Abstract
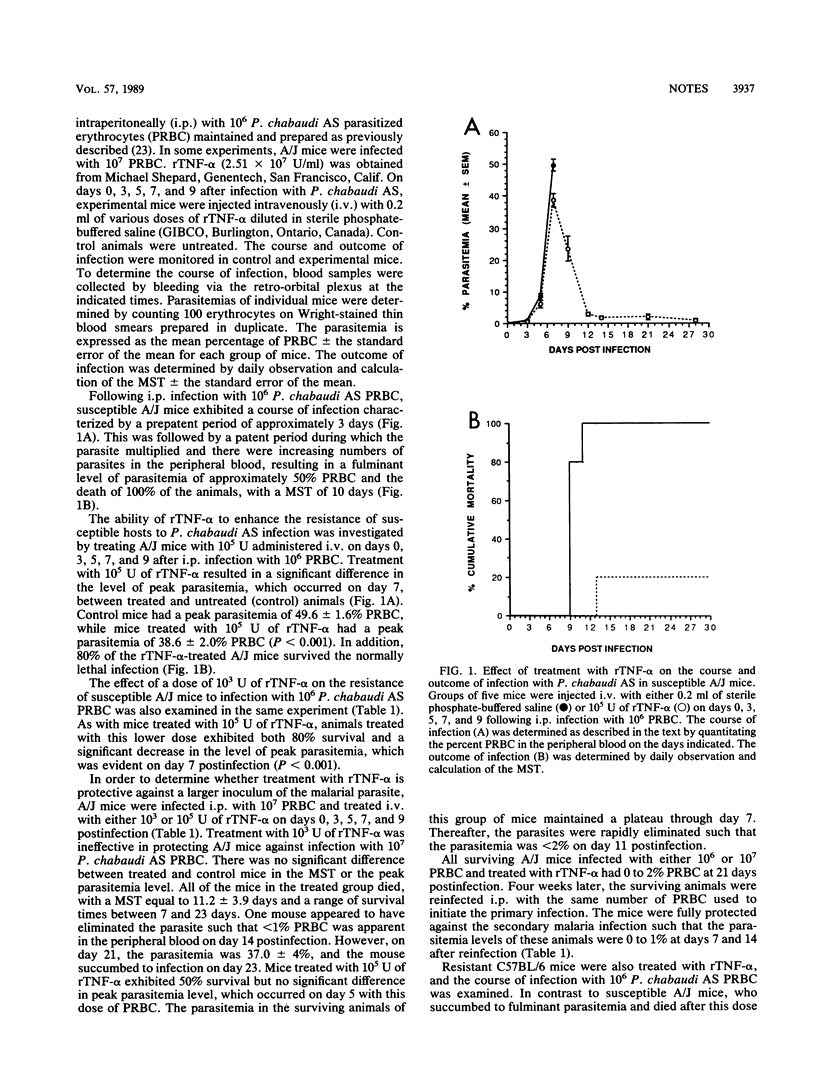
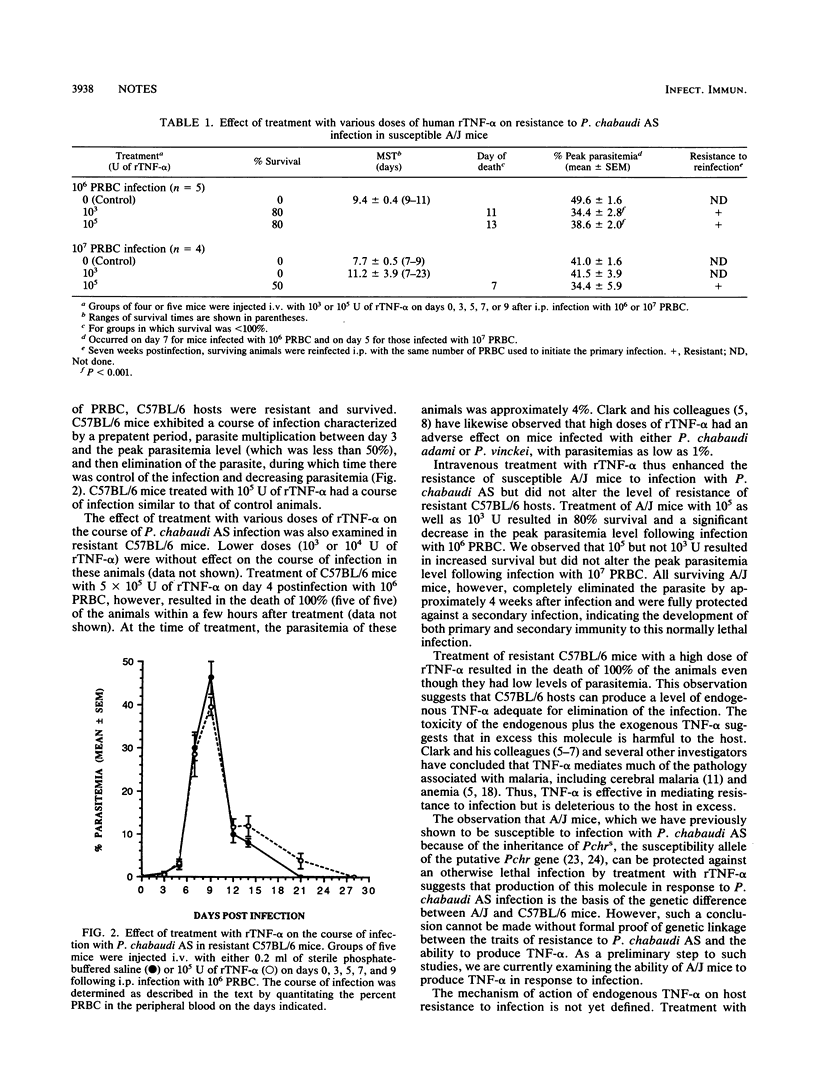
The effect of intravenous treatment with human recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha (rTNF-alpha) on infection of susceptible A/J and resistant C57BL/6 mice with Plasmodium chabaudi AS was examined. Treatment of A/J mice with 10(3) or 10(5) U of rTNF-alpha on days 0, 3, 5, 7, and 9 after intraperitoneal infection with 10(6) parasitized erythrocytes resulted in 80% survival and a significant decrease in the peak parasitemia level. Treatment of susceptible A/J hosts with 10(5) but not 10(3) U of rTNF-alpha resulted in increased survival but did not alter the peak parasitemia level following infection with 10(7) parasitized erythrocytes. Moreover, all surviving A/J mice completely eliminated the parasite by approximately 4 weeks and were fully protected against a secondary infection. Except at a dose of 5 x 10(5) U of rTNF-alpha, which resulted in 100% mortality of infected animals, rTNF-alpha did not alter the course or outcome of infection with P. chabaudi AS in resistant C57BL/6 mice.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake D. A., Long C. A., Weidanz W. P. Adoptive protection against Plasmodium chabaudi adami malaria in athymic nude mice by a cloned T cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1989–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake D. A., Weidanz W. P., Long C. A. Antigen-specific, interleukin 2-propagated T lymphocytes confer resistance to a murine malarial parasite, Plasmodium chabaudi adami. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):347–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Chaudhri G. Tumour necrosis factor may contribute to the anaemia of malaria by causing dyserythropoiesis and erythrophagocytosis. Br J Haematol. 1988 Sep;70(1):99–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cowden W. B., Butcher G. A., Hunt N. H. Possible roles of tumor necrosis factor in the pathology of malaria. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):192–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Virelizier J. L., Carswell E. A., Wood P. R. Possible importance of macrophage-derived mediators in acute malaria. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1058-1066.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. Activity of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1342–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Kiener P. A., Lin P. F., Warr G. A. Protection of mice against Listeria monocytogenes infection by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1615–1617. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1615-1617.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. L., Long C. A., Weidanz W. P. Effects of splenectomy on antibody-independent immunity to Plasmodium chabaudi adami malaria. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):853–858. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.853-858.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. L., Weidanz W. P. Immunity to Plasmodium chabaudi adami in the B-cell-deficient mouse. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):143–145. doi: 10.1038/290143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hviid L., Reimert C. M., Theander T. G., Jepsen S., Bendtzen K. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor is not inhibitory to Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(1):48–49. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Enhancement of human B cell proliferation and differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2970–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Vande Waa J. A., Karadsheh A. J. Tumor necrosis factor does not induce Plasmodium falciparum crisis forms. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1722–1724. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1722-1724.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. L., Silverman P. H., Kullgren B., Mahlmann L. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and the anemia associated with murine malaria. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1542–1546. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1542-1546.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Moore R. N., Mergenhagen S. E. Macrophages as a source of tumoricidal activity (tumor-necrotizing factor). Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):523–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.523-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaetinck G., Declercq W., Tavernier J., Nabholz M., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor can induce interleukin 2 receptor expression and cytolytic activity in a rat x mouse T cell hybrid. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1835–1838. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Cerami A. Hypertriglyceridemia associated with Trypanosoma brucei brucei infection in rabbits: role of defective triglyceride removal. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1980 Oct;2(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(80)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Lyanga J. J., Skamene E. Murine malaria: genetic control of resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Nesbitt M. N., Skamene E. Chromosomal location of the gene determining resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi AS. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;137:325–328. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50059-6_48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Skamene E. Murine malaria: resistance of AXB/BXA recombinant inbred mice to Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):452–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.452-456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Tavernier J., Fiers W., Playfair J. H. Recombinant tumour necrosis factor inhibits malaria parasites in vivo but not in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jan;67(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Kaufman E. N., Tate M. D., Neta R. Recombinant interleukin-1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha synergize in vivo to induce early endotoxin tolerance and associated hematopoietic changes. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2650–2657. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2650-2657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


