Abstract
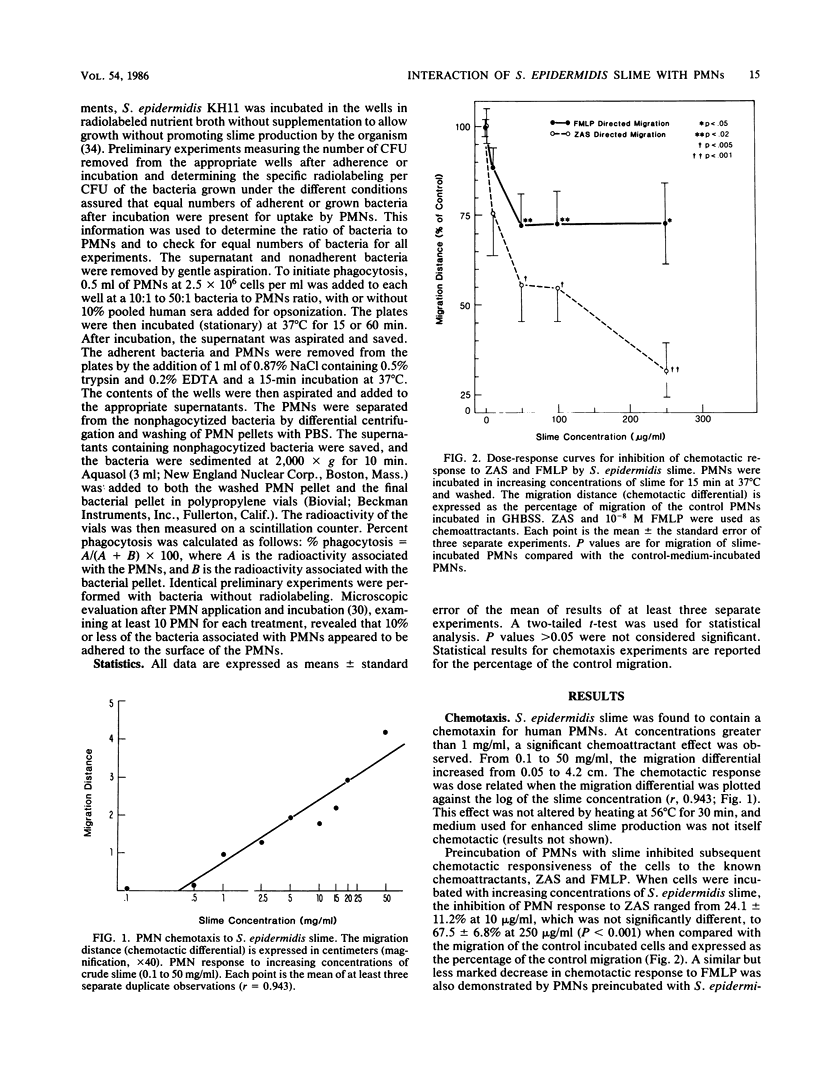
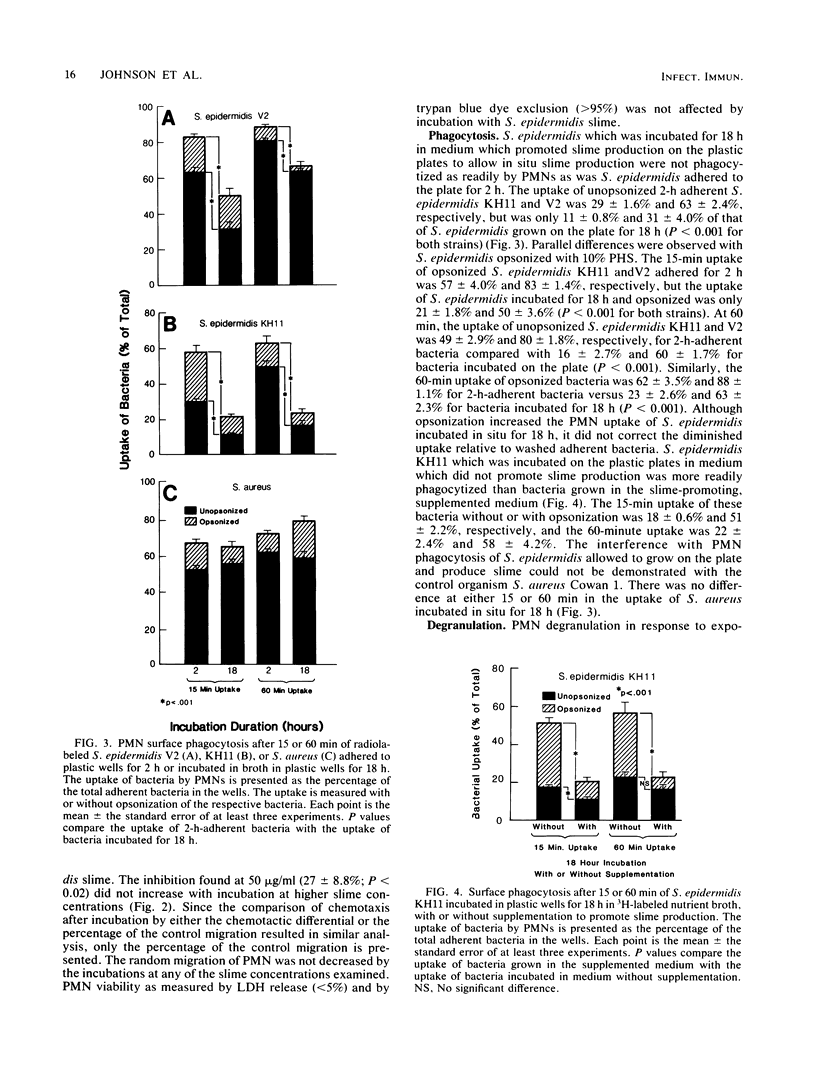
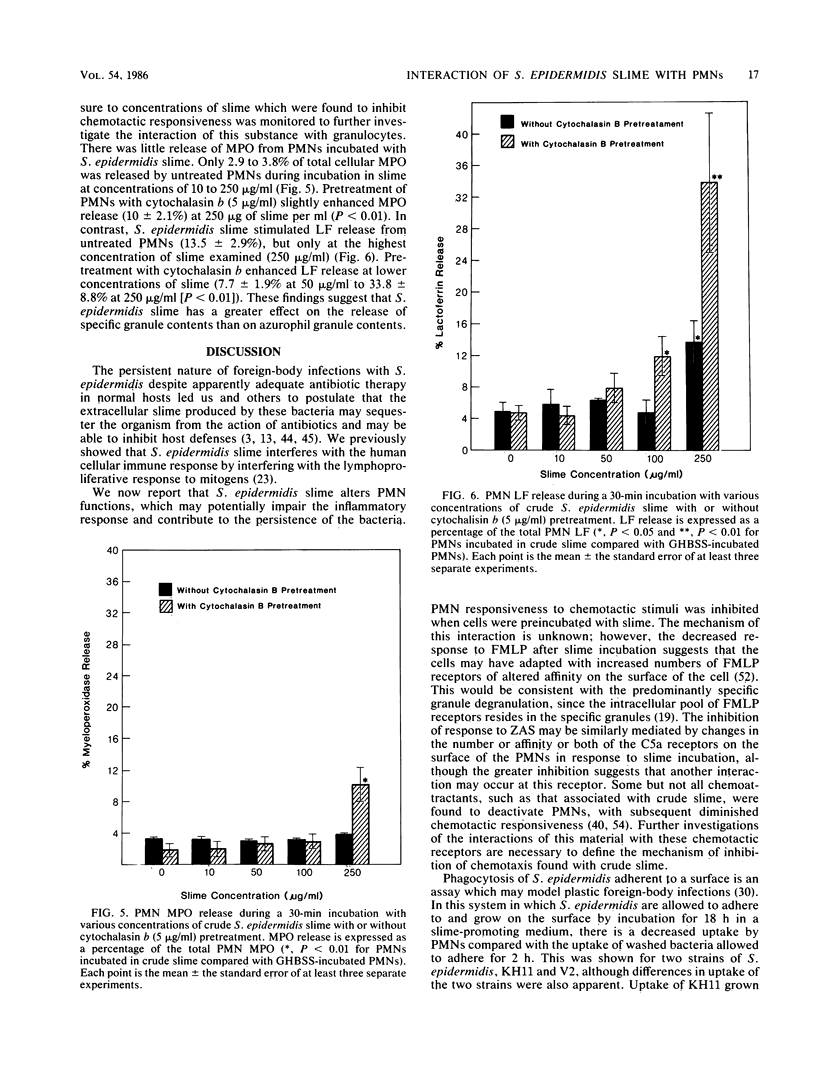
The interaction of Staphylococcus epidermidis slime with human neutrophils (PMN) was examined by using isolated slime and allowing bacteria to elaborate slime and other extracellular products in situ. S. epidermidis slime was found to contain a chemoattractant. Incubation of PMN with 50 micrograms or more of slime per ml inhibited subsequent chemotaxis of the PMN to n-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine by 27% and to zymosan-activated serum by 44 to 67% with increasing slime concentrations. S. epidermidis slime stimulated little degranulation of untreated PMN. After pretreatment of PMN with 5 micrograms of cytochalasin b per ml, slime predominantly induced release of specific granule contents (33.8% lactoferrin release by 250 micrograms of slime per ml versus 10% myeloperoxidase release by 250 micrograms of slime per ml). By a surface phagocytosis assay, PMN uptake of radiolabeled S. epidermidis which were incubated for 18 h on a plastic surface for slime expression was less than that for S. epidermidis adhered to the plastic for 2 h or grown in unsupplemented nutrient broth. These results suggest that S. epidermidis slime interaction with PMN may be potentially detrimental to host defense and may contribute to the ability of this organism to persist on surfaces of foreign bodies in the vascular or central nervous system.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart S., Hall S. E., Campos J. M., Polin R. A. Sepsis with coagulase-negative staphylococci in critically ill newborns. Am J Dis Child. 1983 May;137(5):461–463. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140310043012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayston R., Penny S. R. Excessive production of mucoid substance in staphylococcus SIIA: a possible factor in colonisation of Holter shunts. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1972;27:25–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb09769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. W., Hughes W. T. Fatal Staphylococcus epidermidis sepsis following bone marrow transplantation. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1980 Jan;146(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman M. J., Guerrant R. L., Murad F., Richardson S. H., Weaver D., Mandell G. L. Interaction of polymorphonuclear neutrophils with Escherichia coli. Effect of enterotoxin on phagocytosis, killing, chemotaxis, and cyclic AMP. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):227–234. doi: 10.1172/JCI108931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Björkstén B., Quie P. G. Capsular K1 polysaccharide of Escherichia coli: relationship to virulence in newborn rats and resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):293–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.293-298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Coates T. D., Haak R. A., Wolach J. B., Hoffstein S., Baehner R. L. Lactoferrin deficiency associated with altered granulocyte function. N Engl J Med. 1982 Aug 12;307(7):404–410. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208123070704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLAGHAN R. P., COHEN S. J., STEWART G. T. Septicaemia due to colonization of Spitz-Holter valves by staphylococci. Five cases treated with methicillin. Br Med J. 1961 Mar 25;1(5229):860–863. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5229.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Rowe J. G., Hugli T. E. A modified method for chemotaxis under agarose. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(4):337–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo M. H., Holmes D. R., Jr, Gersh B. J., Maloney J. D., Merideth J., Pluth J. R., Trusty J. Permanent pacemaker infections: characterization and management. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Sep;48(3):559–564. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Experimental foreign body infections in mice challenged with slime-producing Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):407–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.407-410.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E., Karchmer A. W., Buckley M. J., Austen W. G., Swartz M. N. Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Analysis of 38 cases. Circulation. 1973 Aug;48(2):365–377. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld R., Leers W. D., Curtis J. E., Bergsagel D. E. Intravenous catheter infection study: a prospective trial in patients with neoplastic disease. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1975;1(2):175–181. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950010213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Separation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the one-step Hypaque-Ficoll method is dependent on blood column height. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer A., Senders R. C., Visser M. R., Bijlmer R. P., Gerards L. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Verhoef J. Septicemia due to coagulase-negative staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit: clinical and bacteriological features and contaminated parenteral fluids as a source of sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;2(6):426–431. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198311000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Seligmann B. E., Gallin J. I. Correlation of human neutrophil secretion, chemoattractant receptor mobilization, and enhanced functional capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):941–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Rose H. D., Sohnle P. G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal R. Peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jun;9(6):417–420. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. D., Peters G., Verstegen M., Regelmann W. E. Effect of extracellular slime substance from Staphylococcus epidermidis on the human cellular immune response. Lancet. 1984 Feb 18;1(8373):365–367. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruer L. D., Bartlett R., Ayliffe G. A. Species identification and antibiotic sensitivity of coagulase-negative staphylococci from CAPD peritonitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jun;13(6):577–583. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.6.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks P. A., van der Tol M. E., Thyssen R. M., van Asbeck B. S., Verhoef J. Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides diminish and enhance cell function of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.294-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Zanolari B., Schwartzman N. A., Hong S. R. Intracellular control of human neutrophil secretion. I. C5a-induced stimulus-specific desensitization and the effects of cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetherington S. V., Spitznagel J. K., Quie P. G. An enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for measurement of lactoferrin. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupiter J. B., Karchmer A. W., Lowell J. D., Harris W. H. Total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of adult hips with current or quiescent sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Feb;63(2):194–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Archer G. L., Dismukes W. E. Staphylococcus epidermidis causing prosthetic valve endocarditis: microbiologic and clinical observations as guides to therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):447–455. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Hoidal J. R., Clawson C. C., Quie P. G., Peterson P. K. Phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherent to plastic, agar, or glass. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Sep 30;63(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire G. G., Morin J. E., Dobell A. R. Pacemaker infections: a 12-year review. Can J Surg. 1975 Mar;18(2):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locci R., Peters G., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. III. Adhesion of staphylococci to lumina of intravenous catheters perfused with bacterial suspensions. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowder J. N., Lazarus H. M., Herzig R. H. Bacteremias and fungemias in oncologic patients with central venous catheters: changing spectrum of infection. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Aug;142(8):1456–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwicka A., Uhlenbruck G., Peters G., Seng P. N., Gray E. D., Jeljaszewicz J., Pulverer G. Investigation on extracellular slime substance produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Dec;258(2-3):256–267. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(84)80043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Morphology of bacterial attachment to cardiac pacemaker leads and power packs. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):911–914. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.911-914.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of in situ bacterial colonization of intravenous and intraarterial catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):687–693. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.687-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Johnson W. D., Jr Prosthetic valve endocarditis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 Jul;80(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson D. P., Thompson T. R., Johnson D. E., Rhame F. S., VanDrunen N., Ferrieri P. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal septicemia: experience in a newborn intensive care unit. J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;101(4):602–605. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80718-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Verbrugh H. A., Verhoef J. Suppression of phagocytosis and chemotaxis by cell wall components of Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):84–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., McCormack R. T., Fiegel V. D., Simmons R. L. Chemotactic deactivation of human neutrophils: evidence for nonspecific and specific components. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):441–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.441-444.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson F. P., Brown C. S. The McKee-Farrar total hip replacement. Preliminary results and complications of 368 operations performed in five general hospitals. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972 Mar;54(2):257–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Saborowski F., Locci R., Pulverer G. Investigations on staphylococcal infection of transvenous endocardial pacemaker electrodes. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J., Rogers W. A., Taylor H. M., Everett E. D., Prowant B. F., Fruto L. V., Nolph K. D. Peritonitis during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):7–13. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., BLACK P. H., MARK V. H., SWARTZ M. N. Indolent Staphylococcus albus or aureus bacteremia after ventriculoatriostomy. Role of foreign body in its initiation and perpetuation. N Engl J Med. 1961 Feb 9;264:264–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196102092640602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Foderaro J. B., Aber R. C. Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia associated with vascular catheters: an important cause of febrile morbidity in hospitalized patients. Infect Control. 1984 Jun;5(6):279–283. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700060331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeling D. J., Gemmell C. G., Craddock P. R., Quie P. G., Peterson P. K. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on neutrophil migration and adhesiveness. Inflammation. 1981 Dec;5(4):313–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00911095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Gardner P., Shillito J. Infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):543–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Adaptation of human neutrophil responsiveness to the chemoattractant N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine. Heterogeneity and/or negative cooperative interaction of receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6280–6286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff D. B., Foltz E. L., Weeks R. D., Loeser J. Therapy of staphylococcus epidermidis: infections associated with cerebrospinal fluid shunts. Pediatrics. 1974 Jan;53(1):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Patrick R. A., Hassett C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Effects of chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):221–229. doi: 10.1172/JCI109293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speller D. C., Mitchell R. G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci causing endocarditis after cardiac surgery. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jul;26(7):517–522. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.7.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner W. H., Pickard D. J. Immunological relationship between delta-hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative strains of staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):910–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.910-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Bartholomew E., Genco R. J., Slots J., Levine M. J. Inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis by soluble bacterial products. J Periodontol. 1982 Aug;53(8):502–508. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.8.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Garcia M. L. Enhancement of neutrophils function as a result of prior exposure to chemotactic factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):167–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI109841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I. Microbiologic aspects of chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 1983 Jan;23(1):83–92. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Musher D. M., Spika J. S., Verbrugh H. A., Jaspers F. C. The effect of staphylococcal peptidoglycan on polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1983;41:79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Wiernik P. H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):503–508. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Nelson R. D., Cleary P. P. Human neutrophil chemotactic response to group A streptococci: bacteria-mediated interference with complement-derived chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.239-246.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Jr, Salvati E. A., Aglietti P., Kutner L. J. The problem of infection in endoprosthetic surgery of the hip joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973 Oct;(96):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Dudnick D. V., Chapin M., Ho W. G., Gale R. P., Martin W. J. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jan;143(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Waldvogel F. A. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection. Evidence for a local granulocyte defect. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1191–1200. doi: 10.1172/JCI111305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


