Abstract
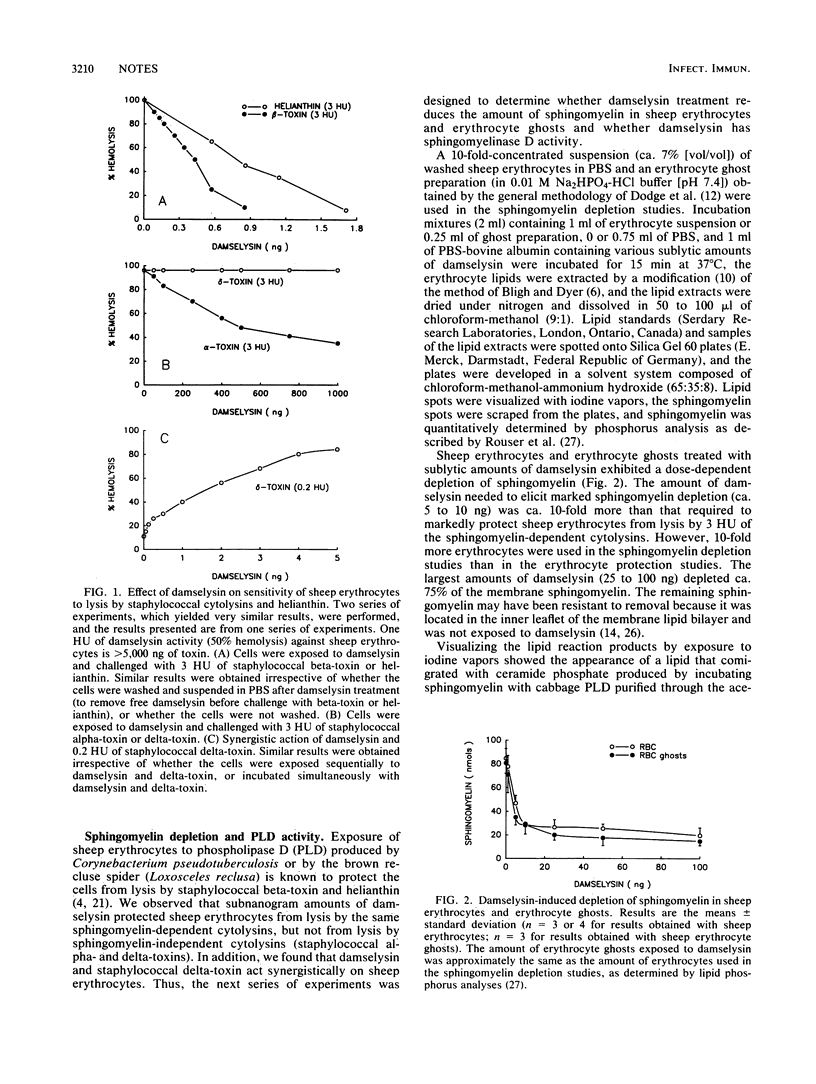
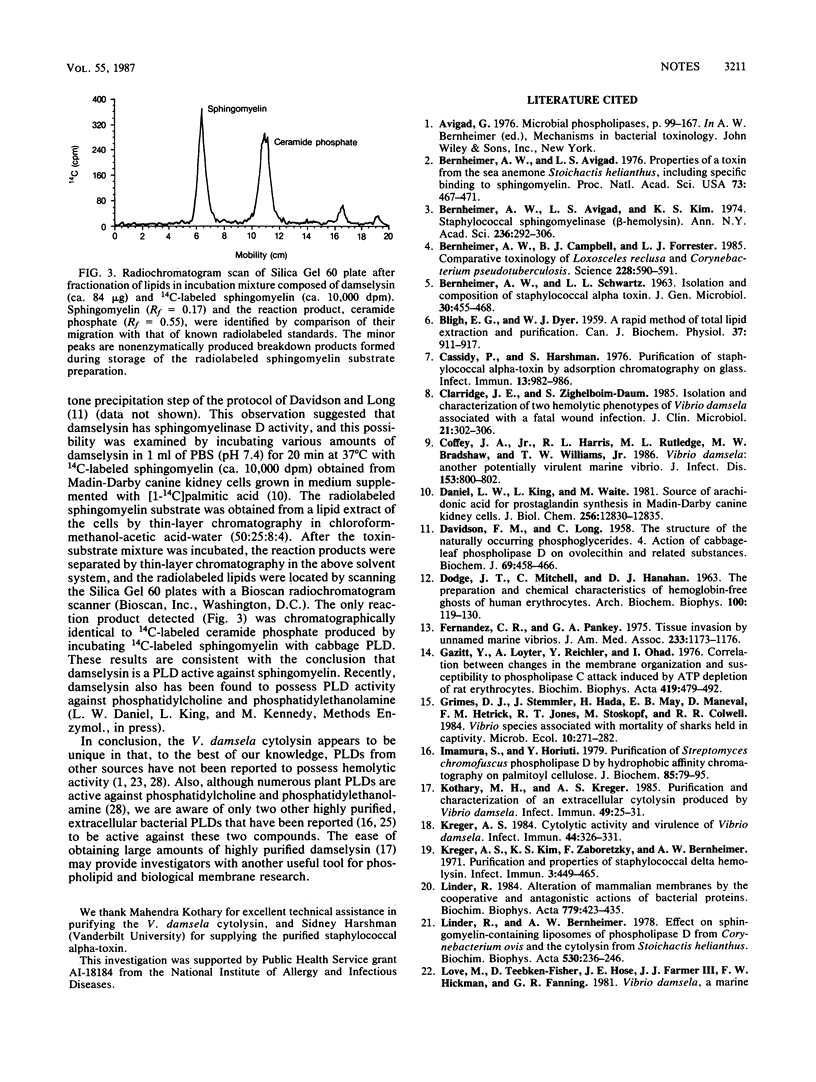
Exposure of sheep erythrocytes to sublytic amounts of Vibrio damsela cytolysin markedly reduced their membrane sphingomyelin content and their sensitivity to lysis by the sphingomyelin-dependent cytolysins staphylococcal sphingomyelinase C (beta-toxin) and helianthin. The toxin was found to be a phospholipase D active against sphingomyelin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Kim K. S. Staphylococcal sphingomyelinase (beta-hemolysin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):292–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Properties of a toxin from the sea anemone Stoichacis helianthus, including specific binding to sphingomyelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):467–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Campbell B. J., Forrester L. J. Comparative toxinology of Loxosceles reclusa and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):590–591. doi: 10.1126/science.3983643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Purification of staphylococcal alpha-toxin by adsorption chromatography on glass. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):982–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.982-986.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarridge J. E., Zighelboim-Daum S. Isolation and characterization of two hemolytic phenotypes of Vibrio damsela associated with a fatal wound infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):302–306. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.302-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey J. A., Jr, Harris R. L., Rutledge M. L., Bradshaw M. W., Williams T. W., Jr Vibrio damsela: another potentially virulent marine vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):800–802. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.800-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON F. M., LONG C. The structure of the naturally occurring phosphoglycerides. 4. Action of cabbage-leaf phospholipase D on ovolecithin and related substances. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):458–466. doi: 10.1042/bj0690458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., King L., Waite M. Source of arachidonic acid for prostaglandin synthesis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12830–12835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C. R., Pankey G. A. Tissue invasion by unnamed marine vibrios. JAMA. 1975 Sep 15;233(11):1173–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt Y., Loyter A., Reichler Y., Ohad I. Correlation between changes in the membrane organization and susceptibility to phospholipase C attack induced by ATP depletion of rat erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):479–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura S., Horiuti Y. Purification of Streptomyces chromofuscus phospholipase D by hydrophobic affinity chromatography on palmitoyl cellulose. J Biochem. 1979 Jan;85(1):79–95. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Kreger A. S. Purification and characterization of an extracellular cytolysin produced by Vibrio damsela. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S. Cytolytic activity and virulence of Vibrio damsela. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):326–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.326-331.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder R. Alteration of mammalian membranes by the cooperative and antagonistic actions of bacterial proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 4;779(4):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder R., Bernheimer A. W. Effect on sphingomyelin-containing liposomes of phospholipase D from Corynebacterium ovis and the cytolysin from Stoichactis helianthus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 25;530(2):236–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Miller H. G., Wilson R., Tacket C. O., Hollis D. G., Hickman F. W., Weaver R. E., Blake P. A. Illness caused by Vibrio damsela and Vibrio hollisae. Lancet. 1982 Jun 5;1(8284):1294–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92853-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okawa Y., Yamaguchi T. Studies on phospholipases from Streptomyces. II. Purification and properties of Streptomyces hachijoensis phospholipase D. J Biochem. 1975 Aug;78(2):363–372. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renooij W., Van Golde L. M., Zwaal R. F., Van Deenen L. L. Topological asymmetry of phospholipid metabolism in rat erythrocyte membranes. Evidence for flip-flop of lecithin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 2;61(1):53–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb09996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


