Abstract
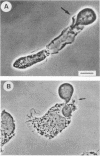
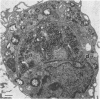
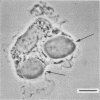
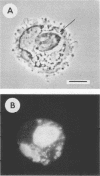
Mononuclear phagocytes may be important effector cells against Giardia lamblia. Human monocyte-derived macrophages were incubated with G. lamblia trophozoites in 13% heat-inactivated autologous serum. At a G. lamblia/macrophage ratio of 1:1, the number of trophozoites ingested per 100 macrophages ranged from 1 to 12 at 0.5 h and increased for all donors (n = 6) to 10 to 92 at 8 h. Ingestion was confirmed by electron microscopy. Increasing the parasite/phagocyte ratio to 5:1 increased the percentage of macrophages with adherent but not ingested trophozoites. Incubating Giardia cells and macrophages with 20% immune serum increased ingestion of parasites eightfold, indicating that anti-G. lamblia antibody can enhance ingestion. Both phase-contrast microscopy and electron microscopy documented trophozoite destruction within macrophages. Ingestion of parasites elicited an oxidative burst as measured by luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence. In vitro, Giardia trophozoites were killed by greater than or equal to 5 X 10(-5) M H2O2. Fusion of lysosomes with parasite-containing phagosomes was suggested by acridine orange-stained preparations. Human macrophages have the capacity to ingest Giardia trophozoites and to kill intracellular parasites, possibly by oxidative microbicidal mechanisms.
Full text
PDF

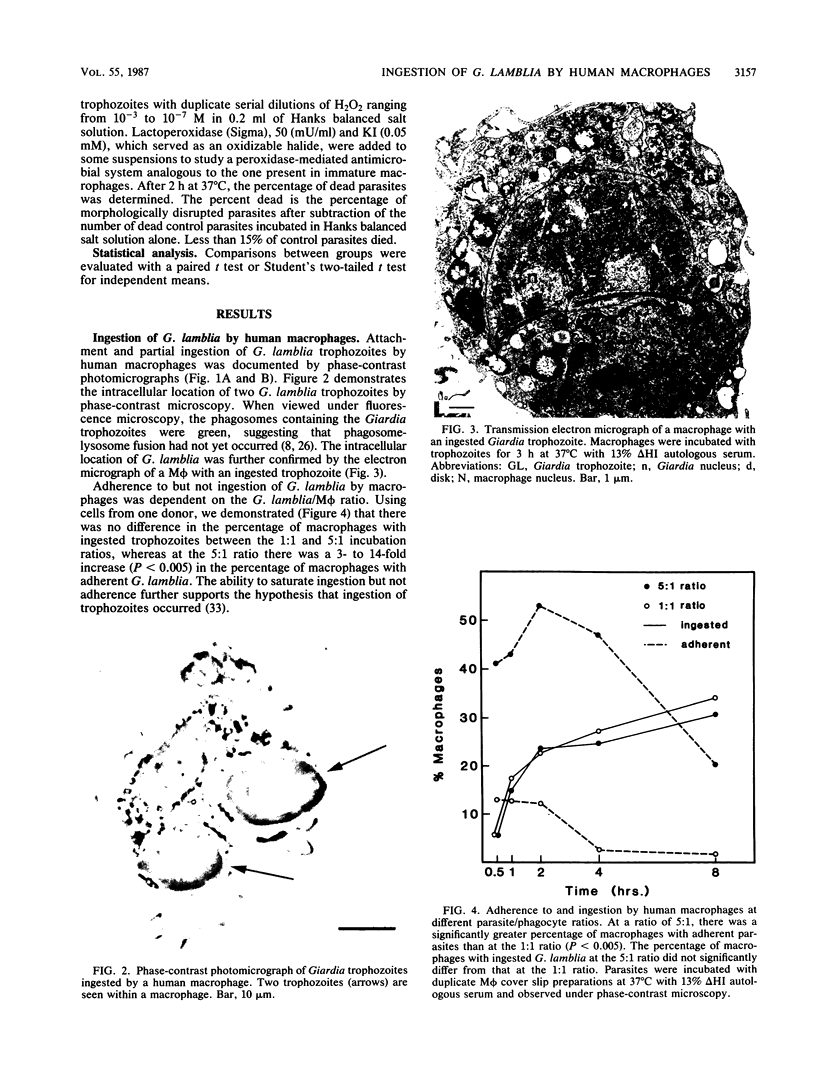
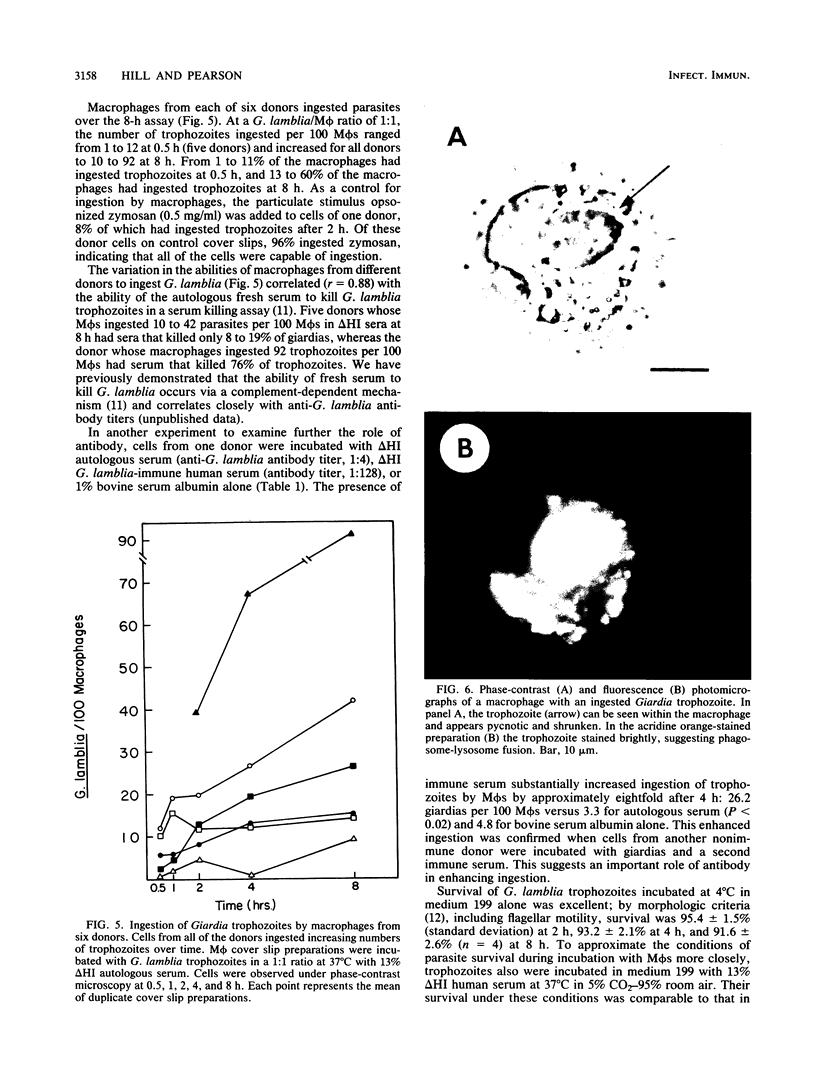
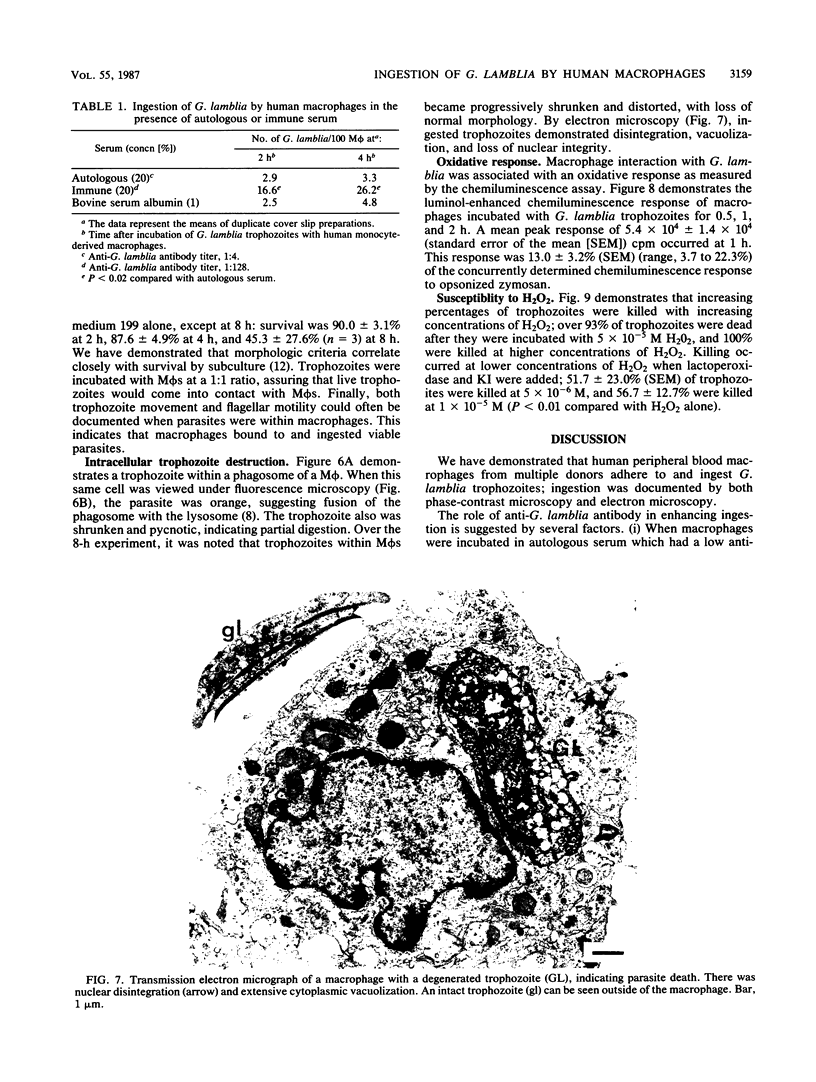

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A., Nash T. E. Lack of cellular cytotoxicity by human mononuclear cells to Giardia. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3486–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews J. S., Jr, Hewlett E. L. Protection against infection with Giardia muris by milk containing antibody to Giardia. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):242–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe V. M., Bolin T. D., Davis A. E., Cummins A. G., Crouch R. L. Histopathology in giardiasis: a correlation with diarrhoea. Aust N Z J Med. 1978 Aug;8(4):392–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1978.tb04908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. Degradation of microorganisms by phagocytic cells. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):106–128. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Heck J. A., Strober W. T-cell regulation of murine IgA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Interference with normal phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages, using ingested yeast cells and suramin. Nature. 1975 Jul 3;256(5512):47–49. doi: 10.1038/256047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth M. F. Antibody response to Giardia muris trophozoites in mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):568–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.568-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth M. F., Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Comparison of leukocytes obtained from the intestinal lumen of Giardia-infected immunocompetent mice and nude mice. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1360–1365. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90656-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Burge J. J., Pearson R. D. Susceptibility of Giardia lamblia trophozoites to the lethal effect of human serum. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2046–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Pohl R., Pearson R. D. Giardia lamblia: a culture method for determining parasite viability. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Nov;35(6):1129–1133. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istre G. R., Dunlop T. S., Gaspard G. B., Hopkins R. S. Waterborne giardiasis at a mountain resort: evidence for acquired immunity. Am J Public Health. 1984 Jun;74(6):602–604. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.6.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Uni S., Aikawa M., Mahmoud A. A. Effector mechanism of host resistance in murine giardiasis: specific IgG and IgA cell-mediated toxicity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1975–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. Epidemiology and transmission of giardiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre M. E., Hammer R., Joel D. D. Macrophages of the mammalian small intestine: a review. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Nov;26(5):553–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshnick S. R., Eaton J. W. Leishmanial superoxide dismutase: a possible target for chemotherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):970–976. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. A. Giardia lamblia: isolation and axenic cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Feb;39(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism in human monocytes during differentiation in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1243–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI110370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Allen C. L., Stevens D. P. Phagocytosis of Giardia muris by macrophages in Peyer's patch epithelium in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):591–601. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.591-601.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyerinde J. P., Ogunbi O., Alonge A. A. Age and sex distribution of infections with Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia intestinalis in the Lagos population. Int J Epidemiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):231–234. doi: 10.1093/ije/6.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T. Phagocytosis and killing of the protozoan Leishmania donovani by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1438–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radulescu S., Meyer E. A. Opsonization in vitro of Giardia lamblia trophozoites. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):852–856. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.852-856.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Mitchell G. F. Giardiasis in mice. I. Prolonged infections in certain mouse strains and hypothymic (nude) mice. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):42–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Stevens D. P., Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S. Acquired resistance to infection in an animal model of giardiasis. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):2036–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha T. K., Ghosh T. K. Invasion of small intestinal mucosa by Giardia lamblia in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):402–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Elson C. O., Keister D. B., Nash T. E. Human host response to Giardia lamblia. I. Spontaneous killing by mononuclear leukocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1372–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. P., Underdown B. J. Quantitative and temporal analyses of murine antibody response in serum and gut secretions to infection with Giardia muris. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):271–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.271-278.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis: recognition and ingestion. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jan;12(1):83–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Cooperation between mononuclear phagocytes and lymphocytes in immunity. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 23;303(17):977–985. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010233031706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S. Axenic growth of Giardia lamblia in Diamond's TPS-1 medium. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(2):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Smith P. D., Healy G. R., Brown W. R. An immunofluorescence test to detect serum antibodies to Giardia lamblia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):802–805. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]