Abstract
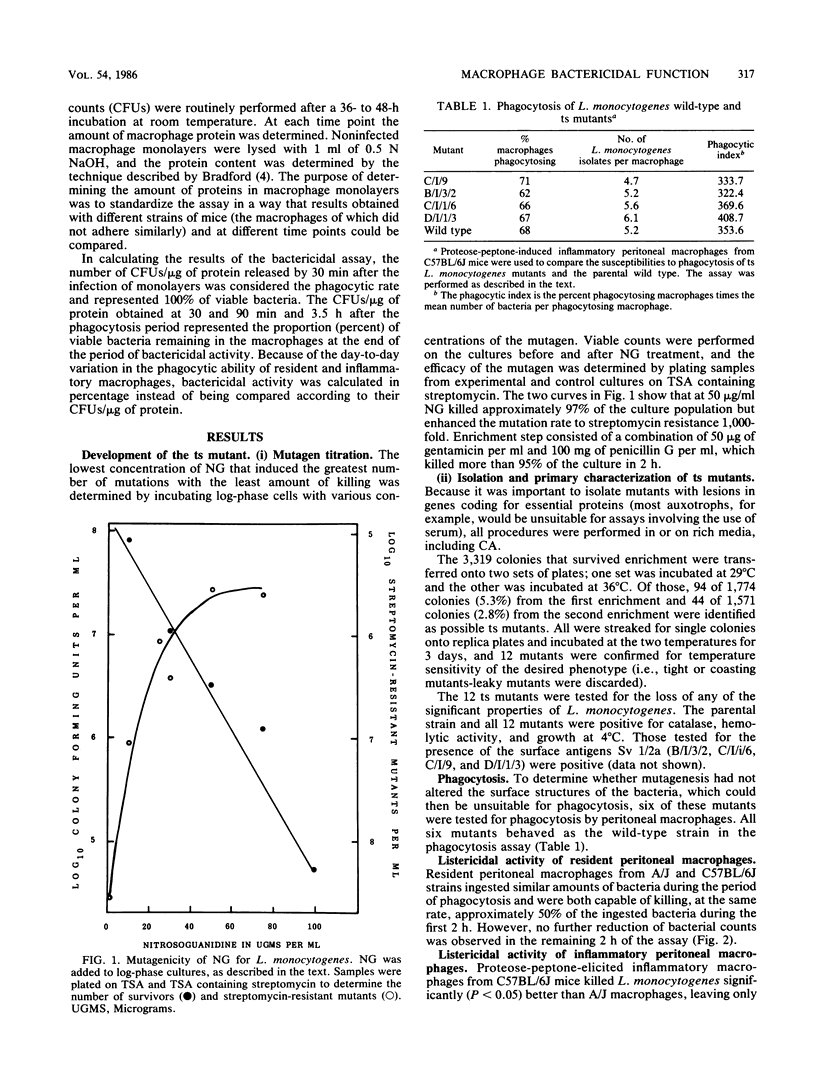
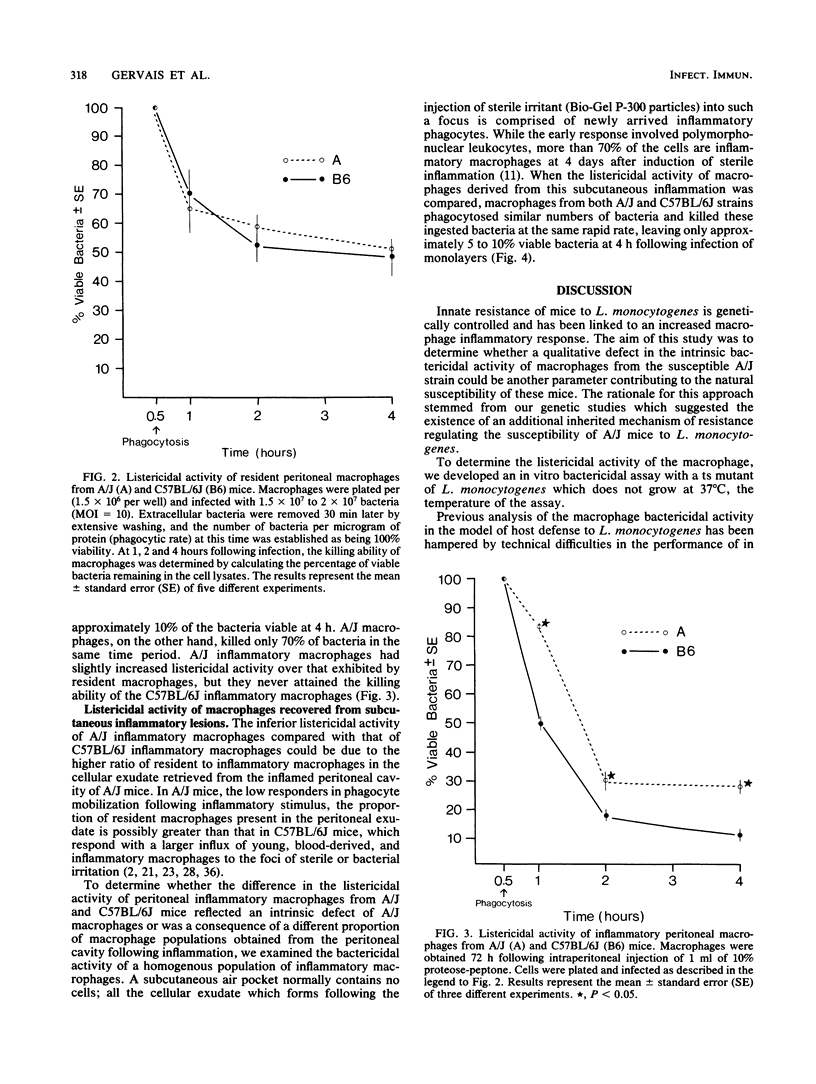
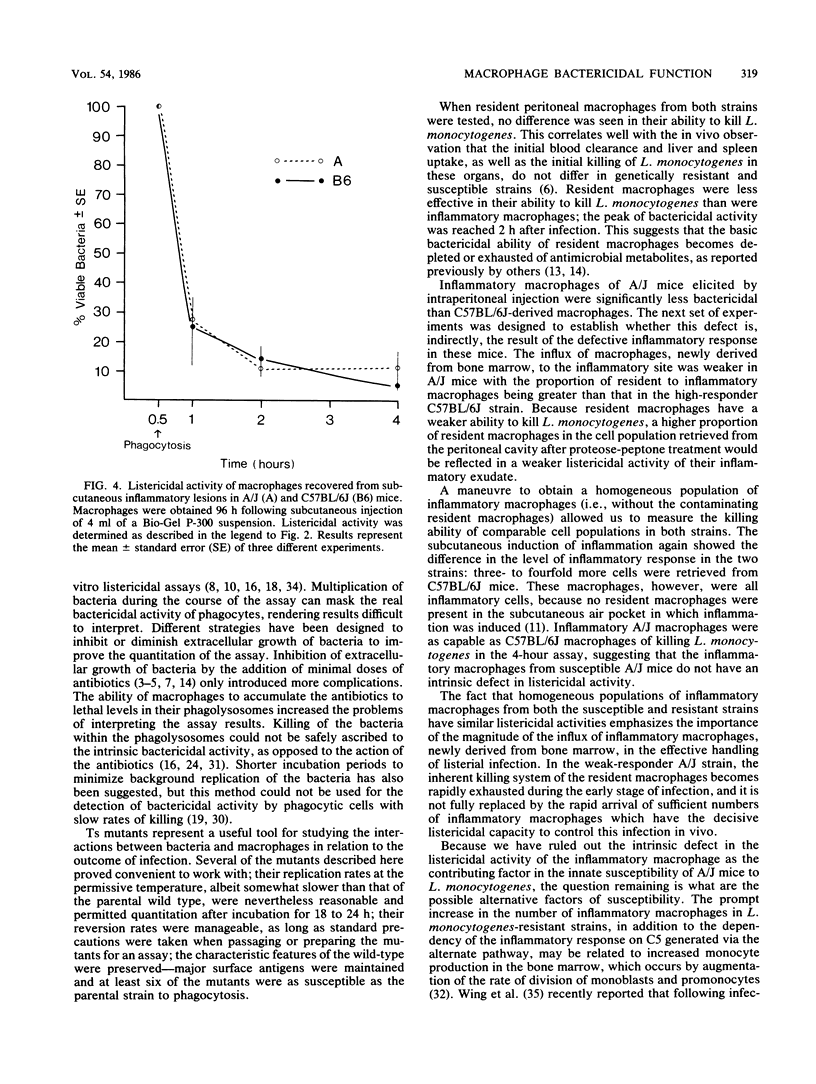
Innate resistance to infection by Listeria monocytogenes is genetically controlled and is critically dependent on prompt macrophage recruitment to the sites of infection. Experiments reported here were designed to examine whether there was an additional, qualitative difference between the intrinsic bactericidal activity of the inflammatory macrophages of genetically resistant (C57BL/6J) and susceptible (A/J) hosts. To critically evaluate the bactericidal (rather than bacteriostatic) function of the macrophage, a temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant of L. monocytogenes was developed. Mutagenesis was induced with nitrosoguanidine, and the ts mutants were isolated following enrichment with penicillin-gentamicin combinations. The ts mutants were found to carry the cell surface and biochemical characteristics of the original wild-type strain of L. monocytogenes. Inflammatory peritoneal macrophages from resistant C57BL/6J mice were found to have enhanced listericidal activity when compared with inflammatory macrophages from susceptible A/J mice. However, further analysis of the macrophage populations revealed that this seemingly qualitative advantage was due to the relatively greater proportion of inflammatory macrophages present in the inflammatory exudates of resistant C57BL/6J mice. When homogeneous populations of pure inflammatory macrophages were compared, no interstrain differences in their listericidal activity in vitro were seen. These results suggest that the susceptibility of A/J strain mice to L. monocytogenes is not due to an intrinsic deficiency of the listericidal activity of the inflammatory macrophage. The slight increase in bactericidal activity of macrophages from resistant mice that was reported by others (C. J. Czuprynski, B. P. Canono, P. M. Henson, and P. A. Campbell, Immunology 55:511-518, 1985) is caused by the difference in the relative percentage of resident cells present in the peritoneal exudates from resistant and susceptible mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker L. A., Campbell P. A., Hollister J. R. Chemotaxigenesis and complement fixation by Listeria monocytogenes cell wall fractions. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1723–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Baker E. E. Marrow-dependent cell function in early stages of infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Uptake of h-dihydrostreptomycin by macrophages in culture. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.89-95.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F., Pavlov H., Waid C., York J. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: course of listeriosis in resistant or susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P., Brostoff J. Intracellular killing of Listeria monocytogenes by activated macrophages (Mackaness system) is due to antibiotic. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):515–517. doi: 10.1038/256515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig C. P., Suter E. Extracellular factors influencing staphylocidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1966 Aug;97(2):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Canono B. P., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Genetically determined resistance to listeriosis is associated with increased accumulation of inflammatory neutrophils and macrophages which have enhanced listericidal activity. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):511–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Davis W. C., Fudenberg H. H. Granulocytopathies: pleomorphism of neutrophil dysfunction. Am J Med. 1969 Jun;46(6):901–909. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauve R. M., Jusforgues H., Hevin B. Maintenance of granuloma macrophages in serum-free medium. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 25;64(3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90442-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais F., Stevenson M., Skamene E. Genetic control of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes: regulation of leukocyte inflammatory responses by the Hc locus. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2078–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey R. W., Horton P. G., Wilder M. S. Time course of antilisterial activity by immunologically activated murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):532–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.532-539.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey R. W., Wilder M. S. Relationships between oxidative metabolism, macrophage activation, and antilisterial activity. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Oct;36(4):533–543. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Henson P. M., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in resident and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Pollara B., Good R. A. Protection of phagocytized bacteria from the killing action of antibiotics. Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2101131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke A. M., Oeschger M. P., Zeligs B. J., Bellanti J. A. Ideal target organism for quantitative bactericidal assays. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.406-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie D. B., Peters T. J., Scoging A. Benzylpenicillin transport and subcellular distribution in mouse peritoneal macrophage monolayers. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 1;31(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Hook E. W. Leukocyte function in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Studies on a seventeen year old boy. Am J Med. 1969 Sep;47(3):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Regulation of granulocyte and monocyte-macrophage proliferation by colony stimulating factor (CSF): a review. Exp Hematol. 1973;1(4):185–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Takeya K., Nomoto K., Shimotori S. Three phases of phagocyte contribution to resistance against Listeria monocytogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 May;106(1):165–171. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Saito S., Nitzan D. W. The influence of lysostaphin on phagocytosis, intracellular bactericidal activity, and chemotaxis of human polymorphonuclear cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Aug;102(2):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadarangani C., Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A. Cellular basis for genetically determined enhanced resistance of certain mouse strains to listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):381–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.381-386.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A., Sachs D. H. Resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice: genetic control by genes that are not linked to the H-2 complex. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):228–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter W., Elzenga-Claasen I., van der Voort van der Kley-van Andel A., van Furth R. Differences in the response of inbred mouse strains to the factor increasing monocytopoiesis. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):524–536. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Phillips J. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Biological activity of complement in vivo. Role of C5 in the accumulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1131–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Genetic linkage of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes with macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):402–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P., Trouet A. The uptake and intracellular accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in lysosomes of cultured rat fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 15;27(4):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder M. S., Edberg J. C. Interaction of virulent and avirulent Listeria monocytogenes with cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.409-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Barczynski L. C., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Effect of Listeria monocytogenes infection on serum levels of colony-stimulating factor and number of progenitor cells in immune and nonimmune mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):325–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.325-328.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Changes in serum colony-stimulating factor and monocytic progenitor cells during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):180–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.180-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeligs B. J., Nerurkar L. S., Bellanti J. A. Maturation of the rabbit alveolar macrophage during animal development. III. Phagocytic and bactericidal functions. Pediatr Res. 1977 Dec;11(12):1208–1211. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197712000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Waarde D., Hulsing-Hesselink E., van Furth R. Properties of a factor increasing monocytopoiesis (FIM) occurring in serum during the early phase of an inflammatory reaction. Blood. 1977 Oct;50(4):727–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


