Abstract
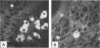
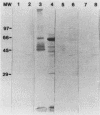
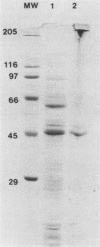
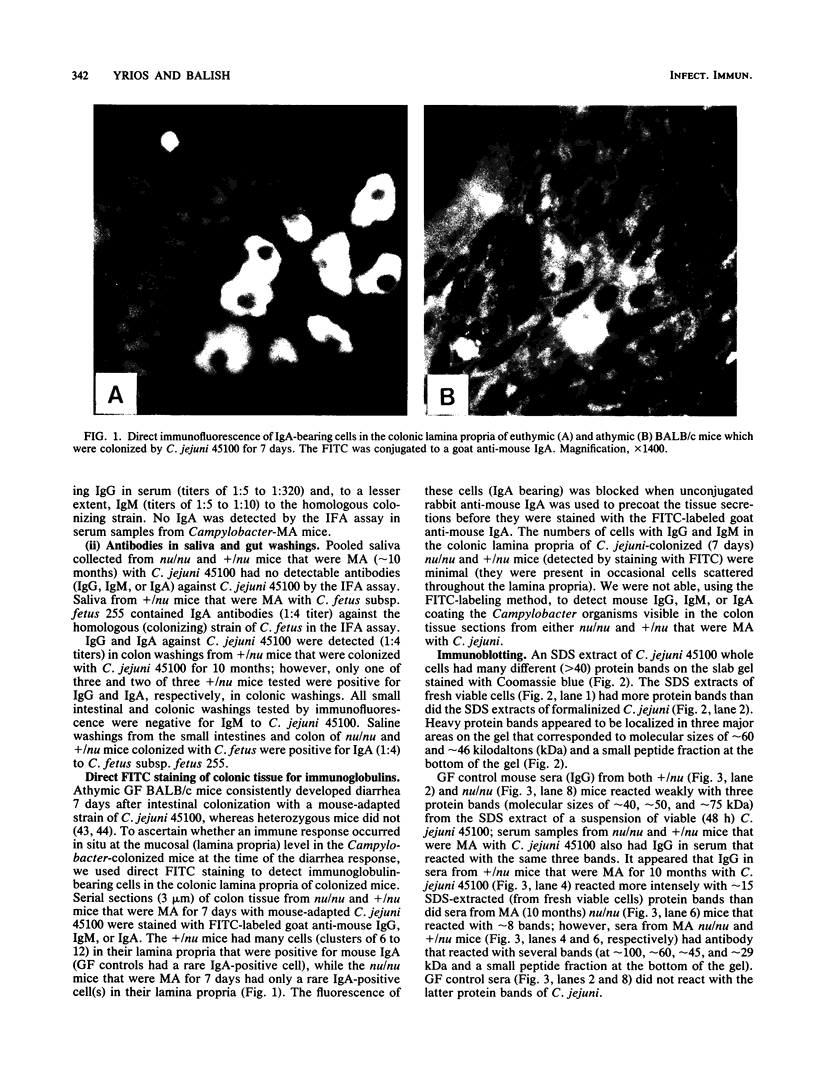
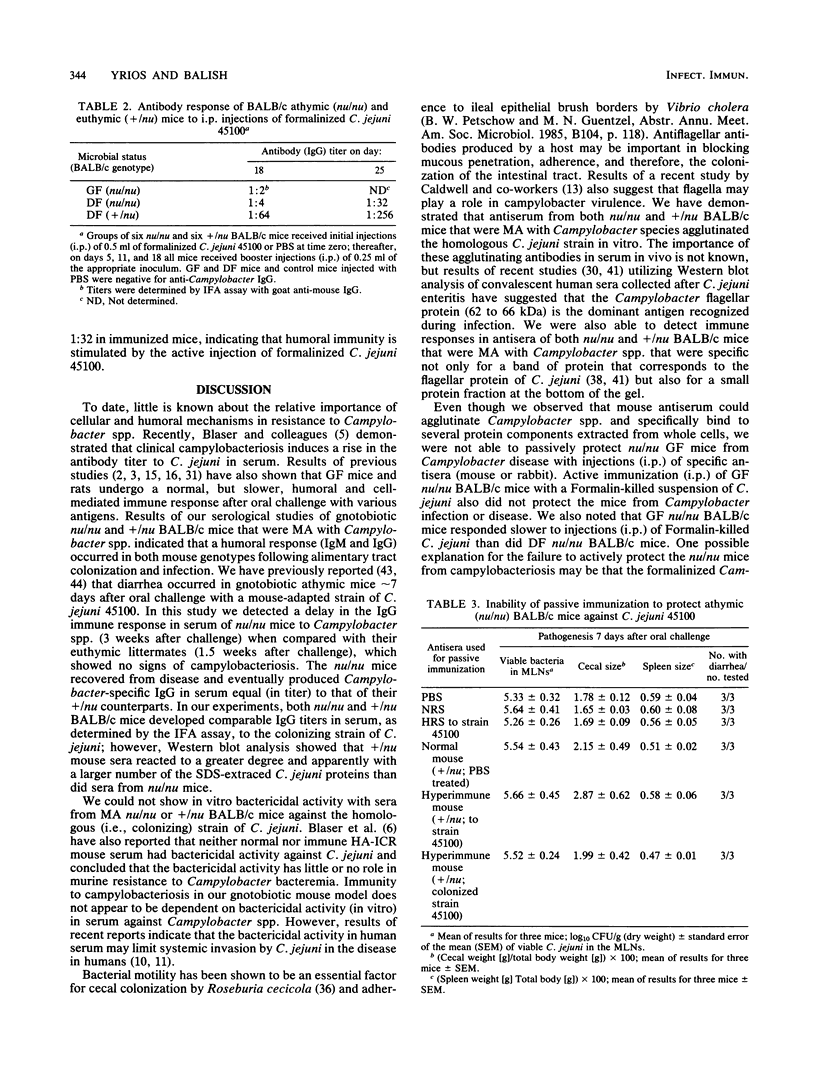
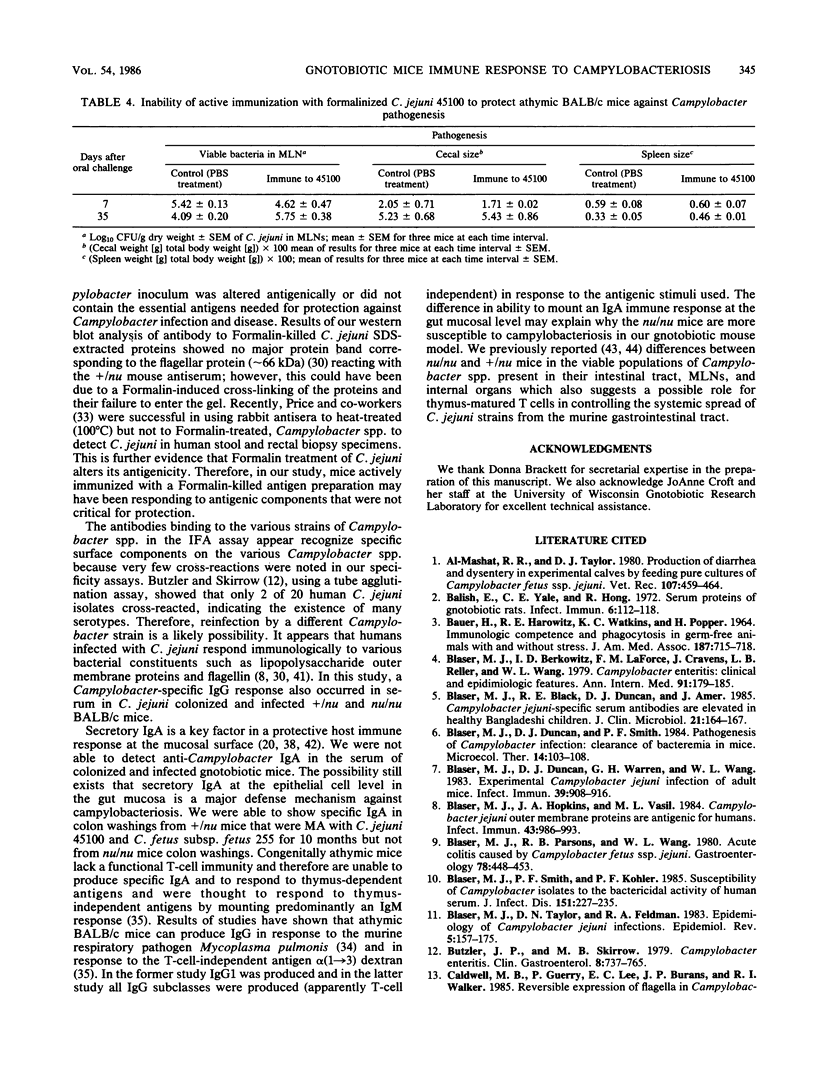
Pure cultures of several Campylobacter spp. induced a specific humoral immune response after they colonized and infected gnotobiotic mice; however, Campylobacter-immune mouse serum was not bactericidal (in vitro), manifested a weak agglutination reaction (in vitro), and showed specificity (strain 45100-immune mouse sera) for the homologous (infecting) Campylobacter strain, but was not able to passively protect germfree athymic (nu/nu) BALB/c mice against Campylobacter infection and diarrhea. Active immunization of germfree nu/nu mice with Formalin-killed C. jejuni also did not protect the gnotobiotic mice from Campylobacter infection and diarrhea. It appears from the results of our initial gnotobiotic studies that antibodies in serum against the infecting strain of C. jejuni may not play an essential role in resistance to Campylobacter disease in mice.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Mashat R. R., Taylor D. J. Production of diarrhoea and dysentery in experimental calves by feeding pure cultures of Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. Vet Rec. 1980 Nov 15;107(20):459–464. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.20.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER H., HOROWITZ R. E., WATKINS K. C., POPPER H. IMMUNOLOGIC COMPETENCE AND PHAGOCYTOSIS IN GERMFREE ANIMALS WITH AND WITHOUT STRESS. JAMA. 1964 Mar 7;187:715–718. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060230043011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balish E., Yale C. E., Hong R. Serum proteins of gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):112–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.112-118.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Black R. E., Duncan D. J., Amer J. Campylobacter jejuni-specific serum antibodies are elevated in healthy Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.164-167.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J., Warren G. H., Wang W. L. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection of adult mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):908–916. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.908-916.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Vasil M. L. Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins are antigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):986–993. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.986-993.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsons R. B., Wang W. L. Acute colitis caused by Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Kohler P. F. Susceptibility of Campylobacter isolates to the bactericidal activity of human serum. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):227–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Walker R. I., Stewart S. D., Rogers J. E. Simple adult rabbit model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1176–1182. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1176-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Pollard M. Host responses to "normal" microbial flora in germ-free mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jun;9(6):580–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Carter P. B. Development of delayed hypersensitivity in gnotobiotic mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;61(2):165–174. doi: 10.1159/000232430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. A., Gilchrist M. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Huizenga K. A., Van Scoy R. E. Diarrhea due to Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni. A clinical review of 63 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Jul;56(7):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Benson J. B., Rubin S. J. Mucosal invasion in campylobacter enteritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;73(5):706–708. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A., Lander K. P. Experimental infection of Rhesus monkeys with a human strain of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Jun;86(3):343–351. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Availability of locally synthesized and systemic antibodies in the intestine. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):965–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.965-981.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Edmonds P., Ward G. E., Kurtz H. J., Brenner D. J. "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" sp. nov.: a new species of Campylobacter found in the intestines of pigs and other animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):715–720. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.715-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Properties of crude Campylobacter jejuni heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. E., Schofield P. F., Ironside A. G., Mandal B. K. Campylobacter colitis. Br Med J. 1979 Mar 31;1(6167):857–859. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6167.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longfield R., O'Donnell J., Yudt W., Lissner C., Burns T. Acute colitis and bacteremia due to Campylobacter fetus. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Dec;24(12):950–953. doi: 10.1007/BF01311952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Hart A. M. Western blot analysis of the human antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni cellular antigens during gastrointestinal infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):33–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.33-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. B., Wostmann B. S. Cellular and humoral immune response of germfree mice stimulated with 7S HGG or Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1966 Aug;97(2):275–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K., Manninen K. I., Miniats O. P. Campylobacter jejuni colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):377–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Dolby J. M., Dunscombe P. R., Stirling J. Detection of campylobacter by immunofluorescence in stools and rectal biopsies of patients with diarrhoea. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1007–1013. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose F. V., Cebra J. J. Isotype commitment of B cells and dissemination of the primed state after mucosal stimulation with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.428-434.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler W., Lehle G., Weiler E., Kölsch E. Immune response against the T-independent antigen alpha (1 leads to 3) dextran. I. Demonstration of an unexpected IgG response of athymic and germ-free-raised euthymic BALB/c mice. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):120–125. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Savage D. C. Colonization of gnotobiotic mice by Roseburia cecicola, a motile, obligately anaerobic bacterium from murine ceca. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1677–1684. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1677-1684.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Patton C. M., Edmonds P., Barrett T. J., Brenner D. J., Blake P. A. Illness associated with Campylobacter laridis, a newly recognized Campylobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):222–225. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.222-225.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Mechanisms of immune regulation at mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S784–S792. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Chai J., Louie T. J., Goudreau C., Lior H., Newell D. G., Pearson A. D., Taylor D. E. Antigenic analysis of Campylobacter flagellar protein and other proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):108–112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.108-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J. Microbial immunity in the reproductive tract. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Nov 15;181(10):1069–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yrios J. W., Balish E. Colonization and pathogenesis of Campylobacter spp. in athymic and euthymic germfree mice. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yrios J. W., Balish E. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter spp. in athymic and euthymic germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):384–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.384-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]