Abstract
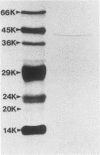
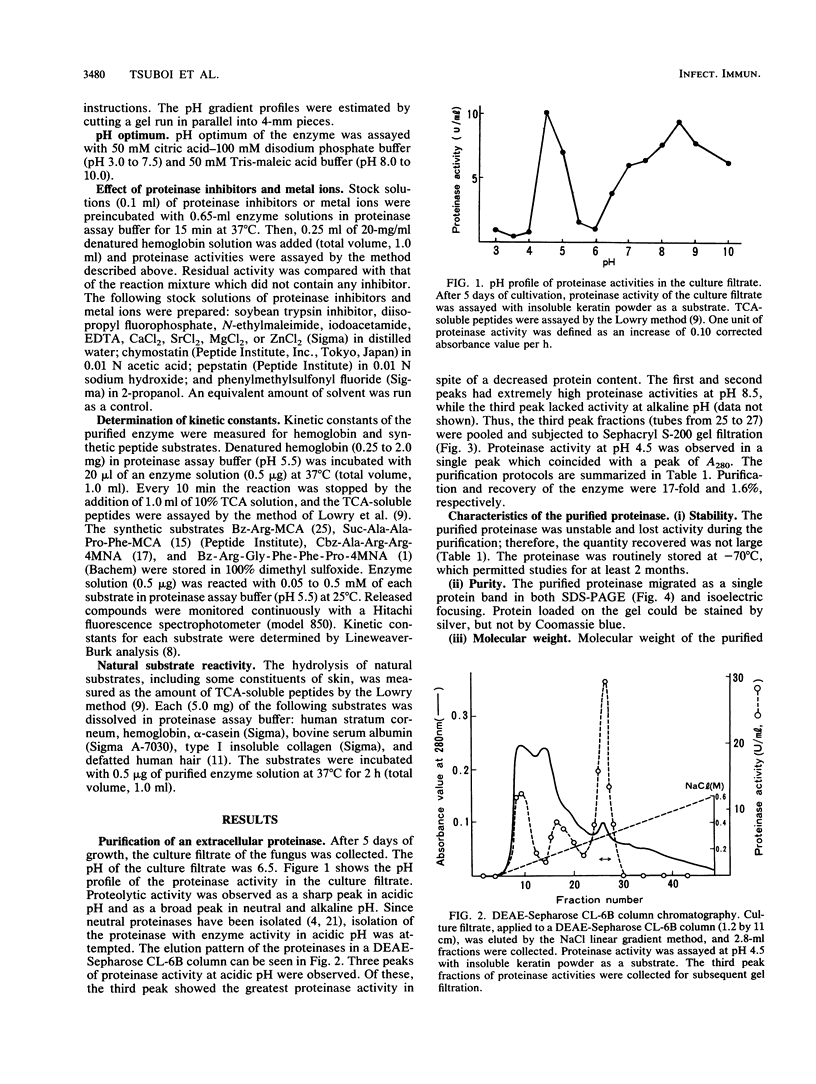
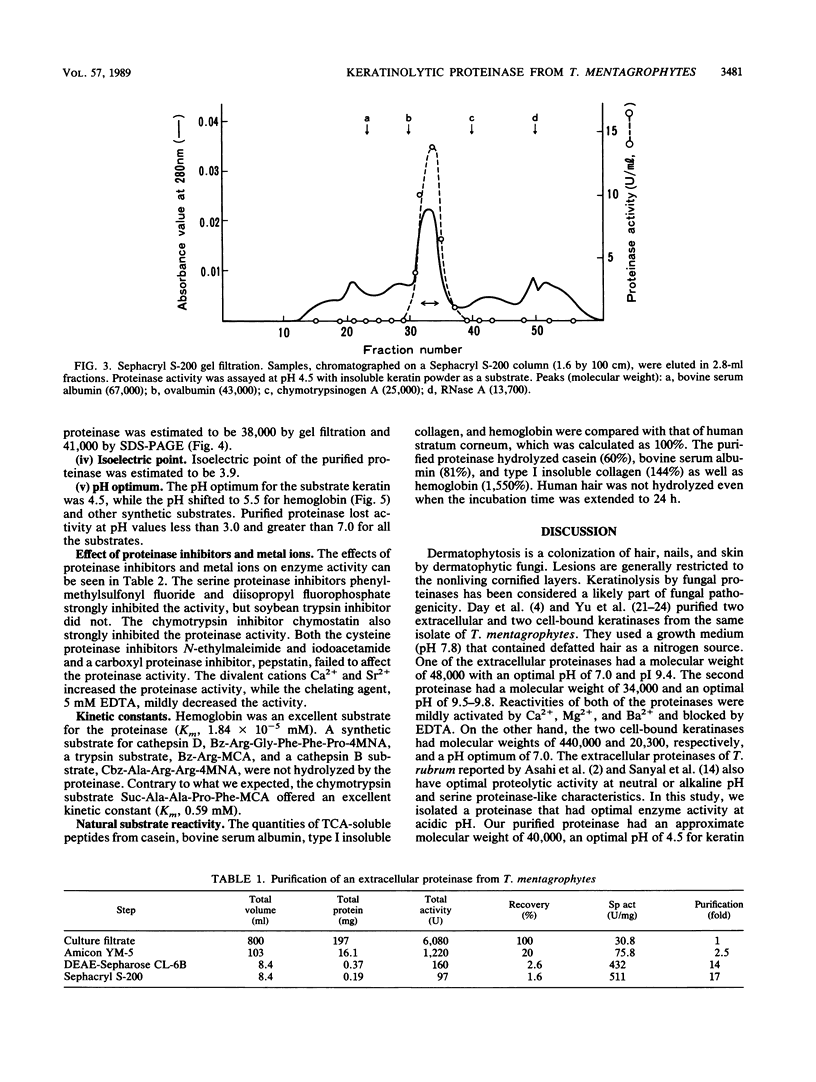
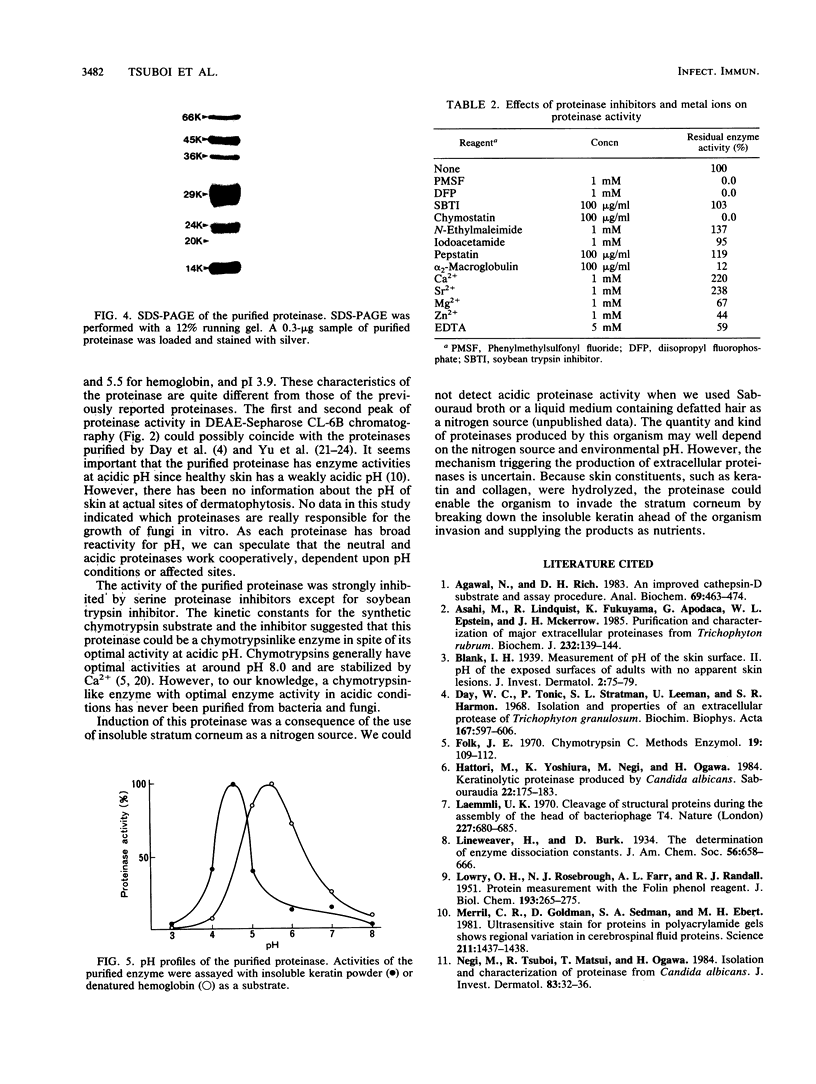
A keratinolytic proteinase with enzyme activity at acidic pH was isolated from culture filtrates of Trichophyton mentagrophytes, a major pathogenic fungus of dermatophytosis. The molecular weight of the proteinase was estimated to be 41,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and 38,000 by gel filtration. The isoelectric point was determined to be 3.9. The proteinase had a pH optimum of 4.5 for keratin and 5.5 for hemoglobin. This enzyme hydrolyzed the synthetic chymotrypsin substrate Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-MCA (Km, 0.59 mM), and its activity was strongly inhibited by chymostatin. Previously reported proteinases from dermatophytes have had enzyme activities in neutral or alkaline pH; however, healthy skin has a weakly acidic pH. Thus, the purified proteinase which has an optimal activity at acidic pH and hydrolyzes skin constituents could be an important virulence factor in dermatophytosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asahi M., Lindquist R., Fukuyama K., Apodaca G., Epstein W. L., McKerrow J. H. Purification and characterization of major extracellular proteinases from Trichophyton rubrum. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):139–144. doi: 10.1042/bj2320139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day W. C., Toncic P., Stratman S. L., Leeman U., Harmon S. R. Isolation and properties of an extracellular protease of Trichophyton granulosum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 19;167(3):597–606. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Yoshiura K., Negi M., Ogawa H. Keratinolytic proteinase produced by Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(3):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negi M., Tsuboi R., Matsui T., Ogawa H. Isolation and characterization of proteinase from Candida albicans: substrate specificity. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1):32–36. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12261656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpot C. The differentiation of Trichophyton mentagrophytes from T. rubrum by a simple urease test. Sabouraudia. 1967 Feb;5(3):189–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUDMAN M. S., SCHMITT J. A. DIFFERENTIATION OF TRICHOPHYTON RUBRUM AND TRICHOPHYTON MENTAGROPHYTES BY PIGMENT PRODUCTION. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:290–290. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.290-290.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal A. K., Das S. K., Banerjee A. B. Purification and partial characterization of an exocellular proteinase from Trichophyton rubrum. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):165–178. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Yokosawa H., Hoshi M., Ishii S. Ascidian sperm chymotrypsin-like enzyme; participation in fertilization. Experientia. 1983 Apr 15;39(4):377–378. doi: 10.1007/BF01963132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiuchi I., Higuchi D., Sei Y., Koga M. Isolation of an extracellular proteinase (keratinase) from Microsporum canis. Sabouraudia. 1982 Dec;20(4):281–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiuchi I., Higuchi D. [Isolation, purification and biochemical properties of keratinase elaborated from Microsporum gypseum (author's transl)]. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1977 Apr;87(5):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. J., Harmon S. R., Blank F. Hair digestion by a keratinase of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 Aug;53(2):166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. J., Harmon S. R., Blank F. Isolation and purification of an extracellular keratinase of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1435–1436. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1435-1436.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. J., Harmon S. R., Grappel S. F., Blank F. Two cell-bound keratinases of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1971 Jan;56(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12291869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. J., Harmon S. R., Wachter P. E., Blank F. Amino acid composition and specificity of a keratinase of Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., Ashe B., Yurewicz E. C., Patel G. Sensitive assays for trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin using new fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]