Abstract
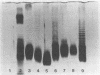
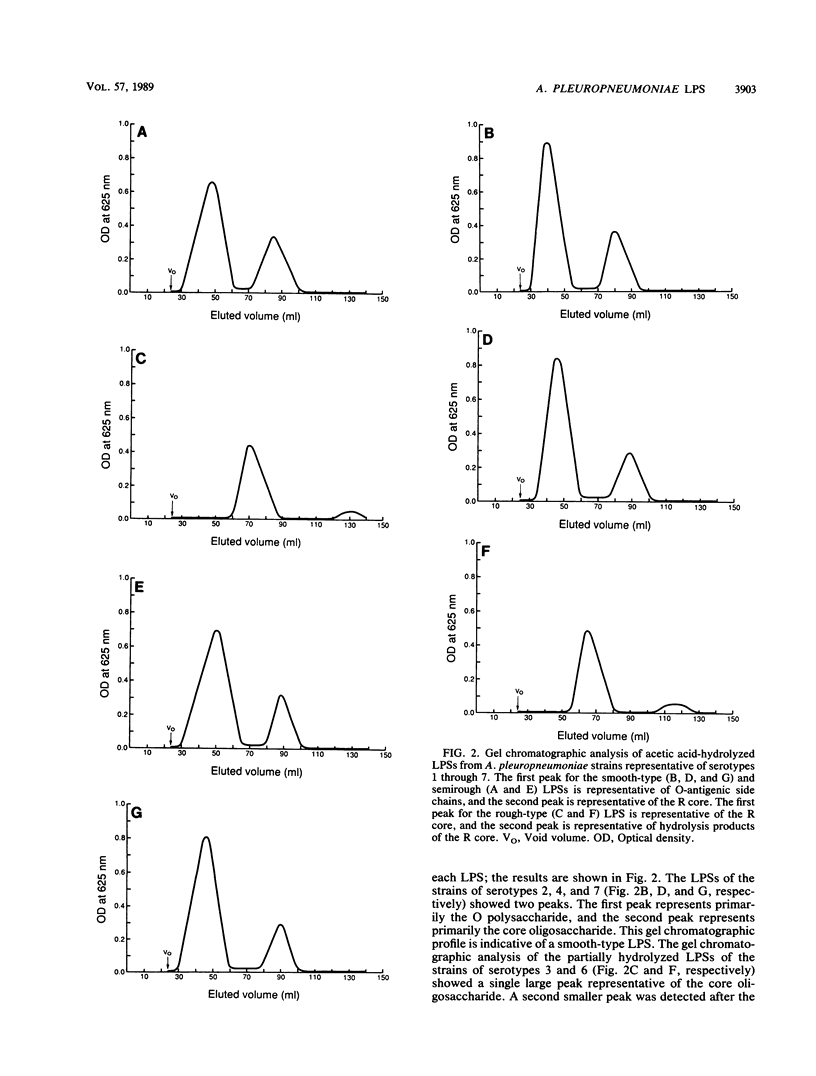
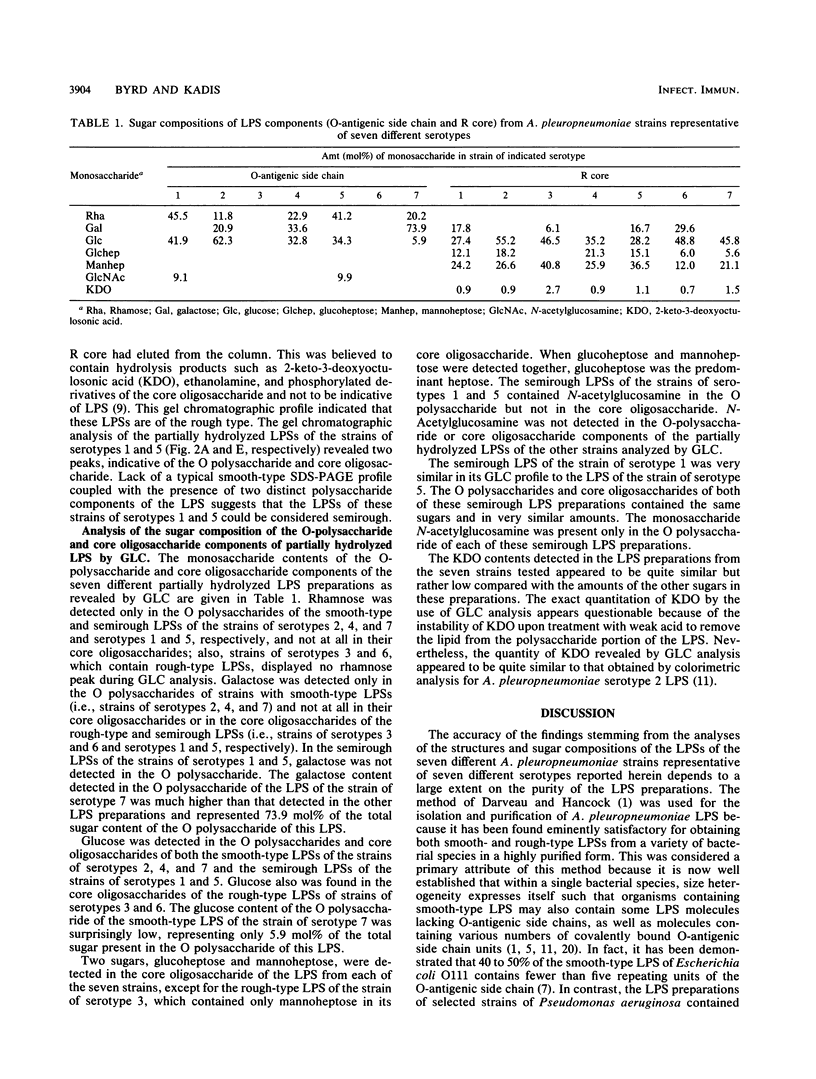
Highly purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) preparations obtained from seven Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae strains representative of seven different serotypes were used to determine the structure and monosaccharide composition of the polysaccharide components of each lipopolysaccharide. An indication of the structure of each LPS was obtained by procedures that included sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by silver staining and gel chromatographic fractionation of acetic acid-hydrolyzed LPS. The polysaccharide components of the LPSs were analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography. The LPSs of the strains of serotypes 2, 4, and 7 were of the smooth type, and those of the strains of serotypes 3 and 6 were of the rough type; the LPSs of the strains of serotypes 1 and 5 could be considered semirough. Rhamnose was present only in the O polysaccharide of the smooth-type and semirough-type LPSs, whereas galactose was present only in the O polysaccharide of the smooth-type LPS and in the core oligosaccharides of the rough-type and semirough-type LPSs. Glucoheptose and mannoheptose were present in the core oligosaccharides of all the LPSs except for the strain of serotype 3, in which only mannoheptose was detected. N-Acetylglucosamine was detected only in the O polysaccharides of the strains of serotypes 1 and 5.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev B. A., Knirel Y. A., Kochetkov N. K. Somatic antigens of shigella. Structural investigation on the O-specific polysaccharide chain of Shigella dysenteriae type 1 lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):559–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Isolation and biological characterization of two lipopolysaccharides and a capsular-enriched polysaccharide preparation from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Resistance of C3H/HeJ mice to the effects of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):474–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.474-479.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Seifert W. E., Jr, Williams R. P. Composition and antigenic activity of the oligosaccharide moiety of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):324–330. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.324-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Wauters G., Otsuki K., Tsubokura M. Identification of Yersinia enterocolitica O15 lipopolysaccharide as a rough antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):272–274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.272-274.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Kuzio J., Angus B. L., Hancock R. E. Chemical and chromatographic analysis of lipopolysaccharide from an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):310–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S., Mayberry W. R. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of a lipopolysaccharide from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.501-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfumo C. J., Rehbinder C., Karlsson K. Swine pleuropneumonia produced by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. III. An electron microscopic study. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1983 Oct;30(9):678–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1983.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Progulske A., Holt S. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane and lipopolysaccharide from Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):166–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.166-177.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeze F. A., Latimer K. S., Kadis S. Role of haemophilus pleuropneumoniae lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in the pathogenesis of porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):768–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Gaston M. A., Wilkinson S. G. Composition of O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides from Enterobacter cloacae. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(11):1169–1179. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G., Galbrath L. Studies of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):331–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]