Abstract
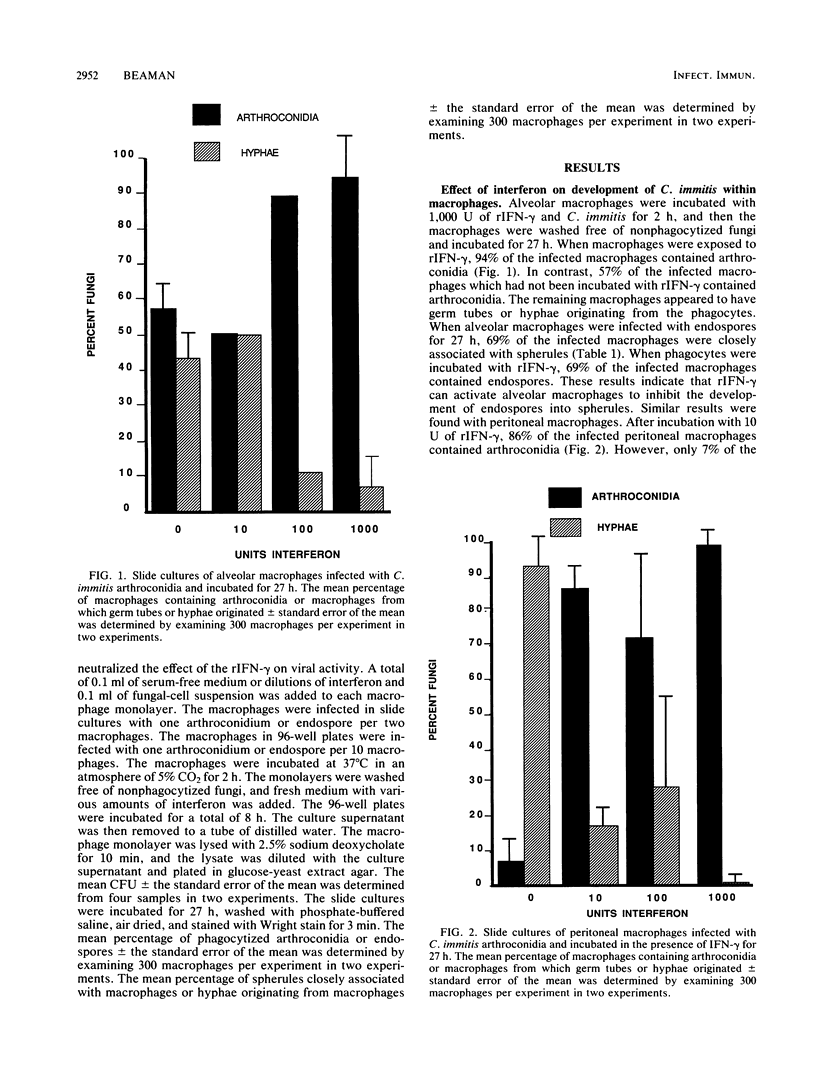
Alveolar macrophages from BALB/c mice readily phagocytized endospores (2 to 5 micron) and arthroconidia of Coccidioides immitis in vitro. Within 24 to 30 h at 37 degrees C, the phagocytized endospores started developing into spherules, and the arthroconidia formed germ tubes and hyphae. However, these processes did not occur if the macrophages were incubated with murine recombinant gamma interferon (rIFN-gamma) during infection with C. immitis. Treatment with rIFN-gamma activated the fungicidal capabilities of the alveolar macrophages, as evidenced by the 50% reduction in the CFU which could be recovered from macrophages infected in the presence of gamma interferon compared with alveolar macrophages infected without gamma interferon (P less than 0.05). Similar results were seen with peritoneal macrophages incubated with rIFN-gamma and infected with C. immitis. As little as 10 U of rIFN-gamma per ml reduced by half the number of C. immitis CFU which could be recovered from the phagocytes 8 h after infection with arthroconidia, although interferon alone did not affect the viability of the fungi.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Activation of macrophages by lymphokines: enhancement of phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1201-1207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Role of lymphocytes in macrophage-induced killing of Coccidioides immitis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):347–353. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.347-353.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Holmberg C. A. In vitro response of alveolar macrophages to infection with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):594–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.594-600.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Catterall J. R., Remington J. S. In vivo and in vitro activation of alveolar macrophages by recombinant interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Morrison C. J., Stevens D. A. Recombinant and natural gamma-interferon activation of macrophages in vitro: different dose requirements for induction of killing activity against phagocytizable and nonphagocytizable fungi. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.724-730.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Krueger D. A. Lymphokine-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia replication in mouse fibroblasts is neutralized by anti-gamma interferon immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1152-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krammer P. H., Kubelka C. F., Falk W., Ruppel A. Priming and triggering of tumoricidal and schistosomulicidal macrophages by two sequential lymphokine signals: interferon-gamma and macrophage cytotoxicity inducing factor 2. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3258–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubelka C. F., Ruppel A., Krammer P. H., Gemsa D. Killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by macrophages: induction by T-cell clone-derived lymphokines and interferon-gamma. Parasitology. 1986 Apr;92(Pt 2):325–336. doi: 10.1017/s003118200006409x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Effect of murine interferon gamma on murine toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):961–962. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Fortier A. H., Meltzer M. S., Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania major: activation of macrophages for intracellular destruction of amastigotes can be induced by both recombinant interferon-gamma and non-interferon lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3505–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Vasil A. Evidence for the identity of murine gamma interferon and macrophage activating factor. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(4):519–532. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel C. D., Byrne G. I., Havell E. A. Effect of interferon on the growth of Chlamydia trachomatis in mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.362-370.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: tumoricidal activity by macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice requires at least two activation stimuli. Cell Immunol. 1978 Nov;41(1):35–51. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(78)80026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Altman A., Katz D. H. Macrophage-activating factor produced by a T cell hybridoma: physiochemical and biosynthetic resemblance to gamma-interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):826–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedersky L. P., Benton C. V., Berger W. H., Rinderknecht E., Harkins R. N., Palladino M. A. Biological and antigenic similarities of murine interferon-gamma and macrophage-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):812–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli D., Holden H. T., Varesio L. Endotoxin requirement for macrophage activation by lymphokines in a rapid microcytotoxicity assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(3-4):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Thompson H. A., Winkler H. H. Interferon-gamma inhibits growth of Coxiella burnetii in mouse fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):781–783. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.781-783.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Cloned mouse interferon-gamma inhibits the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2159–2164. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Comparison of the properties of antirickettsial activity and interferon in mouse lymphokines. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Effect of mouse lymphokines and cloned mouse interferon-gamma on the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii with mouse macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.303-308.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Inhibition of the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by recombinant murine gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1014-1016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Zlotnik A., Howard D. H. T-cell hybridoma-produced lymphokine that activates macrophages to suppress intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):380–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.380-385.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


