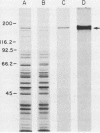
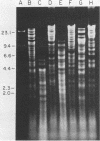
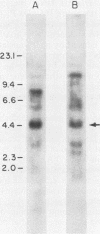
Abstract
Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadhesin P1 was purified by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography followed by preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The N-terminal 18-amino-acid sequence of P1 was determined and used to design two synthetic oligonucleotides, a 14-mer corresponding to amino acids 1 to 5 and an 18-mer corresponding to amino acids 7 to 12. These oligonucleotides served as hybridization probes for the identification of the P1 gene by Southern blot analysis of M. pneumoniae DNA. The P1 gene was cloned into plasmid pUC19 and mapped by using appropriate restriction endonucleases. The DNA sequence of the entire P1 gene was determined by subcloning appropriate DNA fragments into bacteriophage M13 and sequencing the DNA by the dideoxy-chain-termination method. The P1 gene contains an open reading frame of 4,881 nucleotides coding for a protein of 1,627 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 176,288. Properties of the amino-terminal sequence suggest that protein P1 may be synthesized as a precursor with subsequent processing to a mature protein of a calculated molecular weight of 169,758. Potential antigenic sites were determined by hydrophilicity plots. A computer search revealed that part of the predicted P1 sequence is homologous to cytoskeletal keratin of mammalian species and human fibrinogen alpha chain precursor. These results demonstrate the uniqueness of P1 as a cytadhesin and virulence determinant.
Full text
PDF




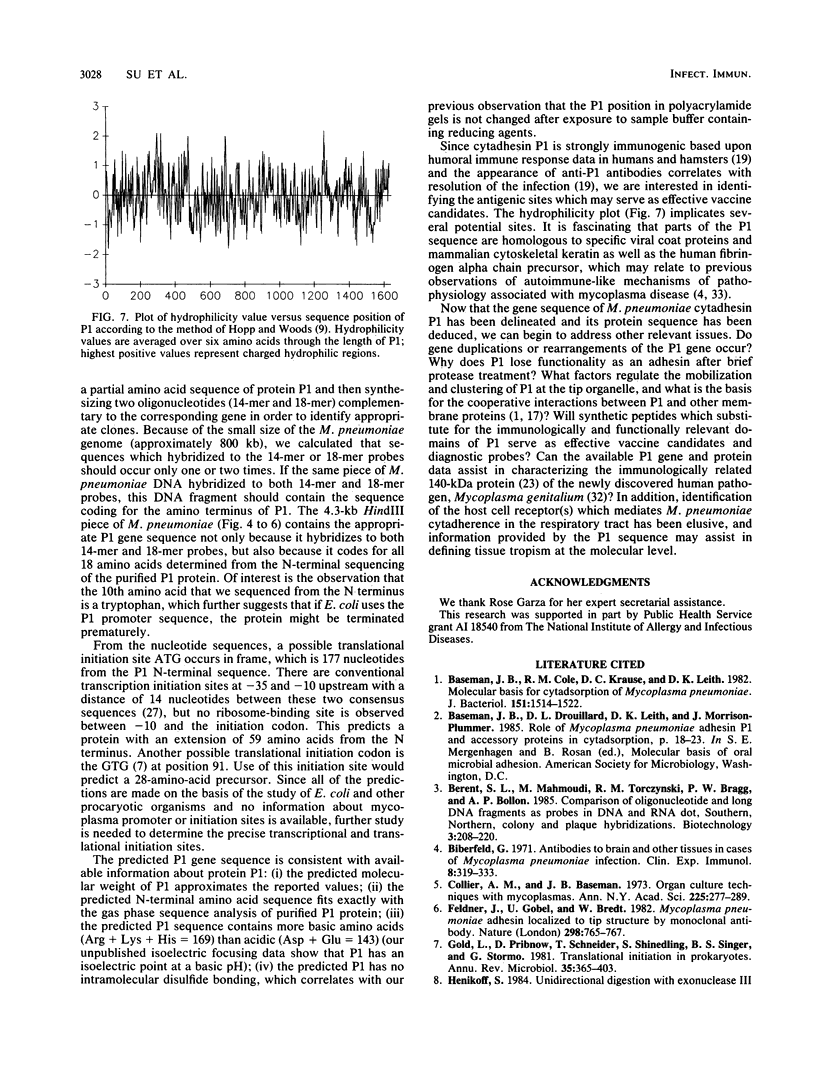

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G. Antibodies to brain and other tissues in cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):319–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Göbel U., Bredt W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin localized to tip structure by monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):765–767. doi: 10.1038/298765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Bennewitz A., Bredt W. Reaction pattern of human anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Tucker S., Baseman J. B. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin (P1) in the nonhemadsorbing population of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):457–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.457-458.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Reacquisition of specific proteins confers virulence in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):830–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.830-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Purification of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):678–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.678-680.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Trevino L. B., Tully J. G., Senterfit L. B., Baseman J. B. Host discrimination of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteinaceous immunogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):502–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Plummer J., Lazzell A., Baseman J. B. Shared epitopes between Mycoplasma pneumoniae major adhesin protein P1 and a 140-kilodalton protein of Mycoplasma genitalium. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):49–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.49-56.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Plummer J., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Biological effects of anti-lipid and anti-protein monoclonal antibodies on Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):398–403. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.398-403.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Hu P. C., Wilson M., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):959–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.959-966.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevino L. B., Haldenwang W. G., Baseman J. B. Expression of Mycoplasma pneumoniae antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.129-134.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Cole R. M., Rose D. L. A newly discovered mycoplasma in the human urogenital tract. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Watson R. K. Antigenic mimicry of mammalian intermediate filaments by mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.587-591.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamao F., Muto A., Kawauchi Y., Iwami M., Iwagami S., Azumi Y., Osawa S. UGA is read as tryptophan in Mycoplasma capricolum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2306–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]