Abstract
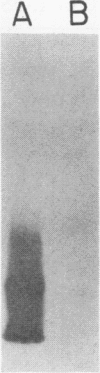
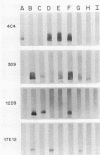
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) directed against epitopes in the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide (LOS) of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHI) were used to characterize the LOS of this pathogen. Western blot (immunoblot) analysis with four LOS-specific MAbs and proteinase K-derived LOS preparations from 69 NTHI strains allowed the classification of these strains into nine LOS antigenic groups. The use of these MAbs in a more sensitive colony blot radioimmunoassay system together with these same NTHI strains identified 14 LOS antigenic groups. Extensive cross-reactivity was detected between the LOS epitopes of these NTHI strains and the LOS of H. influenzae type b. The epitopes recognized by these MAbs were not accessible to antibody on the surface of every strain. These LOS epitopes were also not stably expressed by NTHI growing in vitro; the observed frequency of LOS antigen variation ranged from 1 to 24% when large numbers of colonies of NTHI strains were screened for reactivity with the LOS-directed MAbs in the colony blot radioimmunoassay. This LOS antigenic variation was sometimes associated with alterations in the profile of the LOS molecule as resolved by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis followed by staining with silver. These data indicate that considerable antigenic diversity exists among NTHI strains with regard to the oligosaccharide epitopes in their LOS molecules.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Flesher A., Shaw S., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Phenotypic and genetic variation in the susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae type b to antibodies to somatic antigens. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):885–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI109741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Dudas K. C., Campagnari A., Rice P., Mylotte J. M., Murphy T. F. Antigenic heterogeneity of lipid A of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.9-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J. Protection by serum antibodies in experimental nontypable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.572-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Holtsclaw S. A., Wiener S. L., Smith J. K. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):537–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnari A. A., Gupta M. R., Dudas K. C., Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic diversity of lipooligosaccharides of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):882–887. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.882-887.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen C. A., Cho C. T. Characteristic features of neonatal sepsis due to Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):777–780. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan W. D., Ackerman G. A. Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid and anti-immunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin and goat anti-human immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscopic level: a new method, theory and application. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Nov;25(11):1187–1200. doi: 10.1177/25.11.21217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Ferrieri P. Susceptibility of phenotypic variants of Haemophilus influenzae type b to serum bactericidal activity: relation to surface lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):223–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnehm H. E., Pelton S. I., Gulati S., Rice P. A. Characterization of antigens from nontypable Haemophilus influenzae recognized by human bactericidal antibodies. Role of Haemophilus outer membrane proteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1645–1658. doi: 10.1172/JCI111872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Nankervis G. A. Infectious arthritis in the neonate caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jun;129(6):730–733. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120430062017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Hansen E. J. Coprecipitation of lipopolysaccharide and the 39,000-molecular-weight major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b by lipopolysaccharide-directed monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):819–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.819-827.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Patrick C. C., Hermanstorfer L., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Conservation of epitopes in the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.513-520.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. V., Musher D. M., Baughn R. E. Outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and reactivity of paired sera from infected patients with their homologous isolates. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):843–846. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.843-846.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmans P. L., Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. Cloning and surface expression in Escherichia coli of a structural gene encoding a surface protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):236–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.236-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Anderson P. Serum factor-dependent resistance of Haemophilus influenzae type b to antibody to lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):869–877. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Seifert W. E., Jr, Williams R. P. Composition and antigenic activity of the oligosaccharide moiety of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):324–330. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.324-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasic R. B., Trumpp C. E., Gnehm H. E., Rice P. A., Pelton S. I. Modification of otitis media in chinchillas rechallenged with nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and serological response to outer membrane antigens. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):273–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri-Bulos N., McIntosh K. Neonatal Haemophilus influenzae infection. Report of eight cases and review of the literature. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jan;129(1):57–62. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120380037009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Patrick C. C., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide: stability of expression and association with virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1979–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1979-1986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. O. Microbiology and antimicrobial treatment of otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1981 May-Jun;90(3 Pt 3):30–36. doi: 10.1177/00034894810903s209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. R., Herrick N. C., Thompson D. Bacterial infection in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Dec;47(256):908–913. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.256.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae is a basis for a serotyping system. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.15-21.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M. Haemophilus influenzae infections. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1983 Aug;18(8):158-61, 166, 169-70. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1983.11702617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Hague-Park M., Baughn R. E., Wallace R. J., Jr, Cowley B. Opsonizing and bactericidal effects of normal human serum on nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):297–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.297-304.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Kubitschek K. R., Crennan J., Baughn R. E. Pneumonia and acute febrile tracheobronchitis due to haemophilus influenzae. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):444–450. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr T. R., Jr, Bryan L. E. Lipopolysaccharide composition of three strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1184–1187. doi: 10.1139/m84-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Two physically and serologically distinct lipopolysaccharide profiles in strains of Bordetella pertussis and their phenotype variants. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.224-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Frisch C. F., Gulig P. A., Kettman J. R., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Monoclonal antibodies directed against a cell surface-exposed outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shann F., Gratten M., Germer S., Linnemann V., Hazlett D., Payne R. Aetiology of pneumonia in children in Goroka Hospital, Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 1984 Sep 8;2(8402):537–541. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Pelton S. I., Tager I. B., Kasper D. L. Bactericidal antibody and susceptibility to otitis media caused by nontypable strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):364–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. B., Southwick F. S., Moellering R. C., Jr, Sherman E. Hemophilus influenzae in hospitalized adults: current perspectives. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews G. B., Viroslav S., Hart D. A., Hansen E. J. Pulmonary clearance of encapsulated and unencapsulated Haemophilus influenzae strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):437–442. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.437-442.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Boykins R., Frasch C. E. Heterogeneity and variation among Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):498–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.498-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Musher D. M., Septimus E. J., McGowan J. E., Jr, Quinones F. J., Wiss K., Vance P. H., Trier P. A. Haemophilus influenzae infections in adults: characterization of strains by serotypes, biotypes, and beta-lactamase production. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):101–106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Connelly C. J., Inzana T. J., Moxon E. R. Alteration of the cell wall of Haemophilus influenzae type b by transformation with cloned DNA: association with attenuated virulence. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):485–492. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]