Abstract
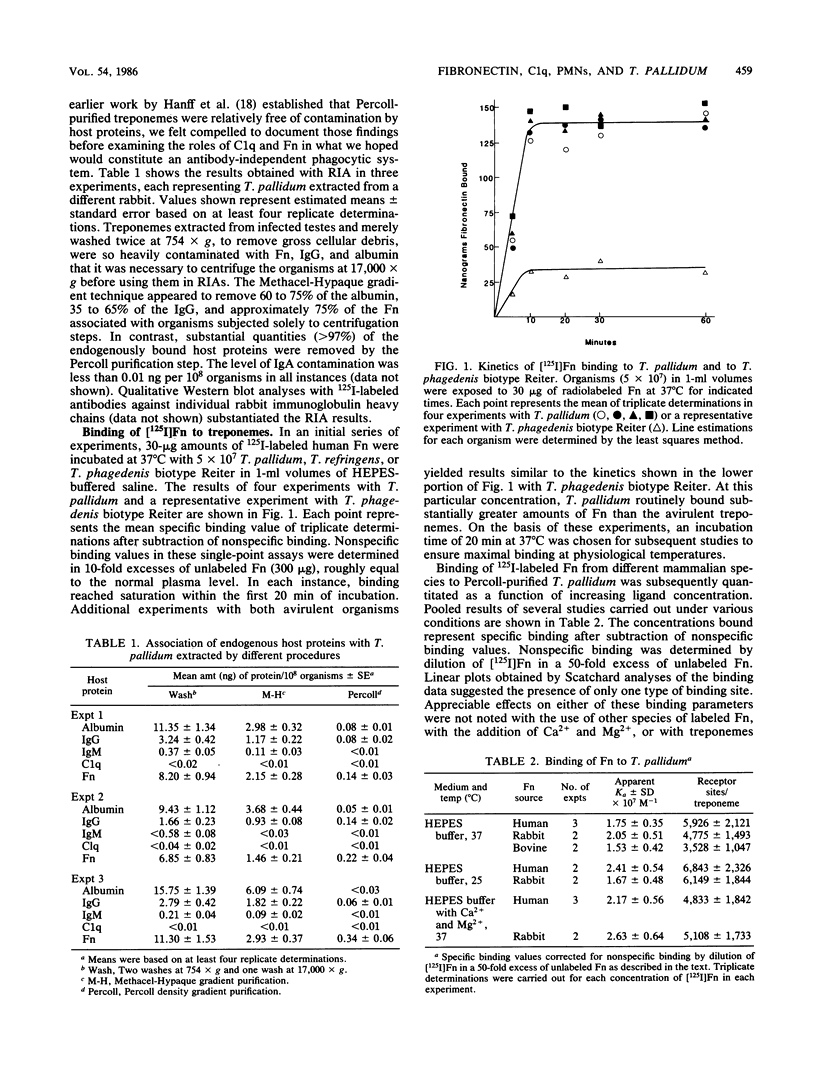
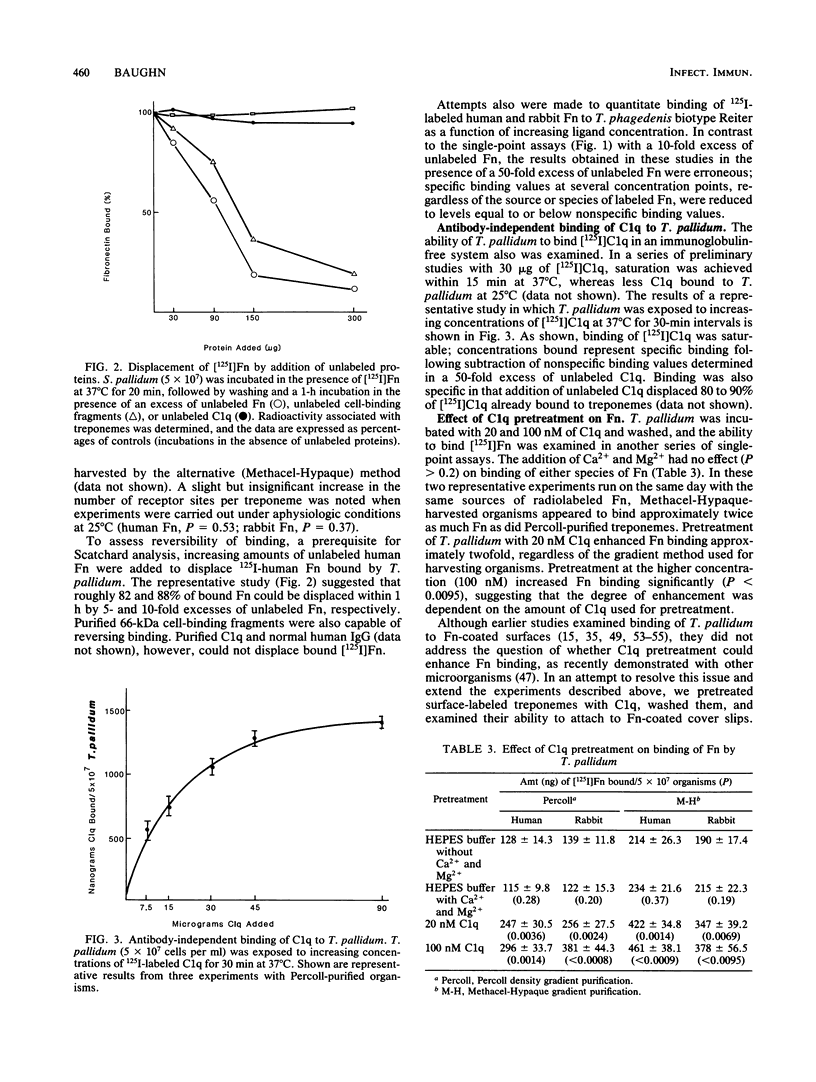
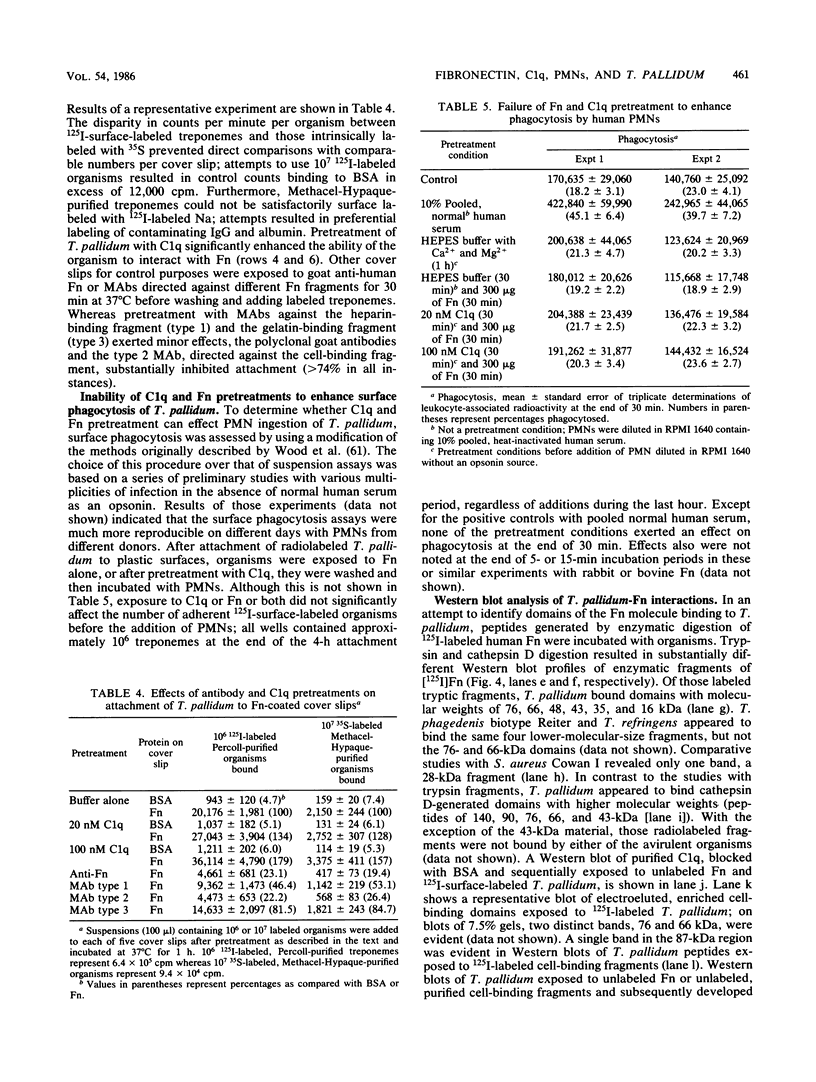
Although recent evidence suggests that fibronectin may be involved in the attachment of treponemes to mammalian cells, its possible role in promoting phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum has not been investigated. In the present study, we examined the antibody-independent interactions of fibronectin, C1q, and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes with T. pallidum. Binding of [125I]fibronectin was specific and saturable with an affinity constant of approximately 2 X 10(7) M-1. The number of binding sites per treponeme at 37 degrees C, irrespective of the mammalian source of fibronectin, was between 2,500 and 7,500, with a mean of approximately 4,700. Binding of [125I]C1q to T. pallidum, in the absence of antibodies to the organism, also was saturable and specific. Pretreatment of treponemes with C1q enhanced binding of soluble [125I]fibronectin two- to threefold and also increased attachment of 125I-surface-labeled treponemes to fibronectin-coated surfaces. Treatment of 125I-labeled T. pallidum with fibronectin alone, or together with C1q, however, did not enhance surface phagocytosis by neutrophils.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S. S., Jr, Colonna G., Edelhoch H. The structure and stability of human plasma cold-insoluble globulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1501–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes E. C. Molecular characterization of receptor binding proteins and immunogens of virulent Treponema pallidum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Adams C. B., Musher D. M. Circulating immune complexes in experimental syphilis: identification of treponemal antigens and specific antibodies to treponemal antigens in isolated complexes. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):585–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.585-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., McNeely M. C., Jorizzo J. L., Musher D. M. Characterization of the antigenic determinants and host components in immune complexes from patients with secondary syphilis. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1406–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Radioimmunoassays for the detection of antibodies to treponemal polypeptide antigens in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):922–929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.922-929.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz S. J., Isliker H. Antibody-independent interactions between Escherichia coli J5 and human complement components. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Almeda S., Isliker H., Lahav J., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to the C1q component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4198–4201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J. The role of extracellular matrix proteins in the control of phagocytosis. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 May;39(5):579–591. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamness G. C., McGuire W. L. Scatchard plots: common errors in correction and interpretation. Steroids. 1975 Oct;26(4):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Golecki J. R., Loos M. Electron microscopic study showing antibody-independent binding of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, to serum-sensitive salmonellae. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):795–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.795-797.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Antibody-independent binding of the first component of complement (C1) and its subcomponent C1q to the S and R forms of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1138-1144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennestad K. L., Bruun L., Wedø E. Pleural effusion disease agent as passenger of Treponema pallidum suspensions from rabbits. Survey of laboratories. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Aug;56(4):198–203. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.4.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A. Interactions of fibronectin with Treponema pallidum. Genitourin Med. 1985 Jun;61(3):147–155. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.3.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hök M. Binding of Escherichia coli to fibronectin. A mechanism of tissue adherence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14899–14905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Yamada K. M. Domain structure of the carboxyl-terminal half of human plasma fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3332–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson L., Venge P. The combined action of hyaluronic acid and fibronectin stimulates neutrophil migration. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2735–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham K. C., Brew S. A., Miekka S. I. Interaction of plasma fibronectin with gelatin and complement C1q. Mol Immunol. 1983 Mar;20(3):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorizzo J. L., McNeely M. C., Baughn R. E., Solomon A. R., Cavallo T., Smith E. B. Role of circulating immune complexes in human secondary syphilis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Saba T. M. Fibronectin as a co-factor necessary for optimal granulocyte phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Nov;30(5):415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist-Welsh P., Bjornson A. B. Immunoglobulin-independent utilization of the classical complement pathway in opsonophagocytosis of Escherichia coli by human peripheral leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2643–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Wellek B., Thesen R., Opferkuch W. Antibody-independent interaction of the first component of complement with Gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.5-9.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel E. J., Smolen J. S., Liotta L., Reid K. B. Interaction of fibronectin with C1q and its collagen-like fragment (CLF). FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80787-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination as a tool for investigation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):214–220. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins M and G immune response to protein antigens of Treponema pallidum in human syphilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.127-132.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Hague-Park M., Gyorkey F., Anderson D. C., Baughn R. E. The interaction between Treponema pallidum and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):77–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Gold L. I., Garcia-Pardo A. Fibronectin: a review of its structure and biological activity. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Feb 8;29(2):103–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Sorvillo J., Gigli I. The interaction of human plasma fibronectin with a subunit of the first component of complement, C1q. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2036–2039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bailey M. J., Cockayne A. The axial filament antigen of Treponema pallidum. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):635–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier C. G., O'Shea J., Chused T., Yancey K., Frank M. M., Takahashi T., Brown E. J. Studies on the fibronectin receptors of human peripheral blood leukocytes. Morphologic and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):137–151. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Prendergast E., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin mediates attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to human neutrophils. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):681–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Textor J. A., Vann J. M., Mosher D. F. Role of fibronectin in human monocyte and macrophage bactericidal activity. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):629–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.629-637.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynor R. H., Doran J. E., Reese A. C. A polymorphonuclear leukocyte monolayer system for studies of phagocytosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Jun;29(6):441–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter H., Hörmann H. A large cathepsin D-derived fragment from the central part of the fibronectin subunit chains. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Mason J. M., Beachey E. H. Fibronectin-mediated binding of group A streptococci to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):805–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.805-810.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. The effect of fibronectin on the processing of C1q- and C3b/bi-coated immune complexes by peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1023–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Pearlstein E. C1q, a subunit of the first component of complement, enhances binding of plasma fibronectin to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):664–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.664-669.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. Fibronectin binding to complement subcomponent C1q. Localization of their respective binding sites. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2260207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J., Gigli I., Pearlstein E. Requirements for the binding of human plasma fibronectin to the C1q subunit of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1400–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R. A., Williams W. F., Raines G., Pedersen J. S., Drummond L. P., Toh B. H., Faine S. Autoantibodies to creatine kinase in rabbits infected with Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):667–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Antibody-independent C1 activation by E. coli. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):886–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Enhanced levels of attachment of fibronectin-primed Treponema pallidum to extracellular matrix. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.736-741.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Fibronectin mediates Treponema pallidum cytadherence through recognition of fibronectin cell-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):514–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Putative Treponema pallidum cytadhesins share a common functional domain. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):833–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.833-835.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water L., Destree A. T., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to some bacteria but does not promote their uptake by phagocytic cells. Science. 1983 Apr 8;220(4593):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.6338594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Smith D. E., Nguyen B. Y., Hoidal J. R., Wilkinson B. J., Verhoef J., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin binding to staphylococcal surface protein and its relative inefficiency in promoting phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.811-819.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. B., Jr, SMITH M. R., PERRY W. D., BERRY J. W. Studies on the cellular immunology of acute bacteremia. I. Intravascular leucocytic reaction and surface phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1951 Dec 1;94(6):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.6.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. C., Janmey P. A., Ferry J. D., Mosher D. F. Conformational states of fibronectin. Effects of pH, ionic strength, and collagen binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14973–14978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]