Abstract
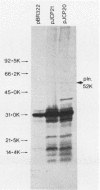
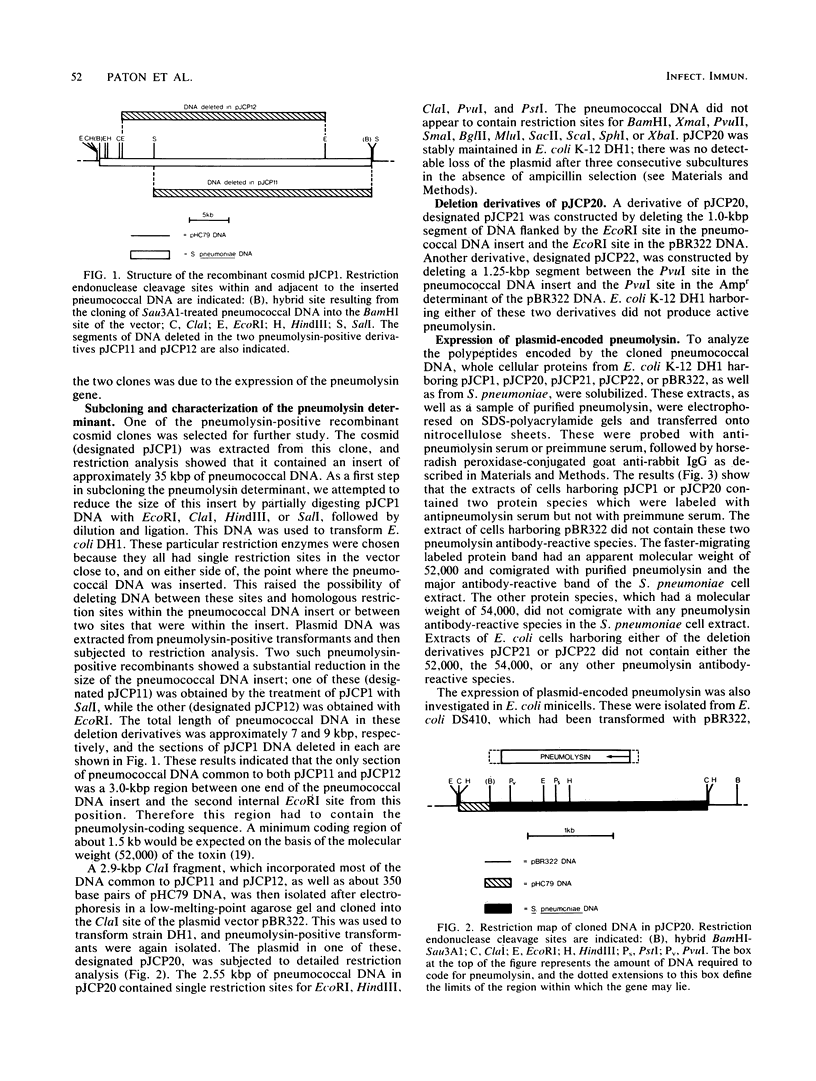
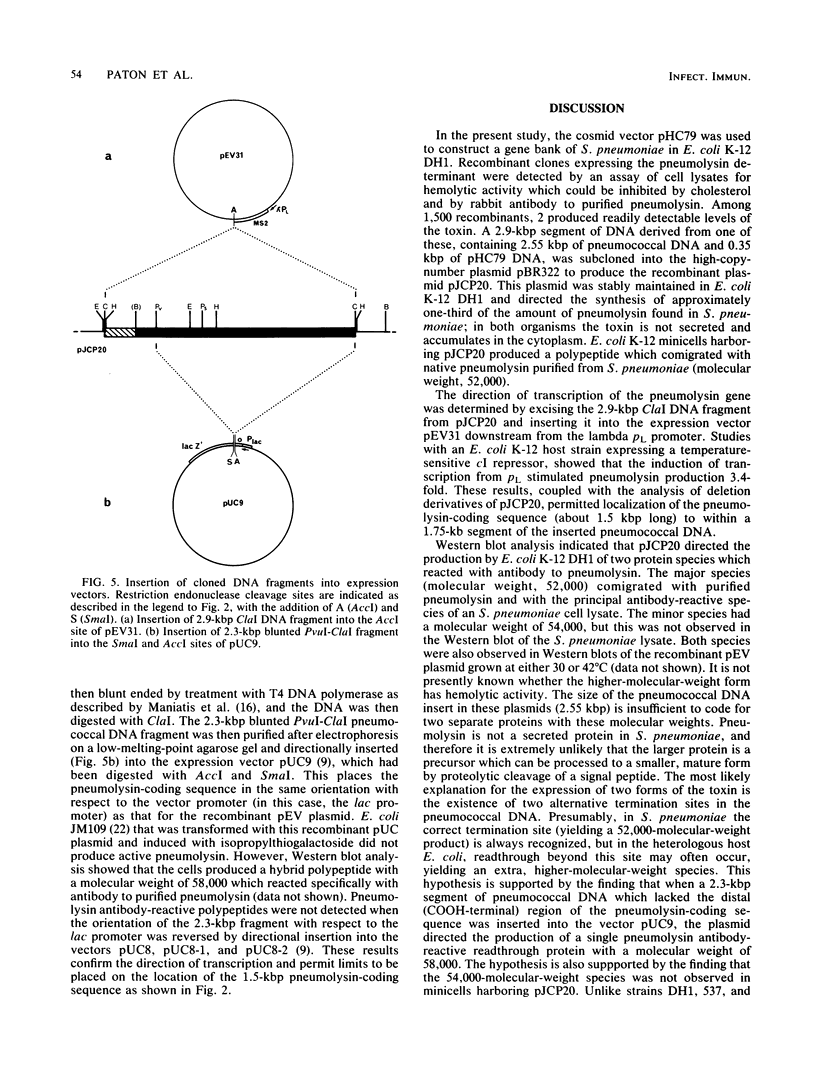
A gene bank of Sau3A1-generated Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments was constructed in Escherichia coli K-12 by cloning into the BamHI site of the cosmid vector pHC79. Clones expressing the pneumolysin determinant were selected by testing for hemolytic activity which could be inhibited by antibody to purified pneumolysin and by cholesterol. Restriction analysis of pneumolysin-positive recombinant cosmid DNA indicated that the coding sequence for the toxin was located within a 2.9-kilobase-pair (kbp) ClaI DNA fragment. This fragment, which included 0.35 kbp of vector pHC79 DNA, was subcloned into the plasmid pBR322. E. coli cells harboring this recombinant plasmid (designated pJCP20) produced approximately one-third of the amount of pneumolysin found in the donor S. pneumoniae strain. Plasmid pJCP20 was stably maintained in E. coli and resulted in the accumulation of active pneumolysin in the cytoplasm. Western blot analysis showed that E. coli harboring pJCP20 produced two forms of the toxin with molecular weights of 54,000 and 52,000. The lower-molecular-weight form was indistinguishable from native pneumolysin. Subcloning the 2.9-kbp DNA fragment into the expression vector pEV31 allowed the determination of the direction of transcription of the pneumolysin gene. The pneumolysin-coding sequence (approximately 1.5 kbp) has been localized to within a 1.75-kbp segment of pneumococcal DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Manning P. A., Edelbluth C., Herrlich P. Export without proteolytic processing of inner and outer membrane proteins encoded by F sex factor tra cistrons in Escherichia coli minicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. J., Wilson J. M., Oxender D. L. Defective transport and other phenotypes of a periplasmic "leaky" mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.351-358.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Rolfe B., Onodera K. Pleiotropic properties and genetic organization of the tolA,B locus of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):74–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.74-83.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., Paton J. C. Inhibition of in vitro human lymphocyte response by the pneumococcal toxin pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):585–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.585-589.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Fregeau C., Préfontaine G., Brousseau R. Construction of a family of universal expression plasmid vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Binding of cholesterol by sulfhydryl-activated cytolysins. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.97-101.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the streptolysin O determinant from Streptococcus pyogenes: characterization of the cloned streptolysin O determinant and demonstration of the absence of substantial homology with determinants of other thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.804-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy N., Beutin L., Achtman M., Skurray R., Rahmsdorf U., Herrlich P. Conjugation proteins encoded by the F sex factor. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):580–585. doi: 10.1038/270580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A., Manning P. A. Cellular localization and export of the soluble haemolysin of Vibrio cholerae El Tor. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):472–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00425733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Ferrante A. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte respiratory burst, bactericidal activity, and migration by pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1212–1216. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1212-1216.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Hansman D. J. Effect of immunization with pneumolysin on survival time of mice challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.548-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Rowan-Kelly B., Ferrante A. Activation of human complement by the pneumococcal toxin pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1085–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1085-1087.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]