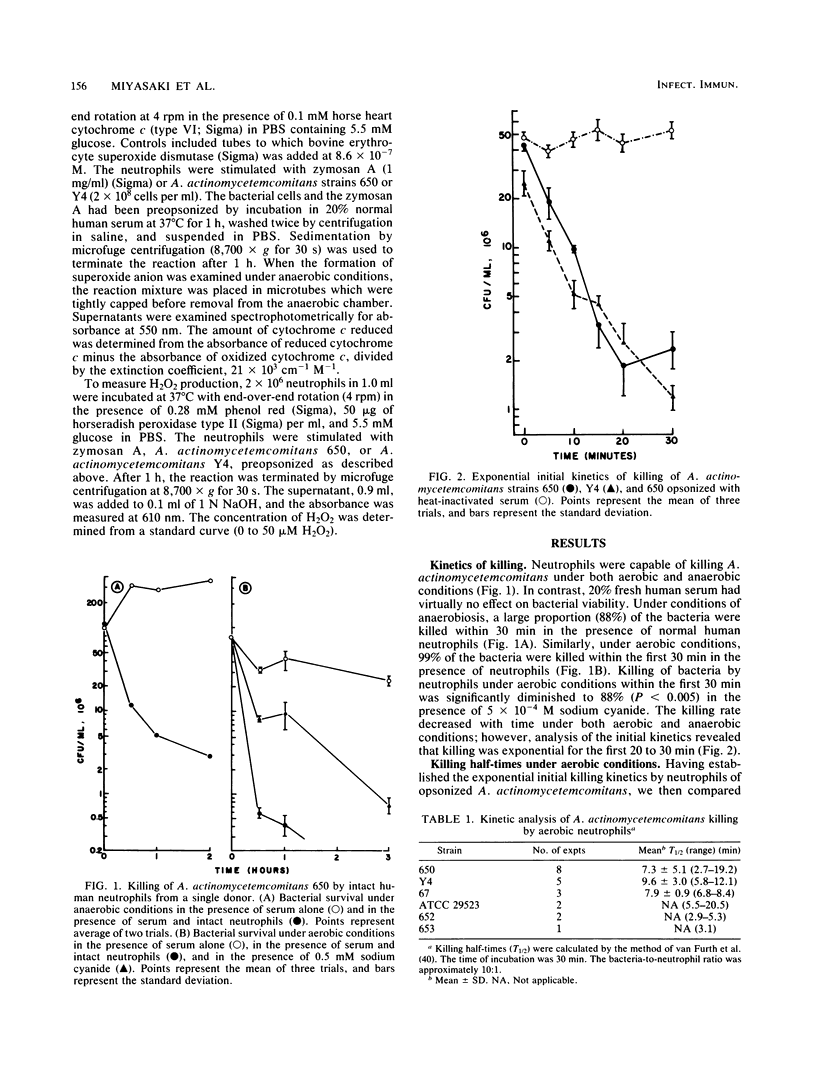
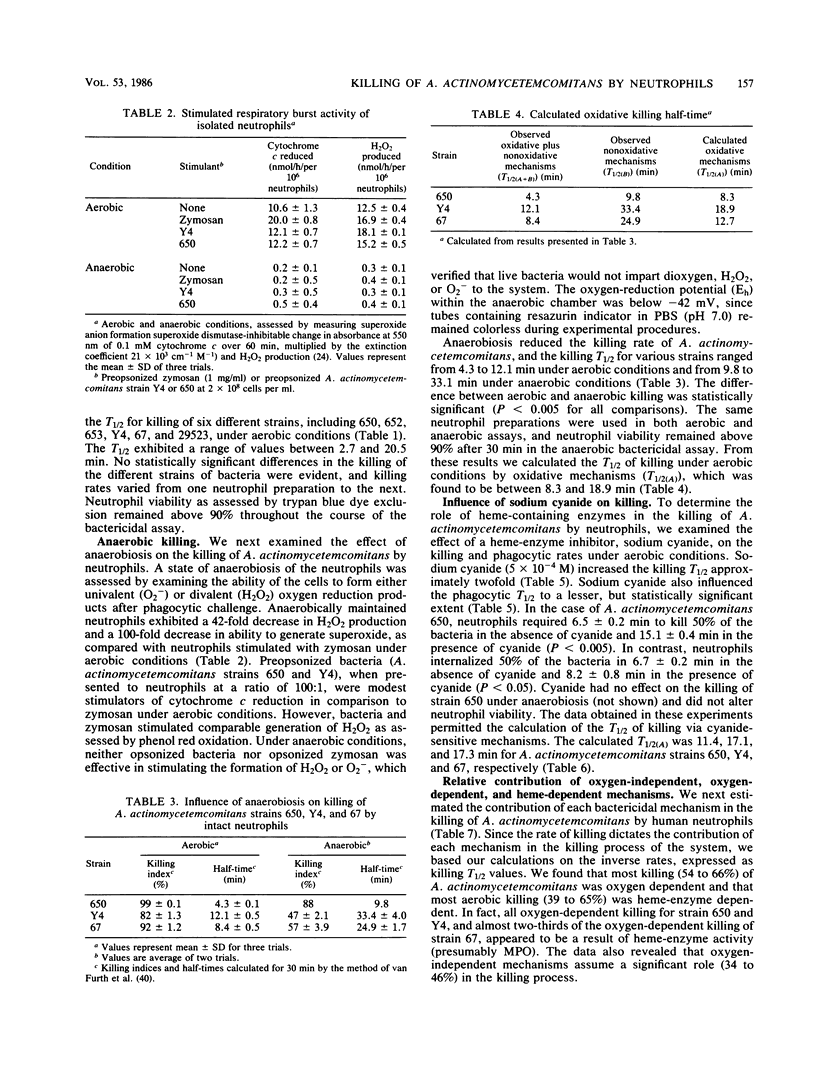
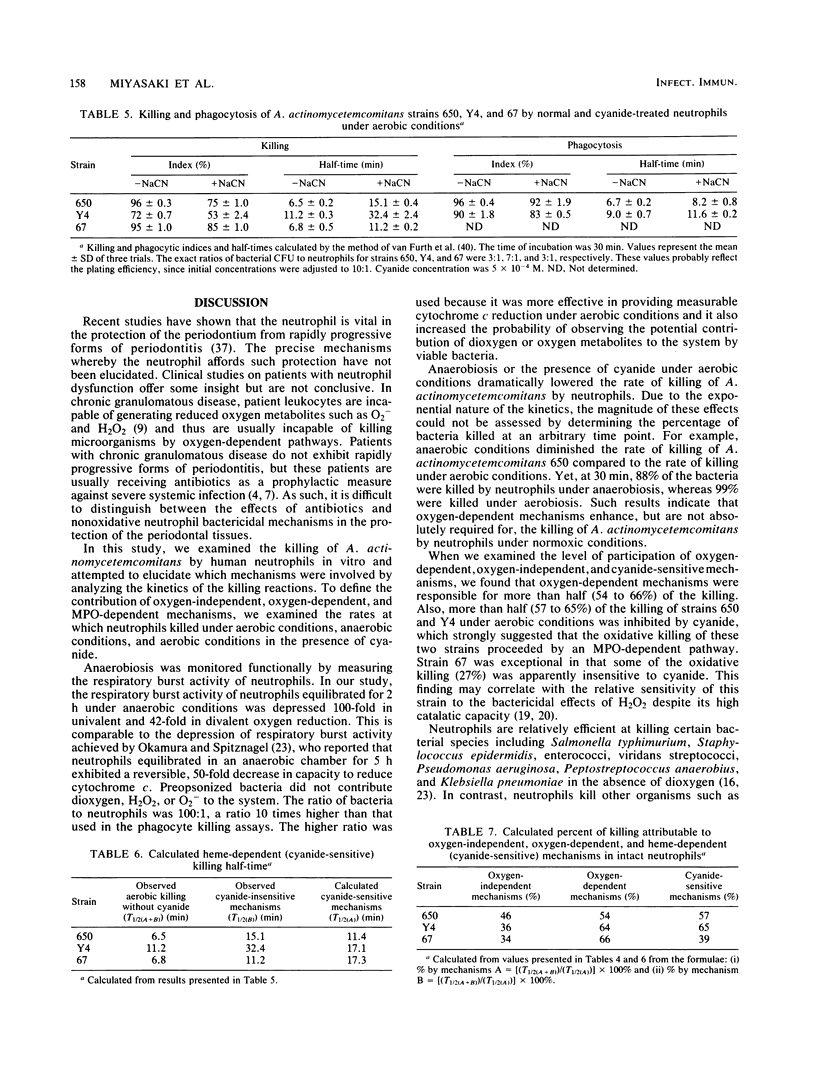
Abstract
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans is a facultative gram-negative microorganism which has been implicated as an etiologic agent in localized juvenile periodontitis and in subacute bacterial endocarditis and abscesses. Although resistant to serum bactericidal action and to oxidant injury mediated by superoxide anion (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), this organism is sensitive to killing by the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride system (K.T. Miyasaki, M.E. Wilson, and R.J. Genco, Infect. Immun. 53:161-165, 1986). In this study, we examined the sensitivity of A. actinomycetemcomitans to killing by intact neutrophils under aerobic conditions, under anaerobic conditions, and under aerobic conditions in the presence of the heme-protein inhibitor sodium cyanide. Intact neutrophils killed opsonized A. actinomycetemcomitans under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, and the kinetics of these reactions indicated that both oxidative and nonoxidative mechanisms were operative. Oxidative mechanisms contributed significantly, and most of the killing attributable to oxidative mechanisms was inhibited by sodium cyanide, which suggested that the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride system participated in the oxidative process. We conclude that human neutrophils are capable of killing A. actinomycetemcomitans by both oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent pathways, and that most oxygen-dependent killing requires myeloperoxidase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold R. R., Cole M. F., McGhee J. R. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.327545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehni P. C., Tsai C. C., McArthur W. P., Hammond B. F., Shenker B. J., Taichman N. S. Leukotoxic activity in different strains of the bacterium Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans isolated from juvenile periodontitis in man. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(8):671–676. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cainciola L. J., Genco R. J., Patters M. R., McKenna J., van Oss C. J. Defective polymorphonuclear leukocyte function in a human periodontal disease. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):445–447. doi: 10.1038/265445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon J. A., Mergenhagen S. E., Gallin J. I. Gingivitis and oral ulceration in patients with neutrophil dysfunction. J Oral Pathol. 1985 Feb;14(2):150–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1985.tb00478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Page R. C., Wilde G. Defective neutrophil chemotaxis in juvenile periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):694–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.694-700.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Leong P. A., Simpson D. M. Phagocytic cells in periodontal defense. Periodontal status of patients with chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Periodontol. 1985 Oct;56(10):611–617. doi: 10.1902/jop.1985.56.10.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Babior B. M. The killing of pathogens by phagocytes. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:313–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.001525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley P., Holt S. C. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 and N27. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):862–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.862-873.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase: contribution to the microbicidal activity of intact leukocytes. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine W. S., Maderazo E. G., Stolman J., Ward P. A., Cogen R. B., Greenblatt I., Robertson P. B. Impaired neutrophil chemotaxis in patients with juvenile and rapidly progressing periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):10–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Gusberti F., Mettraux G., Higgins T., Syed S. Relationship between oxygen tension and subgingival bacterial flora in untreated human periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.659-667.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Bactericidal activity of aerobic and anaerobic polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.337-341.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur W. P., Tsai C. C., Baehni P. C., Genco R. J., Taichman N. S. Leukotoxic effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Modulation by serum components. J Periodontal Res. 1981 Mar;16(2):159–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Wilson M. E., Genco R. J. Killing of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by the human neutrophil myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride system. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.161-165.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Wilson M. E., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Resistance of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and differential susceptibility of oral Haemophilus species to the bactericidal effects of hydrogen peroxide. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):644–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.644-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaki K. T., Wilson M. E., Zambon J. J., Genco R. J. Influence of endogenous catalase activity on the sensitivity of the oral bacterium Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and the oral haemophili to the bactericidal properties of hydrogen peroxide. Arch Oral Biol. 1985;30(11-12):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(85)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Microbicidal mechanisms of human granulocytes: synergistic effects of granulocyte elastase and myeloperoxidase or chymotrypsin-like cationic protein. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1276–1283. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1276-1283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Spitznagel J. K. Outer membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 have lipopolysaccharide-dependent resistance to the bactericidal activity of anaerobic human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1086–1095. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1086-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. B., Lantz M., Marucha P. T., Kornman K. S., Trummel C. L., Holt S. C. Collagenolytic activity associated with Bacteroides species and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1982 May;17(3):275–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J. A. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. Relationship to superoxide anion formation and cellular catabolism of H2O2: studies with normal and cytochalasin B-treated cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1266–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI108886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie F. R., Carranza F. A., Jr, Newman M. G., Cheng L., Lewin K. J. Identification of tissue-invading bacteria in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Sep;17(5):452–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Paul B. B., Strauss R. R., Jacobs A. A., Sbarra A. J. Oxidative peptide cleavage and decarboxylation by the MPO-H2O2-Cl- antimicrobial system. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):255–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.255-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Zgliczynski J. M., Paul B. B., Sbarra A. J. Enhanced killing of myeloperoxidase-coated bacteria in the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-Cl- system. J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):481–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker B. J., McArthur W. P., Tsai C. C. Immune suppression induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. I. Effects on human peripheral blood lymphocyte responses to mitogens and antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: a cross-sectional microbiological investigation. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1013-1020.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Rosling B. G. Suppression of the periodontopathic microflora in localized juvenile periodontitis by systemic tetracycline. J Clin Periodontol. 1983 Sep;10(5):465–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1983.tb02179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable organisms in juvenile periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;84(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelmaszyńska T., Zgliczynski J. M. N-(2-Oxoacyl)amino acids and nitriles as final products of dipeptide chlorination mediated by the myeloperoxidase/H2O2/Cl- system. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G., Johansson E. Bactericidal effect of pooled human serum on Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Scand J Dent Res. 1982 Feb;90(1):29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1982.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thore M., Löfgren S., Tärnvik A., Monsen T., Selstam E., Burman L. G. Anaerobic phagocytosis, killing, and degradation of Streptococcus pneumoniae by human peripheral blood leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):277–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.277-281.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Shenker B. J., DiRienzo J. M., Malamud D., Taichman N. S. Extraction and isolation of a leukotoxin from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans with polymyxin B. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):700–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.700-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Wever R., Roos D. Quantitative aspects of the production of superoxide radicals by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Lampert M. B., Test S. T. Long-lived oxidants generated by human neutrophils: characterization and bioactivity. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6635660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1985 Jan;12(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1985.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., DeLuca C., Slots J., Genco R. J. Studies of leukotoxin from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans using the promyelocytic HL-60 cell line. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):205–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.205-212.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Slots J., Genco R. J. Serology of oral Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and serotype distribution in human periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.19-27.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


