Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies against the Shigella flexneri lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were generated in two fusions by using the myeloma cell line Sp2/0 as a fusion partner with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with S. flexneri serotypes 1b and 3a bacteria. The antibodies were characterized by immunoblotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), hemagglutination, and coagglutination. Four different types of monoclonal antibodies were isolated: antibodies specific for the core antigen of the LPS, antibodies specific for the type I O antigen, antibodies specific for the group 6 O antigen, and antibodies specific for the type III:6,7,8 O antigen. The core-specific antibodies were shown to be specific for the Escherichia coli R3 core, which all S. flexneri LPSs tested, except for S. flexneri serotype 6 LPS, have. The type I O antigen-specific antibodies were shown to bind exclusively to S. flexneri serotypes 1a and 1b in ELISA. The type III:6,7,8 O-antigen-specific antibodies were specific for S. flexneri serotype 3a in ELISA and hemagglutination. Two different group 6 O-antigen-specific antibodies were bound. One was bound in both ELISA and hemagglutination to LPSs of S. flexneri serotypes 1b, 3a, 3b, and 4b, whereas the second was bound only to LPSs of serotypes 3a, 3b, and 4b in ELISA but to LPSs of all four serotypes in hemagglutination. The specificity of the isolated I, III:6,7,8, and group 6 monoclonal antibodies was verified by coagglutination of 363 S. flexneri clinical isolates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beer W., Seltmann G. Studies on the antigenic structure of Shigella. VII. Structure of the O-specific side chains of the lipopolysaccharides from strains 2 (serotype lb) and 1290-63 (variant Y). Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(2):107–113. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin N. I., Lindberg A. A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for O-antigenic polysaccharides of Shigella flexneri: clones binding to II, II:3,4, and 7,8 epitopes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1183–1189. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1183-1189.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
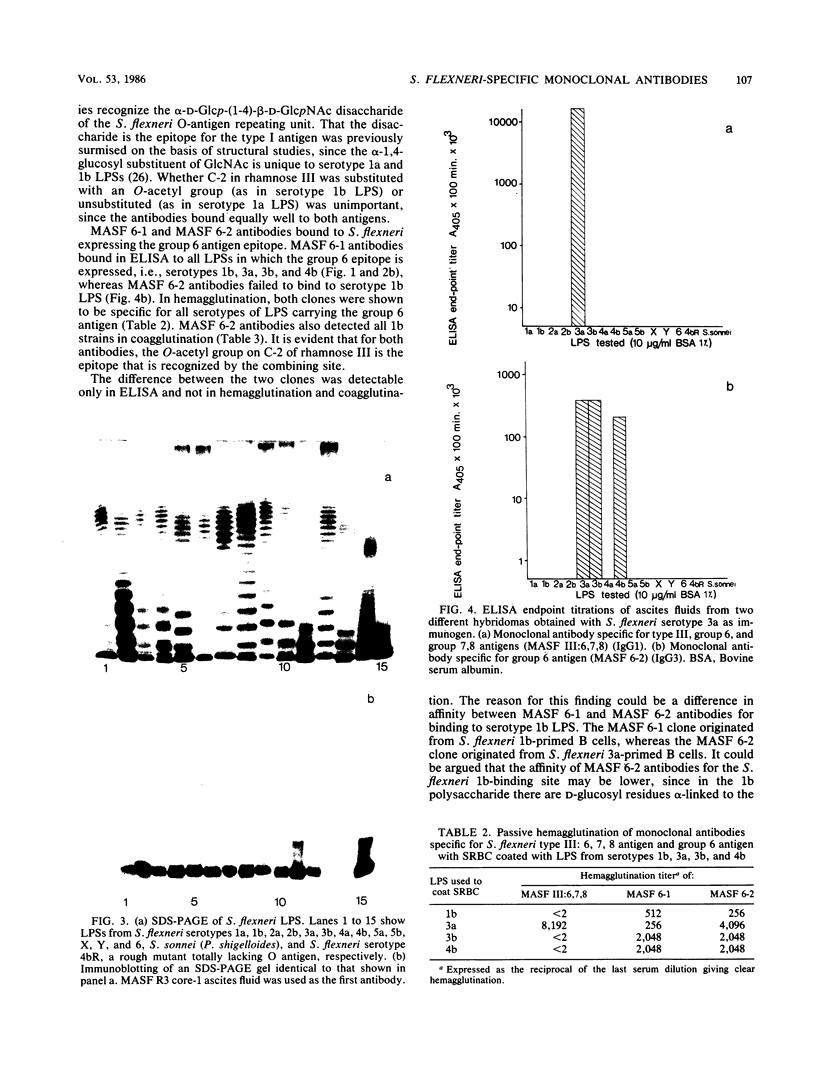
- Carlin N. I., Wehler T., Lindberg A. A. Shigella flexneri O-antigen epitopes: chemical and immunochemical analyses reveal that epitopes of type III and group 6 antigens are identical. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.110-115.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Hammarström S. Titration of antibodies to salmonella O antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.703-708.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. H., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Production of monoclonal antibodies in serum free medium. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A. L., Cherwinski H. M. Detection of antigens on nitrocellulose paper immunoblots with monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitriev B. A., Knirel Y. A., Sheremet O. K., Shashkov A. A., Kochetkov N. K., Hofman I. L. Somatic antigens of Shigella. The structure of the specific polysaccharide of Shigella newcastle (Sh. flexneri type 6) lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella R mutants. 3. The linkage of the heptose units. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):126–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall E., Haeggmann S., Kalin M., Svenungsson B., Lindberg A. A. Antibody response to Shigella sonnei infection determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;2(3):200–205. doi: 10.1007/BF02029516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamian A., Romanowska E. The core structure of Shigella sonnei lipopolysaccharide and the linkage between O-specific polysaccharide and the core region. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):105–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Koeltzow D. E., Formal S. B. Phage conversion of Shigella flexneri group antigens. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.685-691.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson P. E., Lindberg A. A., Lindberg B., Wollin R. Structural studies on the hexose region of the core in lipopolysaccharides from Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. H., Johnston R. J., Simmons D. A. The immunochemistry of Shigella flexneri O-antigens. The biochemical basis of smooth to rough mutation. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):79–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1050079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen E., Romanowska E., Przondo-Hessek A. Serological analysis of core oligosaccharides of Shigella flexneri serotype 6 and its R mutants lipopolysaccharides. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1981;29(5):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K. Basic structure of the oligosaccharide repeating-unit of the Shigella flexneri O-antigens. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Jul;56(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K., Katzenellenbogen E., Romanowska E. Structural studies of Shigella flexneri O-antigens. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Petersson K., Katzenellenbogen E., Romanowska E. Structural studies of the Shigella flexneri variant X, type 5 a and type 5 b O-antigens. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Wollin R., Gemski P., Wohlhieter J. A. Interaction between bacteriophage Sf6 and Shigella flexner. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.38-44.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauss K., Kontrohr T., Vertényi A., Szendrei L. Serological and chemical studies of Sh. sonnei, Pseudomonas shigelloides and C27 strains. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1970;17(2):157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A. Immunochemistry of Shigella flexneri O-antigens: a study of structural and genetic aspects of the biosynthesis of cell-surface antigens. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):117–148. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.117-148.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Draper C., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chagas' disease. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):426–428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]