Abstract
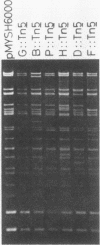
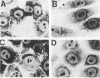
Using Shigella flexneri 2a YSH6000, we isolated 304 independent Tn5 insertion mutants in the 230-kilobase invasion plasmid, pMYSH6000. The site of each Tn5 insertion was assigned to 23 SalI fragments on the previously made SalI cleavage map of pMYSH6000. Among the 304 insertions, 150 were negative in expression of four phenotypes examined (mouse Sereny test [Ser], invasion into epithelial cells [Inv], Congo red binding [Pcr], and inhibition of bacterial growth [Igr] ): 12 were Ser- Inv+ Pcr+ Igr+, and 142 were positive in all four phenotypes. Tn5 insertions in the avirulent mutants were distributed in two separate SalI fragments, F and G, and in four contiguous SalI fragments, B, P, H, and D. Fragment G contains a novel class of determinant(s) which is required only for Ser+ but not for Inv+, Pcr+, and Igr+. Fragment F contains the previously characterized virF locus. B, P, H, and D each contained both virulent and avirulent Tn5 insertions. This indicates that more than two gene clusters exist within this region. Both are required for expression of all four virulence phenotypes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Cloning the gene for Congo red binding in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):165–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.165-168.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama S. Y., Sakai T., Makino S., Kurata T., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M. The use of mice in the Sereny test as a virulence assay of shigellae and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):696–698. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.696-698.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Wingfield M. E., Formal S. B. Plaque formation by virulent Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.124-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Berg D. E. IS50-mediated inverse transposition. Discrimination between the two ends of an IS element. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakamura A. Large plasmids associated with virulence in Shigella species have a common function necessary for epithelial cell penetration. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):260–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.260-262.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]