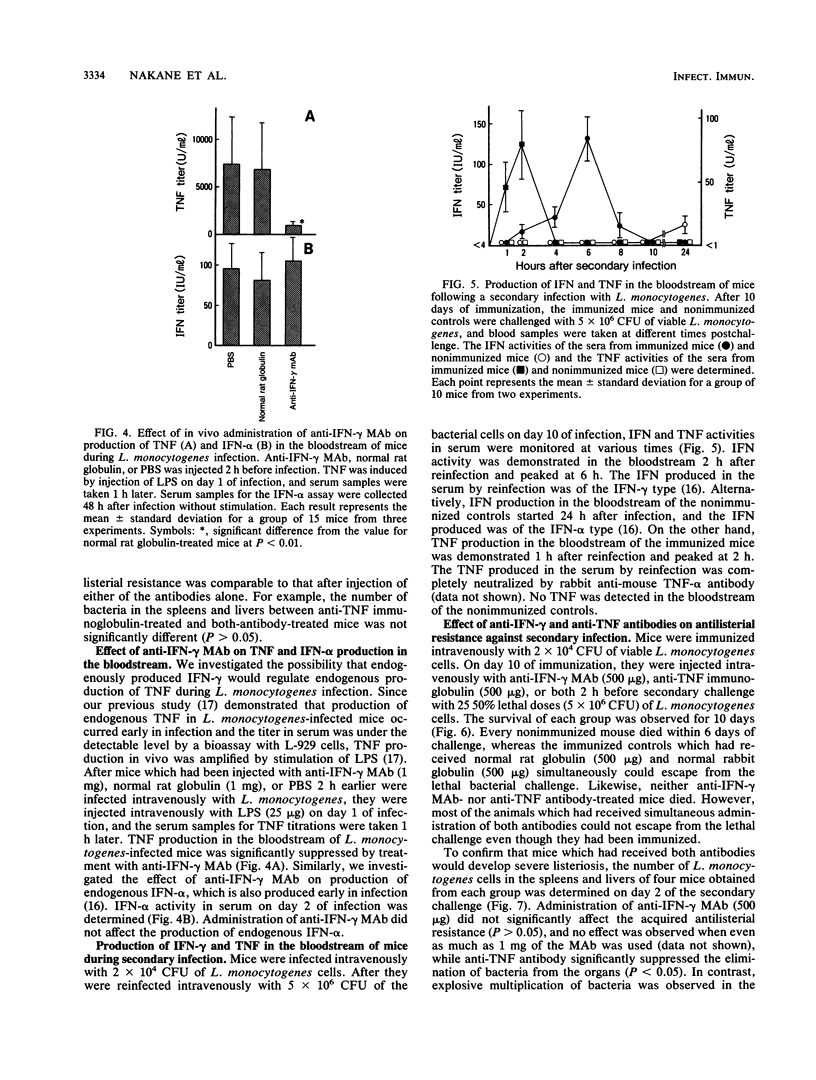
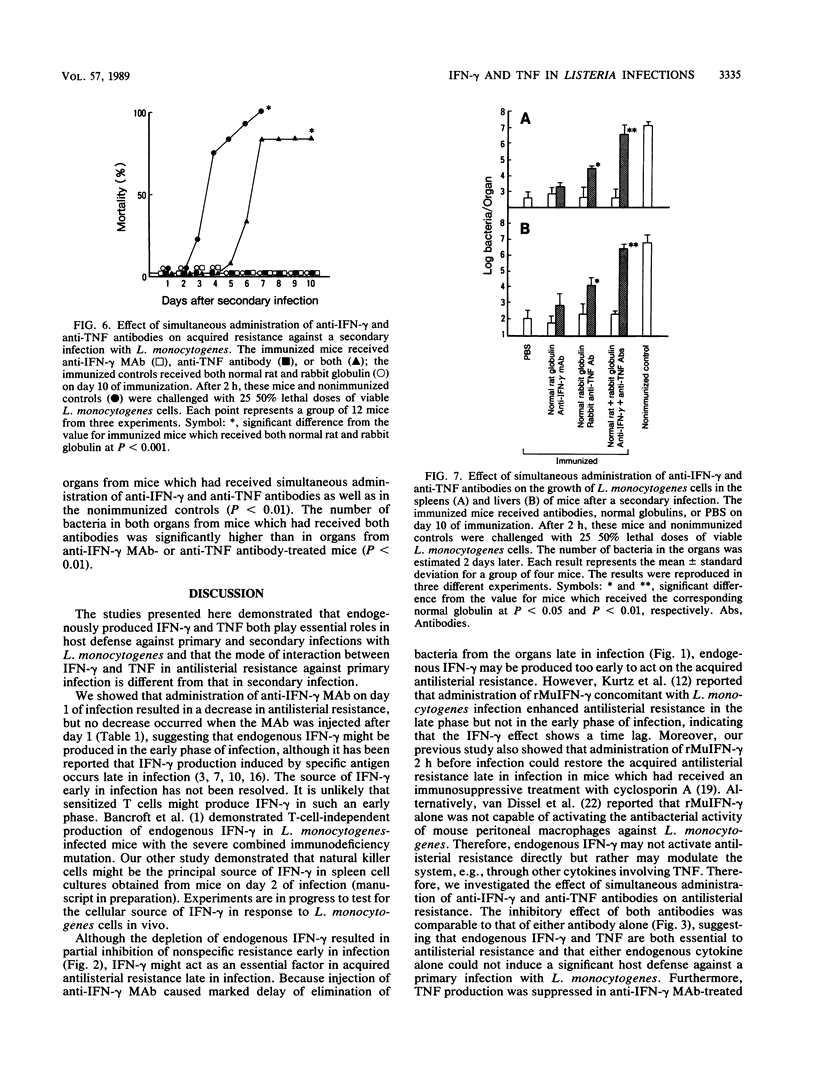
Intravenous injection of rat anti-mouse gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) monoclonal antibody as well as rabbit anti-mouse tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antibody into mice which had received a sublethal infection with Listeria monocytogenes cells resulted in acceleration of listeriosis. Endogenous IFN-gamma seemed to be produced early in infection, because suppression of antilisterial resistance was significant when a single injection of anti-IFN-gamma monoclonal antibody was given on day 0 or day 1 of infection. Production of TNF but not of IFN-gamma in the bloodstream early in infection was inhibited by administration of anti-IFN-gamma monoclonal antibody. The suppressive effect of anti-IFN-gamma and anti-TNF antibodies on antilisterial resistance was not augmented by simultaneous administration of these antibodies. On the other hand, in the secondary infection, simultaneous administration of anti-IFN-gamma and anti-TNF antibodies, but not of either of these antibodies alone, into L. monocytogenes-immune mice resulted in high mortality and explosive multiplication of bacterial cells in the spleens and livers. These results suggest that endogenously produced IFN-gamma and TNF are both essential to the host defense against L. monocytogenes infection and that these cytokines might act by different modes between the primary infection and the secondary infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft G. J., Schreiber R. D., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1104–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. J., Lee S. H. Effects of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the expression of an Ia antigen on a murine macrophage cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2853–2856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Haigh A. M., Kelso A., Metcalf D., Stanley E. R., Young A. M. Production of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) during infection: separate determinations of macrophage-, granulocyte-, granulocyte-macrophage-, and multi-CSFs. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):247–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.247-251.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner A., Moskophidis D., Lehmann-Grube F. Enumeration of single IFN-gamma-producing cells in mice during viral and bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1293–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Purification and further characterization of an anti-murine interferon-gamma monoclonal neutralizing antibody. J Interferon Res. 1986 Oct;6(5):489–497. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Spitalny G. L., Patel P. J. Enhanced production of murine interferon gamma by T cells generated in response to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):112–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratz S. S., Kurlander R. J. Characterization of the pattern of inflammatory cell influx and cytokine production during the murine host response to Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):598–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Virgin H. W., 4th, Unanue E. R. In vivo and in vitro expression of macrophage membrane interleukin 1 in response to soluble and particulate stimuli. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz R. S., Young K. M., Czuprynski C. J. Separate and combined effects of recombinant interleukin-1 alpha and gamma interferon on antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):553–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.553-558.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T. The significance of alpha/beta interferons and gamma interferon produced in mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 1;88(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Yasuda I., Yu C., Kato K. Prevention by gamma interferon of fatal infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice treated with cyclosporin A. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2011–2015. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2011-2015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., Havell E. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine gamma interferon inhibits lymphokine-induced antiviral and macrophage tumoricidal activities. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1560–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Changes in serum colony-stimulating factor and monocytic progenitor cells during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):180–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.180-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Stikkelbroeck J. J., Michel B. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Inability of recombinant interferon-gamma to activate the antibacterial activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1673–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


