Abstract
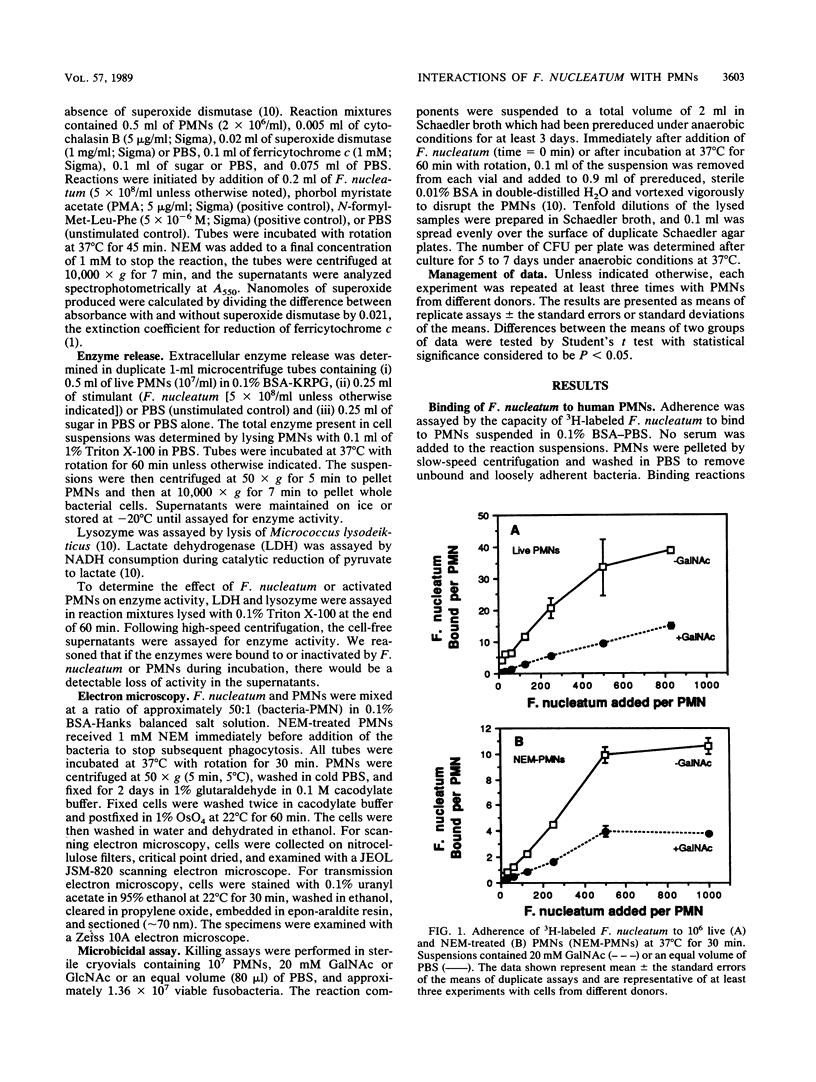
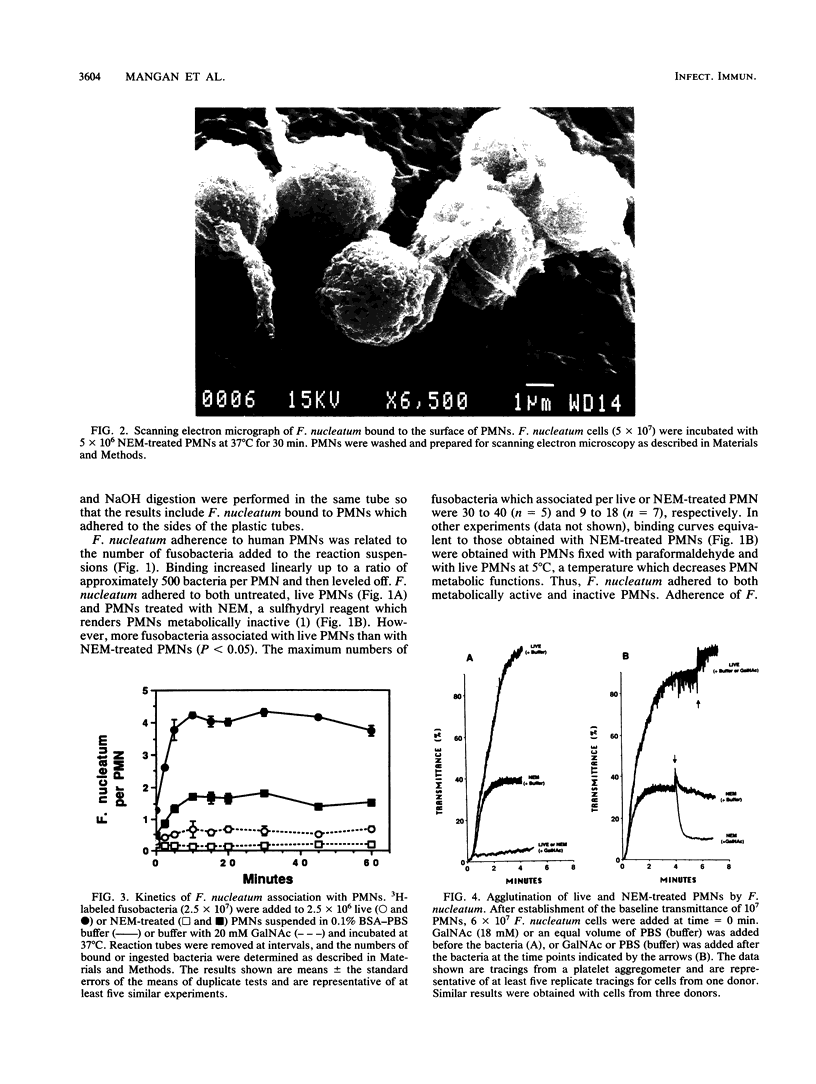
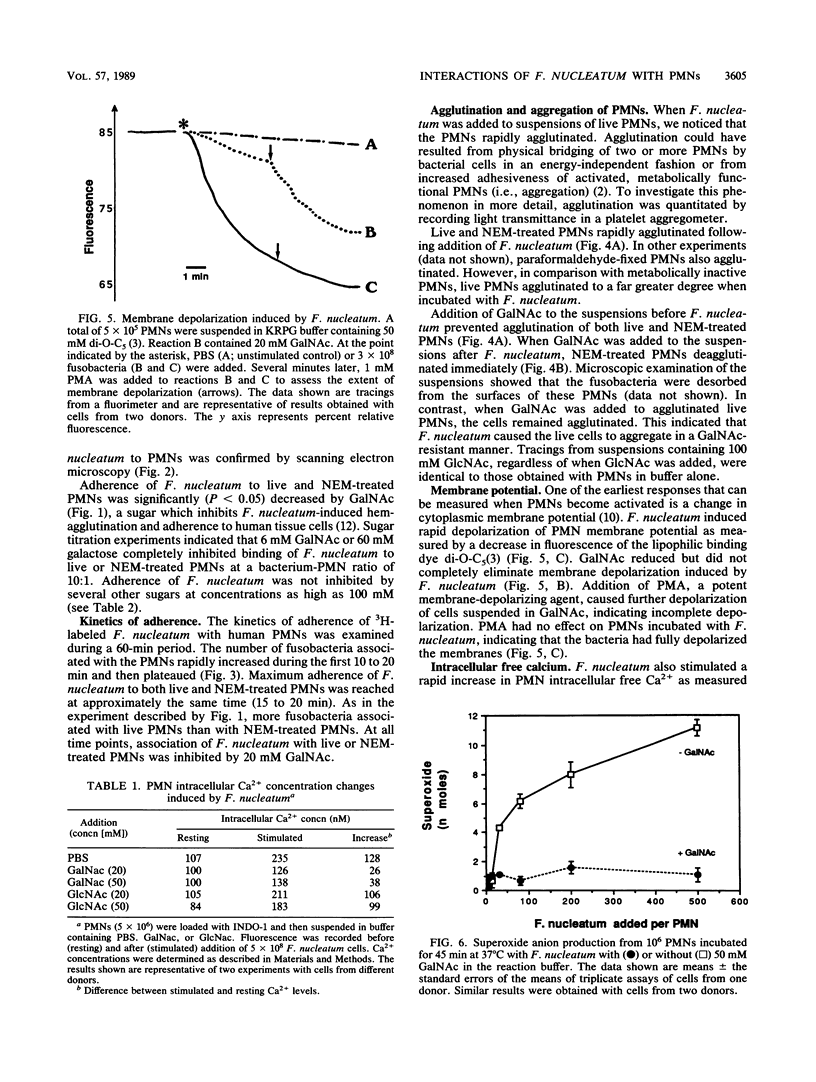
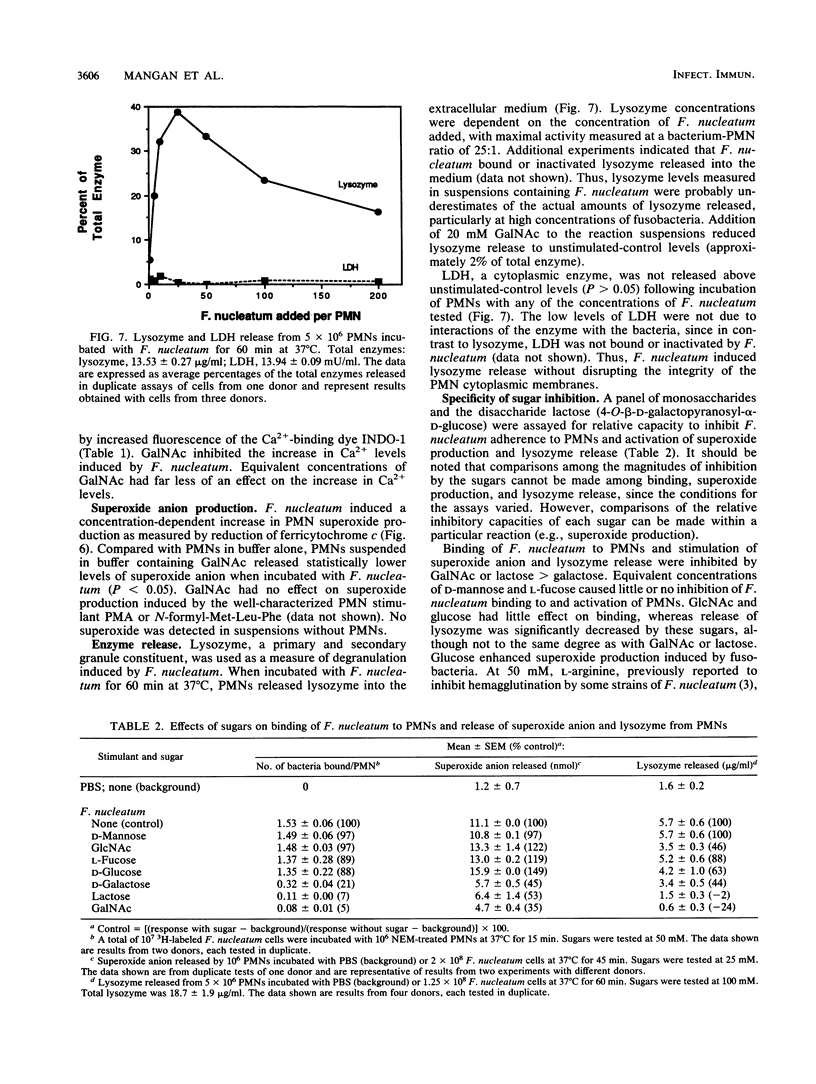
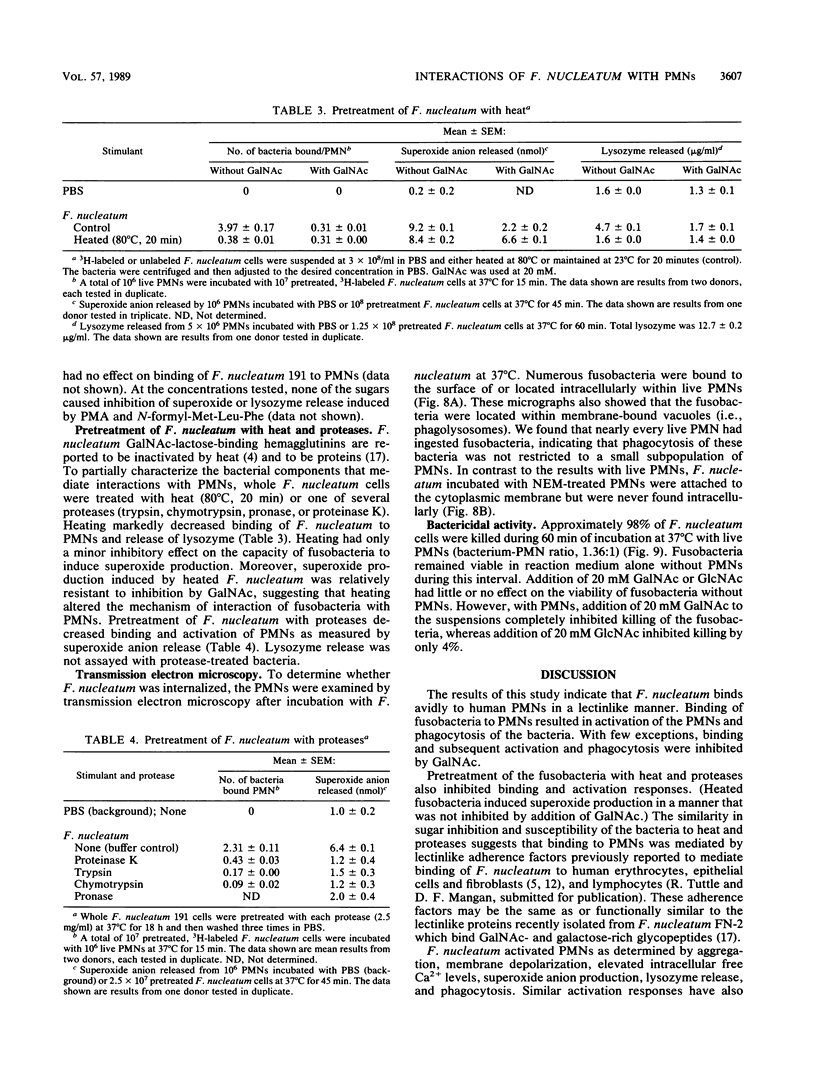
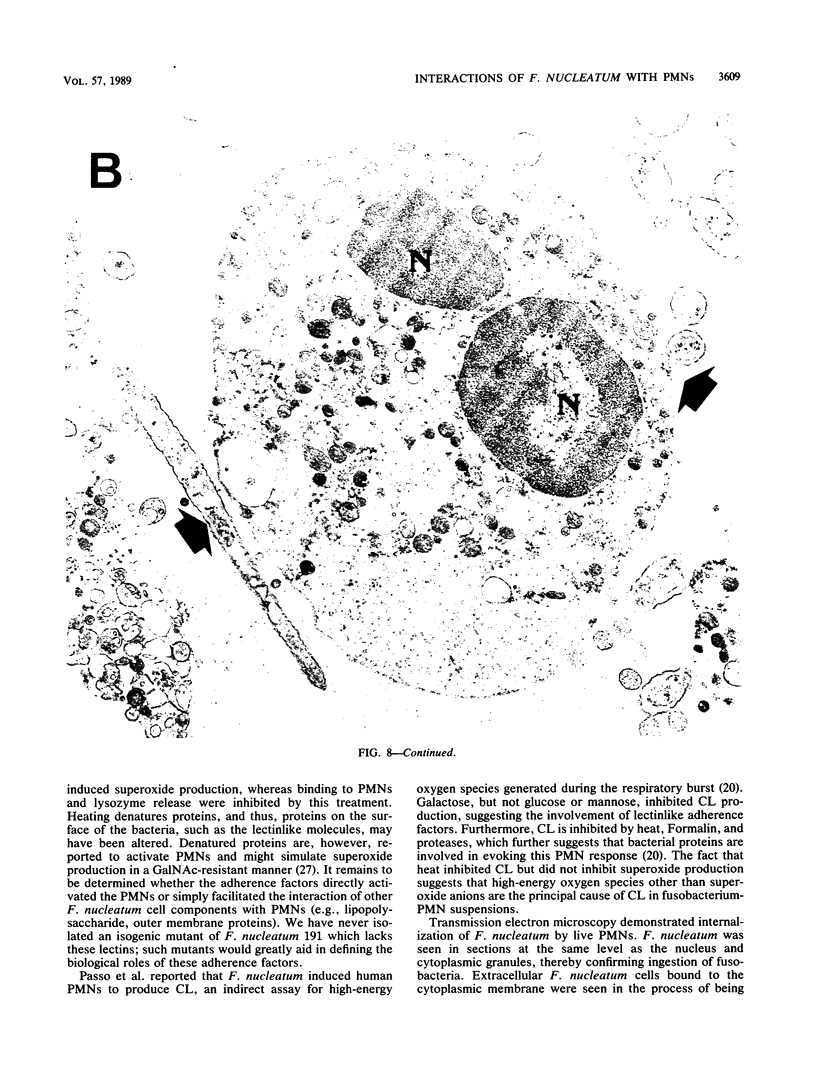
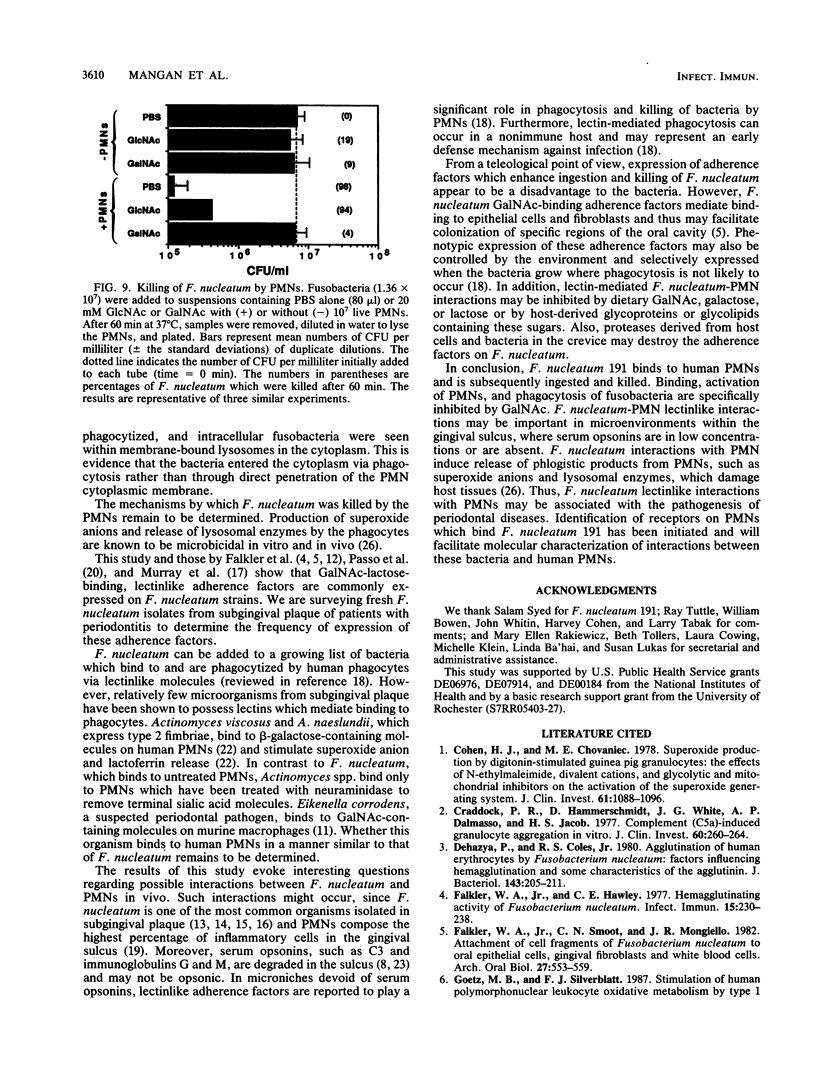
Fusobacterium nucleatum expresses lectinlike adherence factors which mediate binding to a variety of human tissue cells. Adherence is selectively inhibited by galactose, lactose, and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine. In this study, adherence of F. nucleatum to human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) was investigated. The results indicated that the fusobacteria adhered to live and metabolically inactivated or fixed PMNs. Adherence of F. nucleatum resulted in activation of PMNs as determined by PMN aggregation, membrane depolarization, increased intracellular free Ca2+, superoxide anion production, and lysozyme release. Transmission electron micrographs showed that F. nucleatum was phagocytized by the PMNs. Microbicidal assays indicated that greater than 98% of F. nucleatum organisms were killed by PMNs within 60 min. Adherence to and activation of PMNs by F. nucleatum were inhibited by N-acetyl-D-galactosamine or lactose greater than galactose, whereas equal concentrations of glucose, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, mannose, and fucose had little or no effect on F. nucleatum-PMN interactions. Pretreatment of the fusobacteria with heat (80 degrees C, 20 min) or proteases inhibited adherence to and activation of PMNs, but superoxide production was also stimulated by heated bacteria. The results indicate that interaction of F. nucleatum with PMNs is lectinlike and is probably mediated by fusobacterial proteins which bind to other human tissue cells. Adherence of F. nucleatum to PMNs in the absence of serum opsonins, such as antibodies and complement, may play an important role in PMN recognition and killing of F. nucleatum in the gingival sulcus and in the subsequent release of PMN factors associated with tissue destruction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehazya P., Coles R. S., Jr Agglutination of human erythrocytes by Fusobacterium nucleatum: factors influencing hemagglutination and some characteristics of the agglutinin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):205–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.205-211.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkler W. A., Jr, Hawley C. E. Hemagglutinating activity of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):230–238. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.230-238.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkler W. A., Jr, Smoot C. N., Mongiello J. R. Attachment of cell fragments of Fusobacterium nucleatum to oral epithelial cells, gingival fibroblasts and white blood cells. Arch Oral Biol. 1982;27(7):553–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(82)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz M. B., Silverblatt F. J. Stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte oxidative metabolism by type 1 pili from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):534–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.534-540.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. D., Cole M. F. Structural integrity of host defense factors in dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):398–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.398-402.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Lopatin D. E. Polyclonal activation of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1104–1111. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1104-1111.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Ebisu S., Okada H. The adherence of Eikenella corrodens to guinea pig macrophages in the absence and presence of anti-bacterial antibodies. J Periodontal Res. 1987 Sep;22(5):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1987.tb01599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongiello J. R., Falkler W. A., Jr Sugar inhibition of oral Fusobacterium nucleatum haemagglutination and cell binding. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(7):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P., Smibert R. M., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Comparative bacteriology of juvenile periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):507–519. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.507-519.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P., Smibert R. M., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of moderate (chronic) periodontitis in mature adult humans. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.510-515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Good I. J., Burmeister J. A., Palcanis K. G., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of experimental gingivitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):651–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.651-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Kern D. G., Winkler J. R. Identification of a galactose-binding lectin on Fusobacterium nucleatum FN-2. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1314-1319.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis: a molecular mechanism of recognition between cell surface sugars and lectins in the phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):539–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.539-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. A., Syed S. A., Silva J., Jr Neutrophil chemiluminescence in response to Fusobacterium nucleatum. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Nov;17(6):604–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Mudrick L. L., Cisar J. O., Brennan M. J., Mergenhagen S. E., Vatter A. E. Type 2 fimbrial lectin-mediated phagocytosis of oral Actinomyces spp. by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):472–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.472-476.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Mudrick L. L., Cisar J. O., Metcalf J. A., Malech H. L. Stimulation of superoxide and lactoferrin release from polymorphonuclear leukocytes by the type 2 fimbrial lectin of Actinomyces viscosus T14V. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):267–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.267-269.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein H. A., Genco R. J. Gingival fluid and serum in periodontal diseases. I. Quantitative study of immunoglobulins, complement components, and other plasma proteins. J Periodontol. 1977 Dec;48(12):772–777. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.12.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Gallin J. I. Use of lipophilic probes of membrane potential to assess human neutrophil activation. Abnormality in chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):493–503. doi: 10.1172/JCI109880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seow W. K., Seymour G. J., Thong Y. H. Direct modulation of human neutrophil adherence by coaggregating periodontopathic bacteria. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;83(2):121–128. doi: 10.1159/000234344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Denatured proteins as chemotactic agents: mitogens as lymphocyte locomotion activators. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:180–192. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






