Abstract
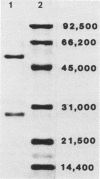
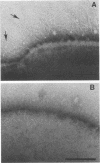
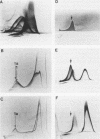
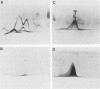
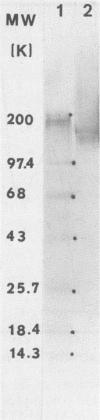
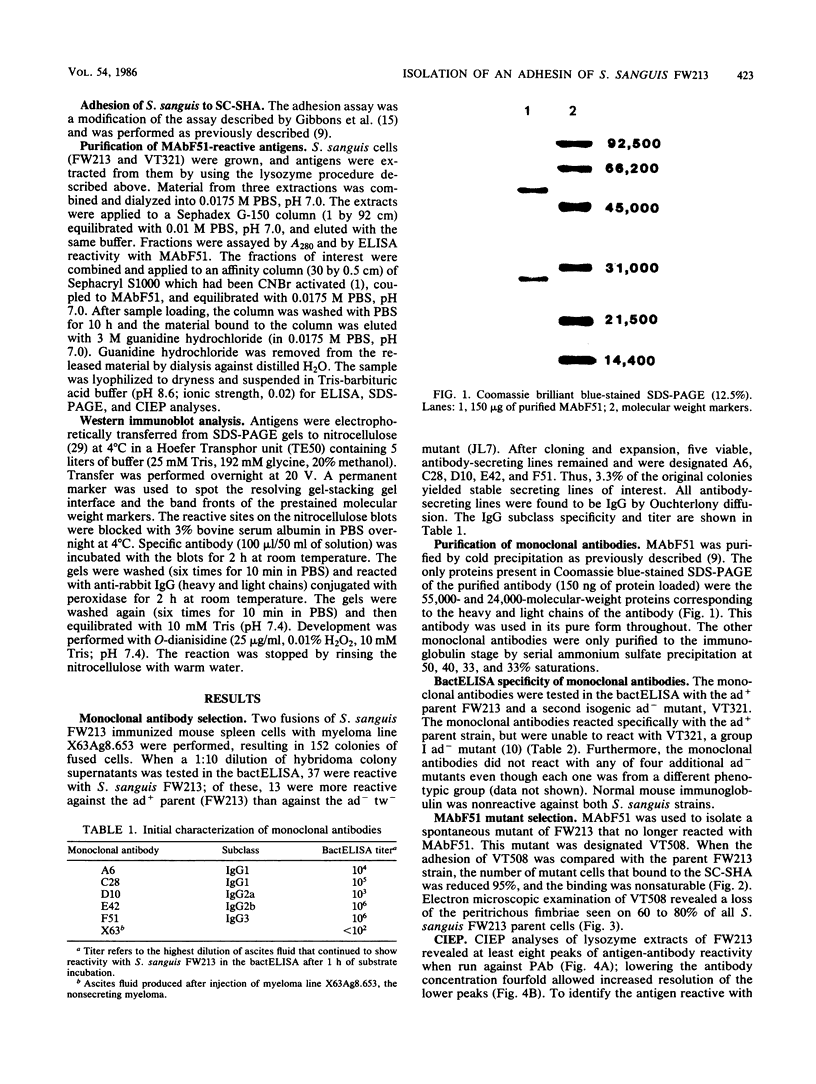
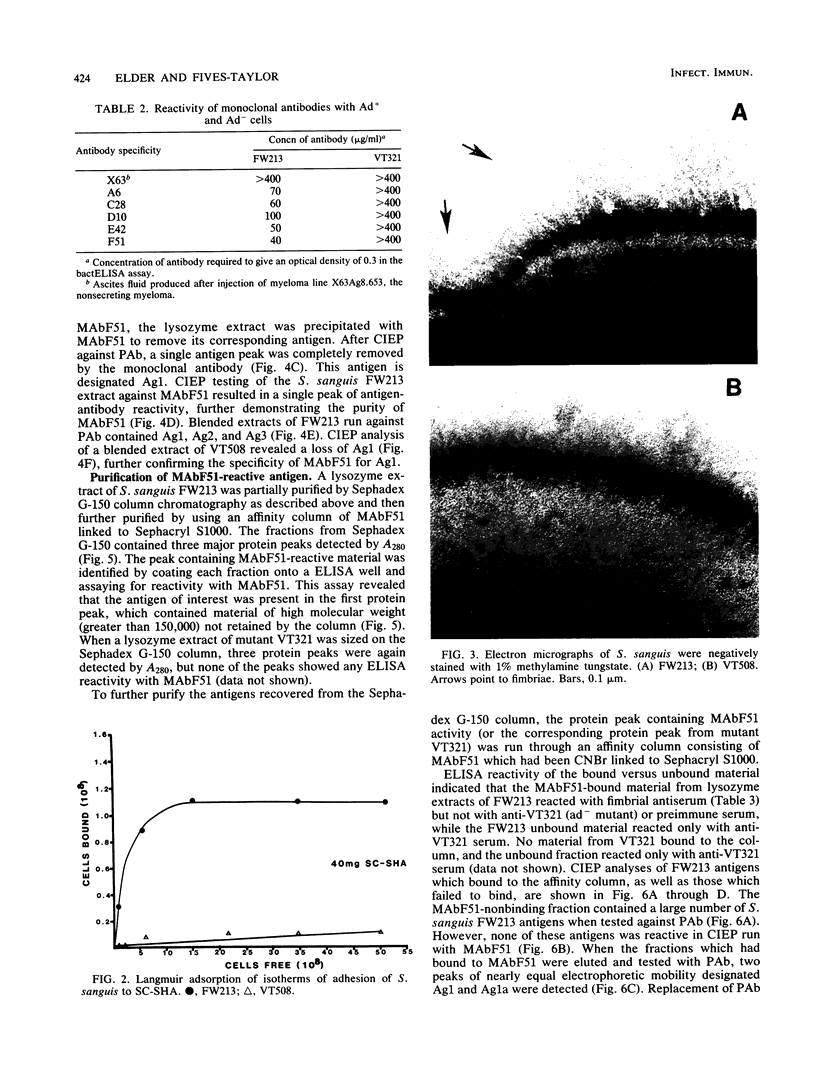
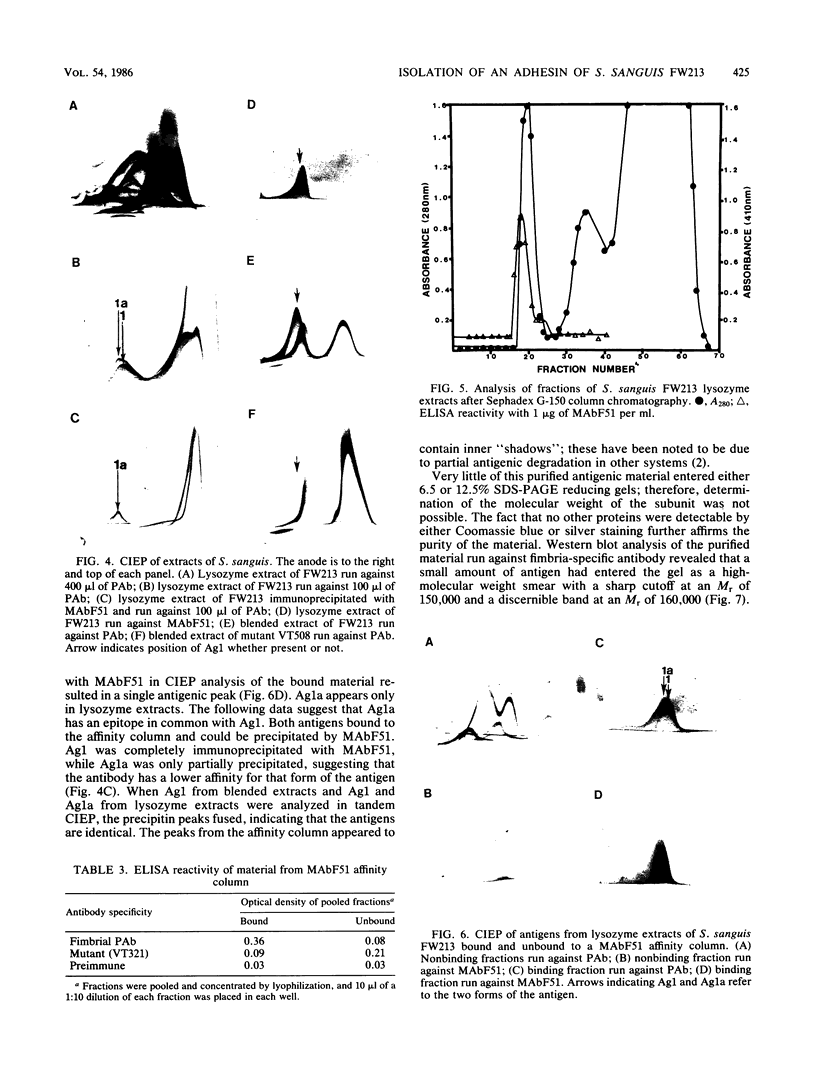
Monoclonal antibodies reactive to an adhesive strain of Streptococcus sanguis (FW213) and nonreactive to a nonadhesive mutant (JL7) were derived from the fusion of myeloma line X63Ag8.653 and spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with live S. sanguis cells. Five cell lines, belonging to subclasses of immunoglobulin G, produced monoclonal antibodies specifically directed against the adhesive strain. All five antibodies also failed to react with five additional, independently isolated, nonadhesive mutants. A spontaneous mutant of FW213 (VT508) that no longer reacted with monoclonal antibody F51 (MAbF51) was isolated by serial agglutination with the antibody. Langmuir adsorption isotherms of VT508 indicated that this mutant also had altered ability to adhere to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite further confirming the specificity of MAbF51 for adhesion. Electron microscopy revealed that VT508 had lost the peritrichous fimbriae associated with the adhesion of FW213. MAbF51 was used to purify the adhesin from lysozyme cell extracts by using an affinity column of MAbF51 linked to Sephacryl S1000. Purity was suggested by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and crossed immunoelectrophoresis (CIEP). The adhesin had a molecular weight greater than 150,000 and was not denatured in sodium dodecyl sulfate reducing gels. Two peaks of near electrophoretic mobility were detected in CIEP when the purified material was run against polyclonal antibody to the whole cell. Tandem CIEP analysis and immunoprecipitation provided evidence that the two peaks represented the same antigen in two different forms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Grahnén H., Jonsson G., Wikner S. Establishment of Streptococcus sanguis in the mouths of infants. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1143–1148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Wheeler T. T., Cisar J. O. Specific inhibition of adsorption of Actinomyces viscosus T14V to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite by antibody against type 1 fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):497–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.497-501.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke H. G., Freeman T. Quantitative immunoelectrophoresis of human serum proteins. Clin Sci. 1968 Oct;35(2):403–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Gronowicz E., Möller G. Mechanism of B-cell activation and paralysis by thymus-independent antigens. Additive effects between NNP-LPS and LPS in the specific response to the hapten. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Clements J. R., Dodd D. C. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against type 1 fimbriae organelles from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.333-340.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder B. L., Boraker D. K., Fives-Taylor P. M. Whole-bacterial cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Streptococcus sanguis fimbrial antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):141–144. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.141-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fachon-Kalweit S., Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Margulies D. H., Scharff M. D. A simple method for polyethylene glycol-promoted hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01551818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Moreno E. C., Etherden I. Concentration-dependent multiple binding sites on saliva-treated hydroxyapatite for Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):280–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.280-289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Moreno E. C., Spinell D. M. Model delineating the effects of a salivary pellicle on the adsorption of Streptococcus miteor onto hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1109–1112. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1109-1112.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Fielding J. Streptococcus salivarius strains carry either fibrils or fimbriae on the cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):64–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.64-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D., Henrichsen J. Twitching motility and possession of polar fimbriae in spreading Streptococcus sanguis isolates from the human throat. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Apr;83(2):133–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Listgarten M., Rosan B. Serology of Streptococcus sanguis: localization of antigens with unlabeled antisera. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):475–481. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.475-481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Reider J. L., Virgili S. S., Kopecko D. J. Survey of the extrachromosomal gene pool of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):215–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.215-226.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite: evidence for two binding sites. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]