Abstract
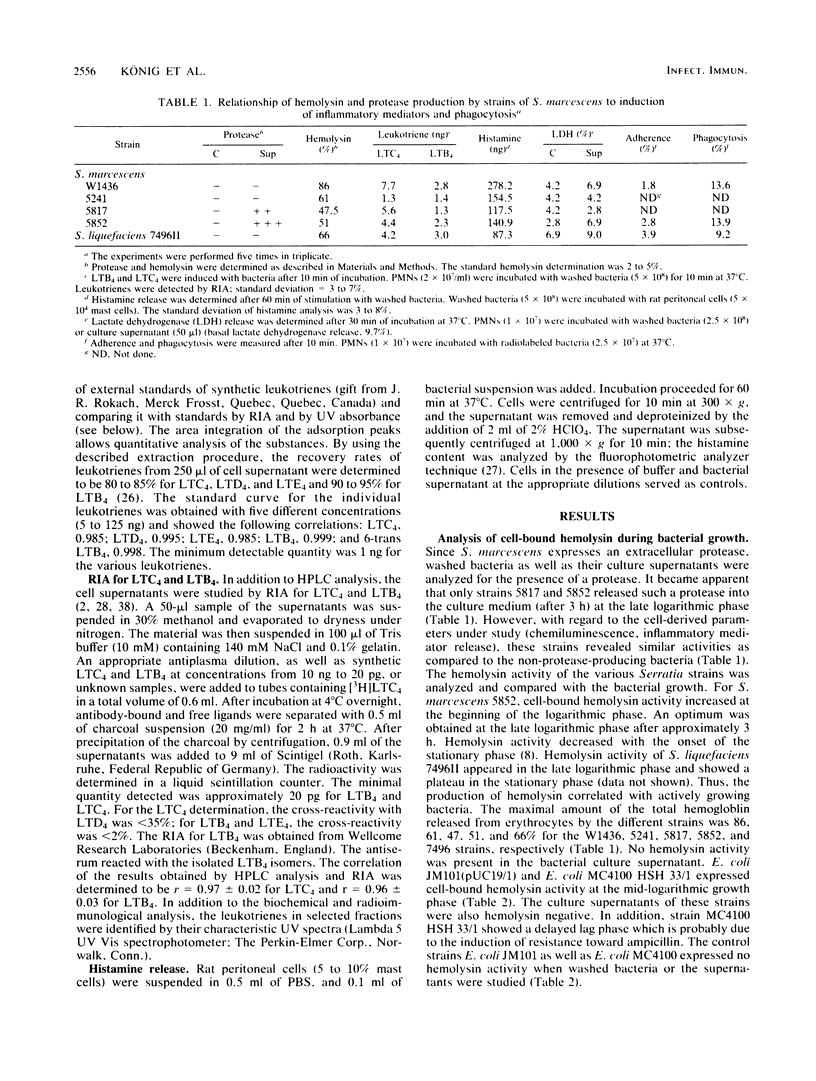
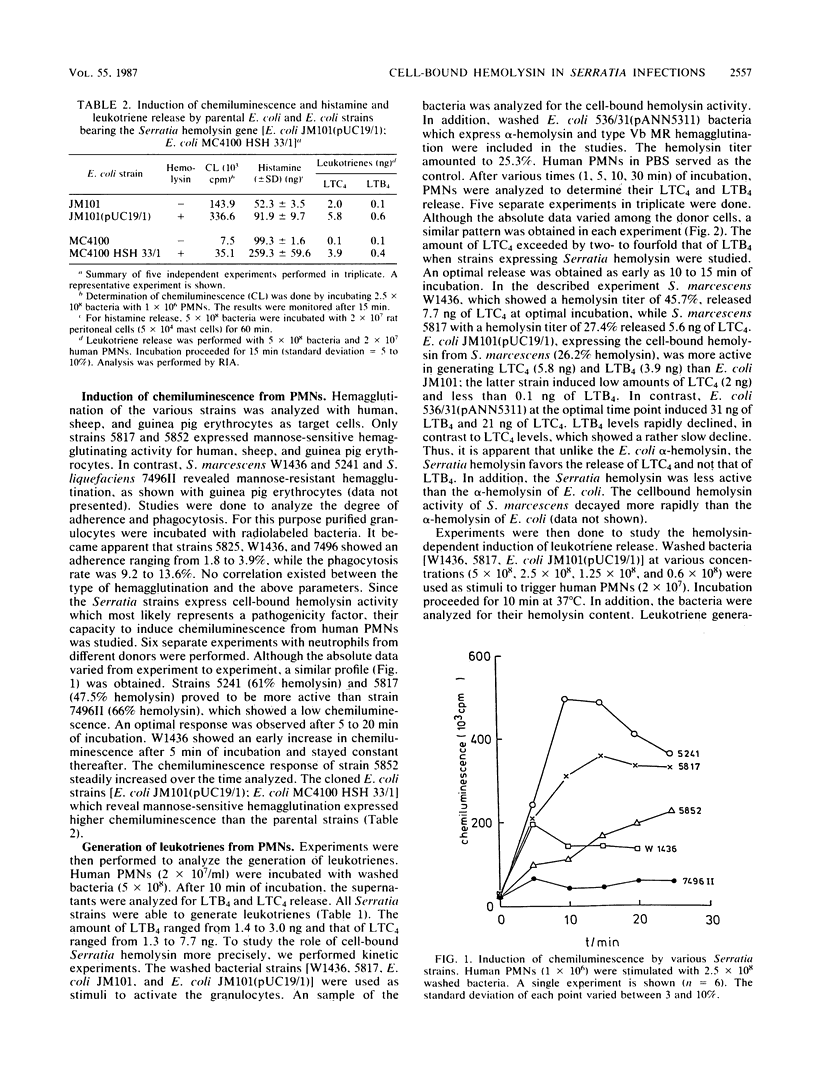
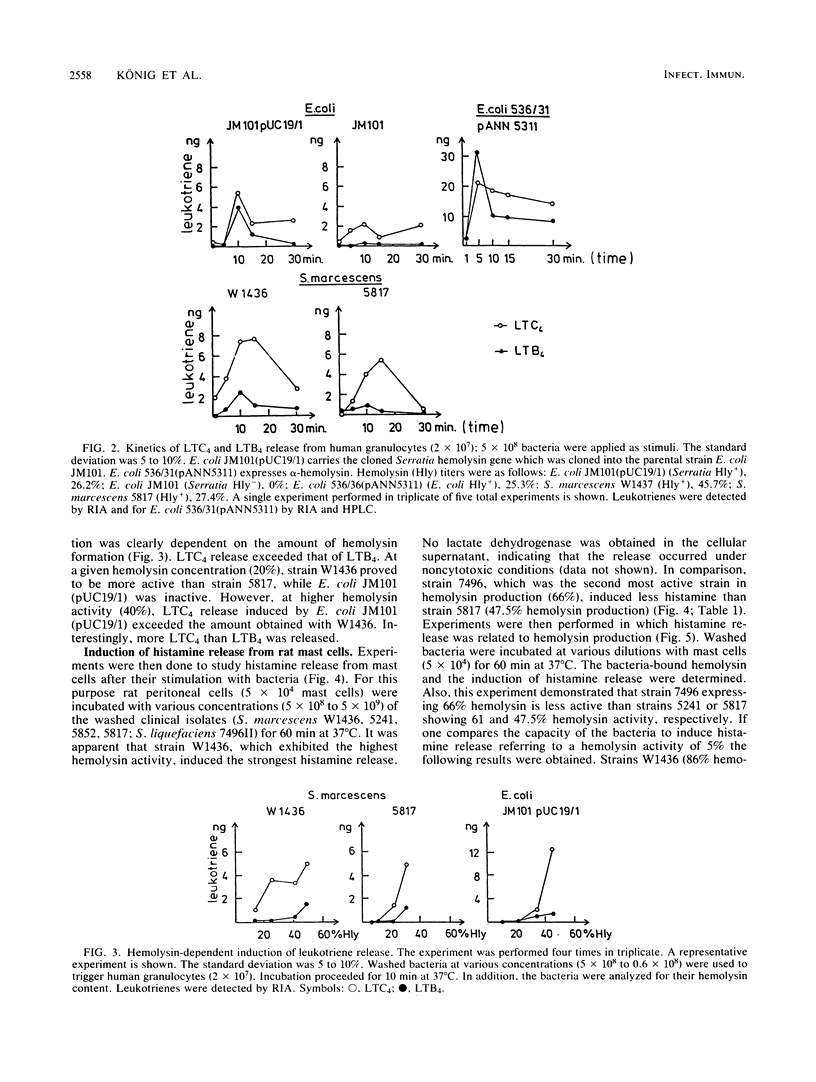
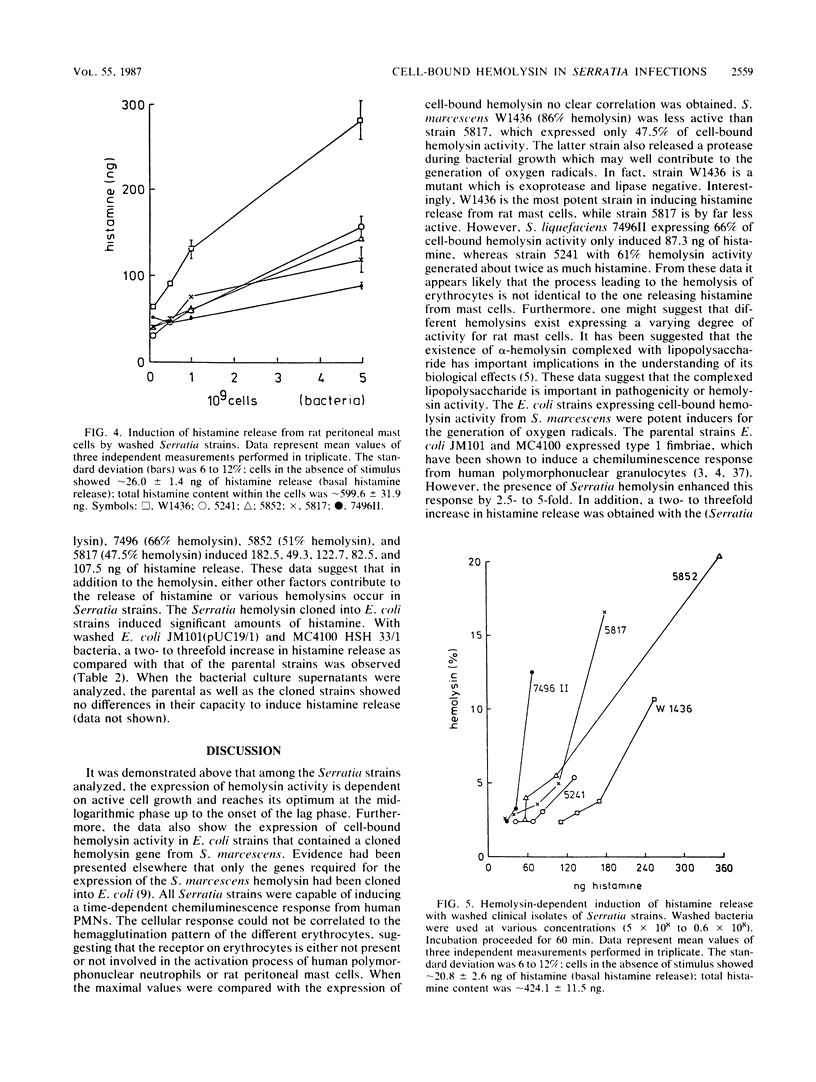
The hemolytic activities of clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens, of Serratia liquefaciens, and of Escherichia coli strains containing a cloned hemolysin gene of S. marcescens were determined. Hemolysis was induced only by cells and not by spent media. The hemolytically active bacteria induced the release of the leukotriene C4 and of much less leukotriene B4 from polymorphonuclear leukocytes, the release of histamine from rat mast cells, and chemoluminescence of neutrophils. The hemolytic activity was correlated with the response of the leukocytes, but quantitative differences were recorded with regard to the release of the inflammatory mediators. Therefore, other factors in addition to the hemolysin contribute to the stimulation of leukotriene generation and histamine release. It is concluded that the hemolysin via these inflammatory mediators can increase vascular permeability, edema formation, and granulocyte accumulation and thus contributes to the pathogenicity of Serratia species.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adegbola R. A., Old D. C. New fimbrial hemagglutinin in Serratia species. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):306–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.306-315.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aehringhaus U., Wölbling R. H., König W., Patrono C., Peskar B. M., Peskar B. A. Release of leukotriene C4 from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as determined by radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80715-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Wadström T. Interaction of Escherichia coli with different fimbriae and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):298–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.298-305.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock E., Jann K. Adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli strains to phagocytes: differences between bacteria with mannose-sensitive pili and those with mannose-resistant pili. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):264–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.264-269.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Snyder I. S. Chemical and immunological analysis of the complex structure of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1071–1080. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1071-1080.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Fruteau de Laclos B., Rabinovitch H., Picard S., Braquet P., Hébert J., Laviolette M. Eosinophil-rich human polymorphonuclear leukocyte preparations characteristically release leukotriene C4 on ionophore A23187 challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;74(3 Pt 2):310–315. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Günther H., Neuss B., Tautz C. Hemolytic activity of Serratia marcescens. Arch Microbiol. 1985 May;141(4):371–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00428852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Neuss B., Ruan Y., Schiebel E., Schöffler H., Jander G. Identification of the Serratia marcescens hemolysin determinant by cloning into Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2113–2120. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2113-2120.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Cunningham F. M., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B4: a mediator of vascular permeability. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;72(3):483–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb11000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom H. J., Alouf J. E., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Peters W. Generation of leukotrienes from human granulocytes by alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.188-193.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom J., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Bhakdi S., Lutz F., Fehrenbach F. J. Generation of leukotrienes and lipoxygenase factors from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes during bacterial phagocytosis and interaction with bacterial exotoxins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;254(4):500–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., König W., Pfeiffer P., Rauschen I., Theobald K., Thelestam M., Alouf J. E. Effect of thiol-activated toxins (streptolysin O, alveolysin, and theta toxin) on the generation of leukotrienes and leukotriene-inducing and -metabolizing enzymes from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):844–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.844-851.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Galanos C. Generation of slow-reacting substance (leukotrienes) by endotoxin and lipid A from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):299–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretz U., Baggiolini M. Biochemical and morphological characterization of azurophil and specific granules of human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):251–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. A one-stage procedure for isolation of granulocytes and lymphocytes from human blood. General sedimentation properties of white blood cells in a 1g gravity field. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:51–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri S. J., Snyder I. S. Cytotoxic activity of partially purified Escherichia coli alpha haemolysin. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):11–21. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg S., Hull S., Hull R., Pruckler J. Construction and comparison of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 fimbriae of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.275-279.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerr M., Traub W. H. Purification and characterization of two Serratia marcescens proteases. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 May;257(1):6–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Young L. S., Pitt J. Hemagglutination typing of Escherichia coli: definition of seven hemagglutination types. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.235-242.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadeberg O. V., Orskov I., Rhodes J. M. Cytotoxic effect of an alpha-hemolytic Escherichia coli strain on human blood monocytes and granulocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):358–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Schröter G., Schrettenbrunner A., Hughes C., Goebel W. Hemolytic Escherichia coli strains in the human fecal flora as potential urinary pathogens. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 May;254(3):370–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Müller D., Hacker J., Goebel W. Genetics and pathogenic role of Escherichia coli haemolysin. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop H. L., Lambert P. A. Immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex of Serratia marcescens and identification of the antigens accessible to antibodies on the cell surface. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2343–2348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata R., Yamamoto T., Matsumoto K., Maeda H. A serratial protease causes vascular permeability reaction by activation of the Hageman factor-dependent pathway in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):747–753. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.747-753.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Yamamoto T., Kuroiwa A., Amako K. Purification and characterization of Serratia marcescens US5 pili. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):295–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.295-300.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köller M., Schönfeld W., Knöller J., Bremm K. D., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Peters W. The metabolism of leukotrienes in blood plasma studied by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 9;833(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., König W., Scheffer J., Hacker J., Goebel W. Role of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin and bacterial adherence in infection: requirement for release of inflammatory mediators from granulocytes and mast cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.886-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Ishizaka K. Binding of rat IgE with the subcellular components of normal rat mast cells. Immunochemistry. 1976 Apr;13(4):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Kunau H. W., Borgeat P. Induction and comparison of the eosinophil chemotactic factor with endogenous hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids: its inhibition by arachidonic acid analogs. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1982;9:301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linggood M. A., Ingram P. L. The role of alpha haemolysin in the virulence of Escherichia coli for mice. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):23–30. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Kreger A. S. Importance of serratia protease in the pathogenesis of experimental Serratia marcescens pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.113-119.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Hennekens C. G., Phillips C. W., Shaw W. V., Bennett J. V. Nosocomial urinary tract infection with Serratia marcescens: an epidemiologic study. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):579–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Maeda H., Takata K., Kamata R., Okamura R. Purification and characterization of four proteases from a clinical isolate of Serratia marcescens kums 3958. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):225–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.225-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yamamoto T., Kamata R., Maeda H. Pathogenesis of serratial infection: activation of the Hageman factor-prekallikrein cascade by serratial protease. J Biochem. 1984 Sep;96(3):739–749. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Skov P. S., Jensen C., Jarløv J. O., Espersen F. Histamine release induced by bacteria. A new mechanism in asthma? Agents Actions. 1987 Feb;20(1-2):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01965622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Salmon J. A. Release of leukotriene B4 from human neutrophils and its relationship to degranulation induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, serum-treated zymosan and the ionophore A23187. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):65–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A., Ofek I., Silverblatt F. J. Enhancement of mannose-mediated stimulation of human granulocytes by type 1 fimbriae aggregated with antibodies on Escherichia coli surfaces. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1334–1345. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1334-1345.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulf M., Stüning M., König W. Metabolism of leukotrienes by L-gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase and dipeptidase from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Immunology. 1985 May;55(1):135–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer J., König W., Hacker J., Goebel W. Bacterial adherence and hemolysin production from Escherichia coli induces histamine and leukotriene release from various cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):271–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.271-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer J., Vosbeck K., König W. Induction of inflammatory mediators from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes and rat mast cells by haemolysin-positive and -negative E. coli strains with different adhesins. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):541–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Bauer D. Fibrinolytic activity of purified Serratia marcescens metalloproteases. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Aug;260(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Passive protection of NMRI mice against Serratia marcescens: comparative efficacy of commercial human IgG immunoglobulin preparations and rabbit anti-O, -H, -K, -life cell and -protease immune sera. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;254(4):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Virulence of nosocomial isolates of Serratia marcescens for NMRI mice: correlation with O-antigens O6 and O14. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Jul;252(3):360–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., MacLaren D. M., de Graaff J. In vivo function of hemolysin in the nephropathogenicity of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):245–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.245-249.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



