Abstract
This study documents the formation of leukocyte foci in the livers of mice infused with either normal or immune T cells and then challenged intravenously with Listeria monocytogenes. The results show that the transfer of antilisterial resistance occurred before mononuclear cell granuloma formation and was associated instead with the appearance of foci of infiltrating lymphocytes and neutrophils. Numbers of these foci remained low in mice which received immune cells but increased progressively until death in mice which received normal cells. These findings do not support the previous hypothesis that a major component of acquired resistance against Listeria infection involves the rapid generation of mononuclear cell granuloma formation under the control of immune T cells.
Full text
PDF
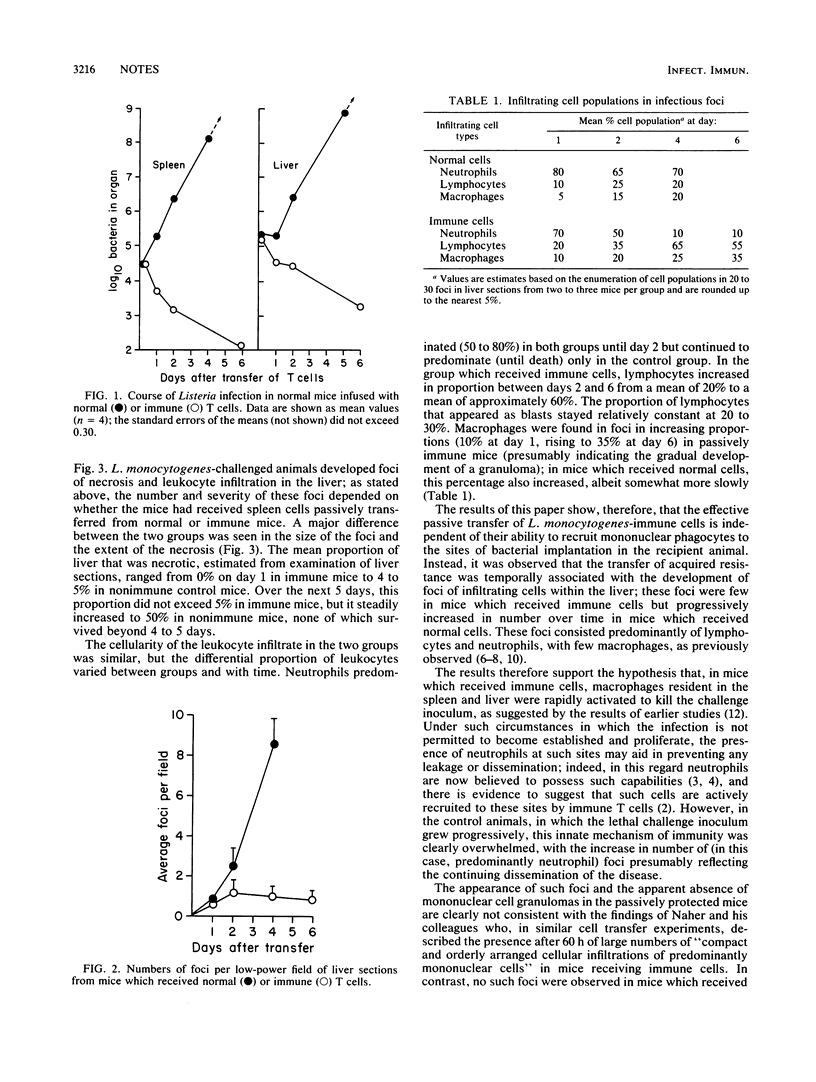
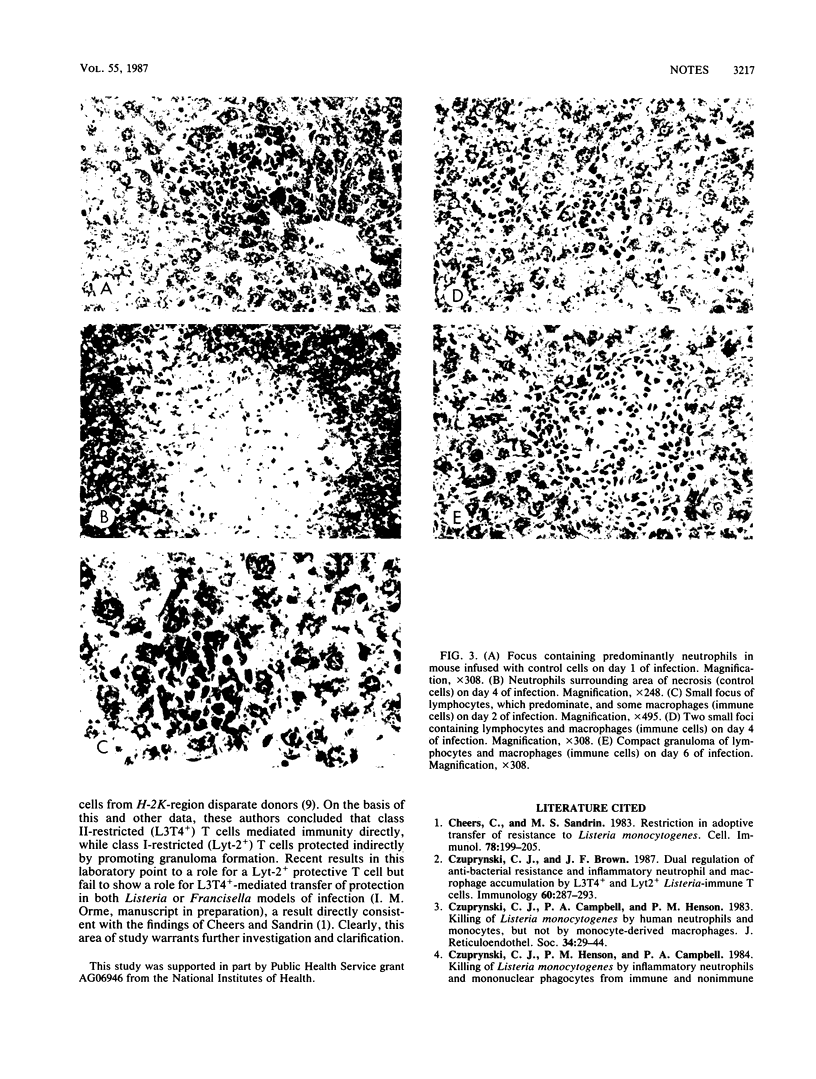

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheers C., Sandrin M. S. Restriction in adoptive transfer of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. II. Use of congenic and mutant mice show transfer to be H-2K restricted. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jun;78(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Dual regulation of anti-bacterial resistance and inflammatory neutrophil and macrophage accumulation by L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ Listeria-immune T cells. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):287–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Campbell P. A., Henson P. M. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by human neutrophils and monocytes, but not by monocyte-derived macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Jul;34(1):29–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T. E., Cheers C. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: histopathology of listeriosis in resistant and susceptible strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):851–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.851-861.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näher H., Sperling U., Hahn H. H-2K-restricted granuloma formation by Ly-2+ T cells in antibacterial protection to facultative intracellular bacteria. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):569–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A., Adler B., Blanden R. V., Davidson W. F., Kees U., Dunlop M. B., Shreffler D. C. H-2 restriction of cell-mediated immunity to an intracellular bacterium: effector T cells are specific for Listeria antigen in association with H-21 region-coded self-markers. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1353–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




