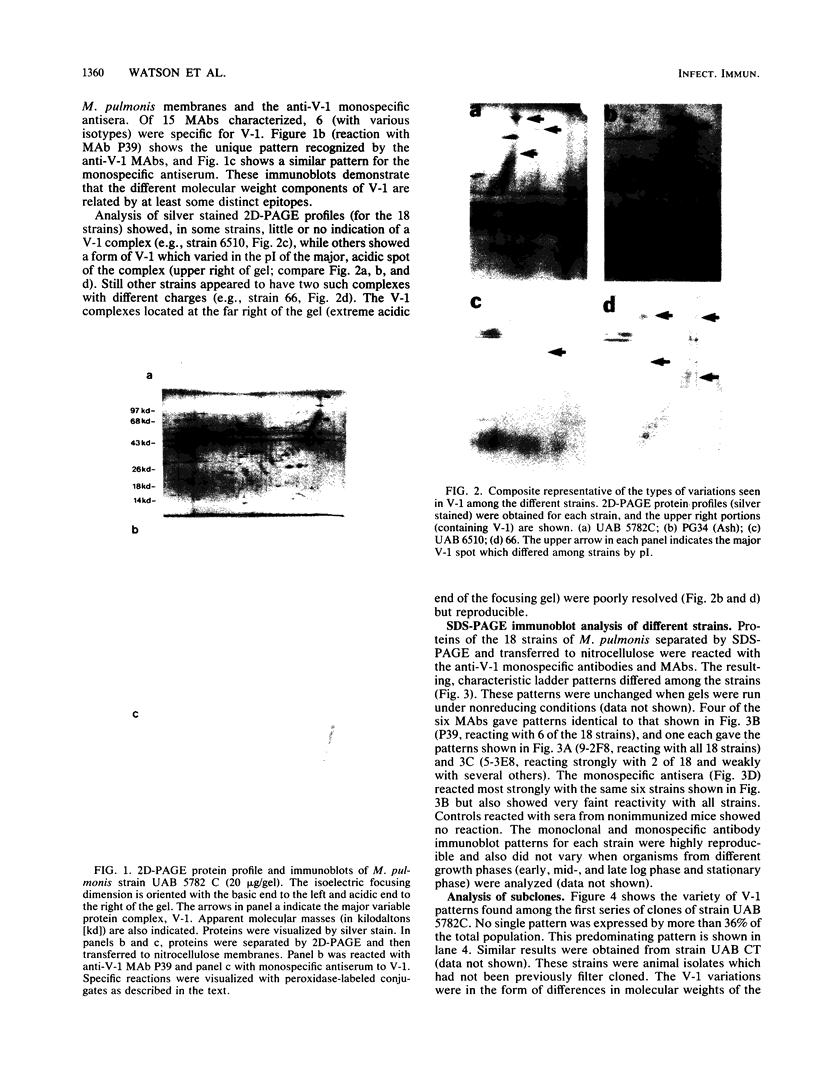
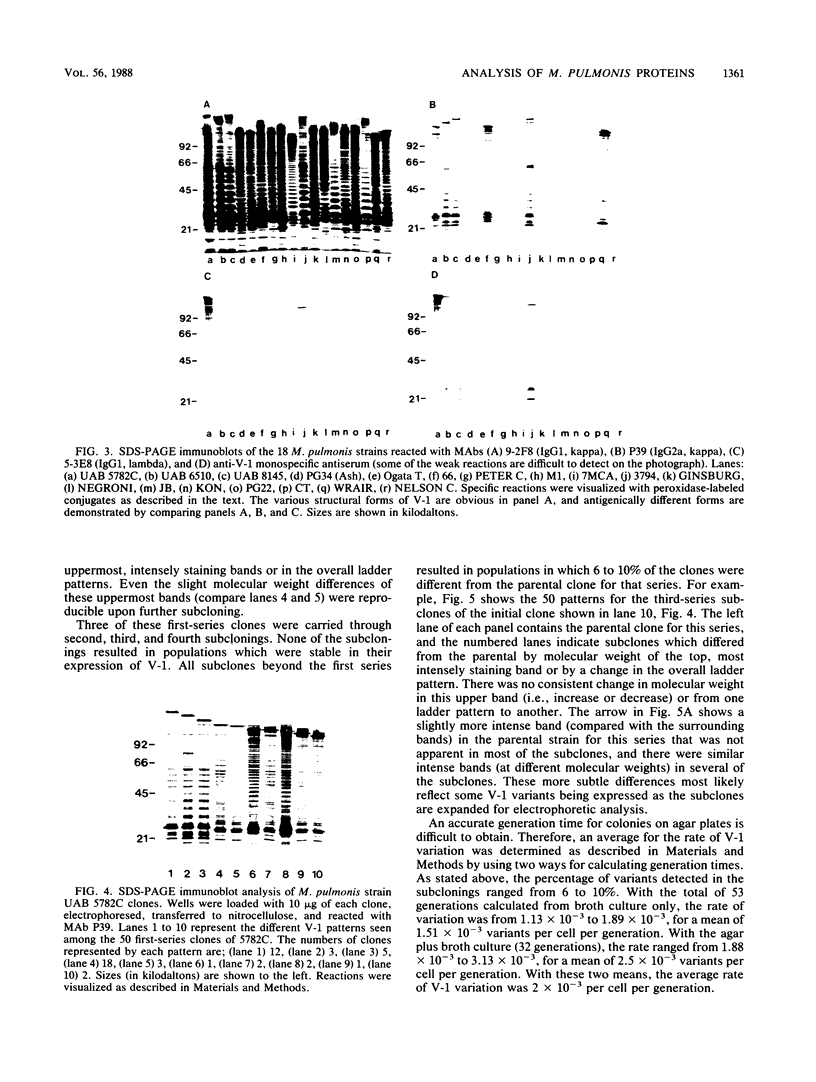
Abstract
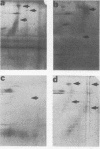
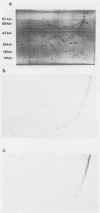
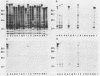
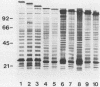
Monoclonal and monospecific antibodies were used to characterize a major Mycoplasma pulmonis surface antigen complex, V-1. Heterogeneity of V-1 was detected among strains and a high frequency of variation was detected within subclones of single strains. Analysis of 18 different strains showed that no two displayed identical electrophoretic immunoblot patterns for V-1. Analysis of 50 filter clones from an individual strain (not previously filter cloned) revealed at least 10 different V-1 patterns. The two most frequently occurring patterns were expressed by 36% and 24%, respectively, of the total population. Serial subcloning (four separate series) of several of these original clones showed that the average rate of V-1 variation was 2 x 10(-3) per cell per generation. Immunoblots with different anti-V-1 monoclonal antibodies demonstrated that there were both structurally and antigenically different forms of this antigen. Also, two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel analyses showed that different forms of V-1 could vary in charge. This potential for variability in a major surface antigen of mycoplasmas could have important implications as to how the organism interacts with its host.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassell G. H. Derrick Edward Award Lecture. The pathogenic potential of mycoplasmas: Mycoplasma pulmonis as a model. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S18–S34. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Lindsey J. R., Davis J. K., Davidson M. K., Brown M. B., Mayo J. G. Detection of natural Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in rats and mice by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Lab Anim Sci. 1981 Dec;31(6):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Simecka J. W., Williamson J. S., Ross S. E., Juliana M. M., Thorp R. B., Cassell G. H. Nonspecific lymphocyte responses in F344 and LEW rats: susceptibility to murine respiratory mycoplasmosis and examination of cellular basis for strain differences. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.152-158.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Thorp R. B., Parker R. F., White H., Dziedzic D., D'Arcy J., Cassell G. H. Development of an aerosol model of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):194–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.194-201.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice R. A., Robillard N. F., Carski T. R. Immunofluorescence identification of Mycoplasma on agar by use of incident illumination. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1205–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1205-1209.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. The pleuropneumonia group of organisms: a review, together with some new observations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nicolet J. Extensive transformation of lymphocytes by a mycoplasma organism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 5;246(153):143–146. doi: 10.1038/newbio246143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. A., Garrett B., Davis J. K., Cassell G. H. Isolation of Mycoplasma pulmonis membranes and identification of surface antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1314–1320. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1314-1320.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Johnston K. H., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Location of variable and conserved epitopes among the multiple serotypes of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):623–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Cassell H. Experimental Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in pathogen-free mice. Models for studying mycoplasmosis of the respiratory tract. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jul;72(1):63–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Scott G., Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Monoclonal antibodies against protease-sensitive pneumococcal antigens can protect mice from fatal infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Identification of cross-reactive antigens between Mycoplasma pulmonis and Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.115-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Tully J. G., Ginsburg H. Lymphocyte activation by various Mycoplasma strains and species. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.310-317.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Ota T., Atobe H. [Studies on Mycoplasma of roden origin--Mycoplasma from chronic respiratory diseases in rats]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1967 Dec;22(11):618–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H., Kaufman B., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. Immunoenzymatic analysis by monoclonal antibodies of bacterial lipopolysaccharides after transfer to nitrocellulose. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G., So M. Phase and antigenic variation of pili and outer membrane protein II of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):196–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Goodman G. W. Endotoxin protein: a B-cell mitogen and polyclonal activator of C3H/HeJ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):821–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Davies H. A., Manchee R. J., Mouches C., Bove J. M. Mycoplasmal adherence with particular reference to the pathogenicity of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J., Gourlay R. N. Protective effect of vaccines on Mycoplasma pulmonis-induced respiratory disease of mice. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):422–431. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.422-431.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rask-Nielsen R. Mycoplasma in leukemic and nonleukemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., Davidson M. K., Cox N. R., Davis J. K., Dybvig K., Cassell G. H. Protein variability among strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2838–2840. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2838-2840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]