Abstract
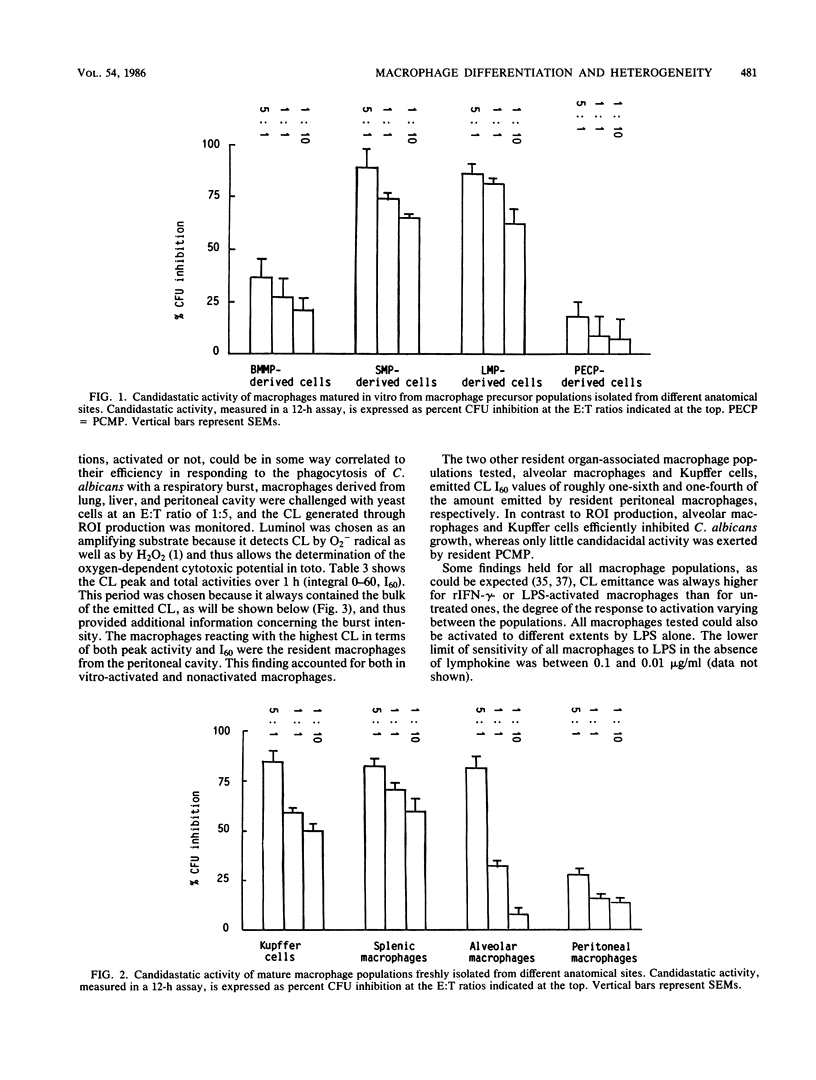
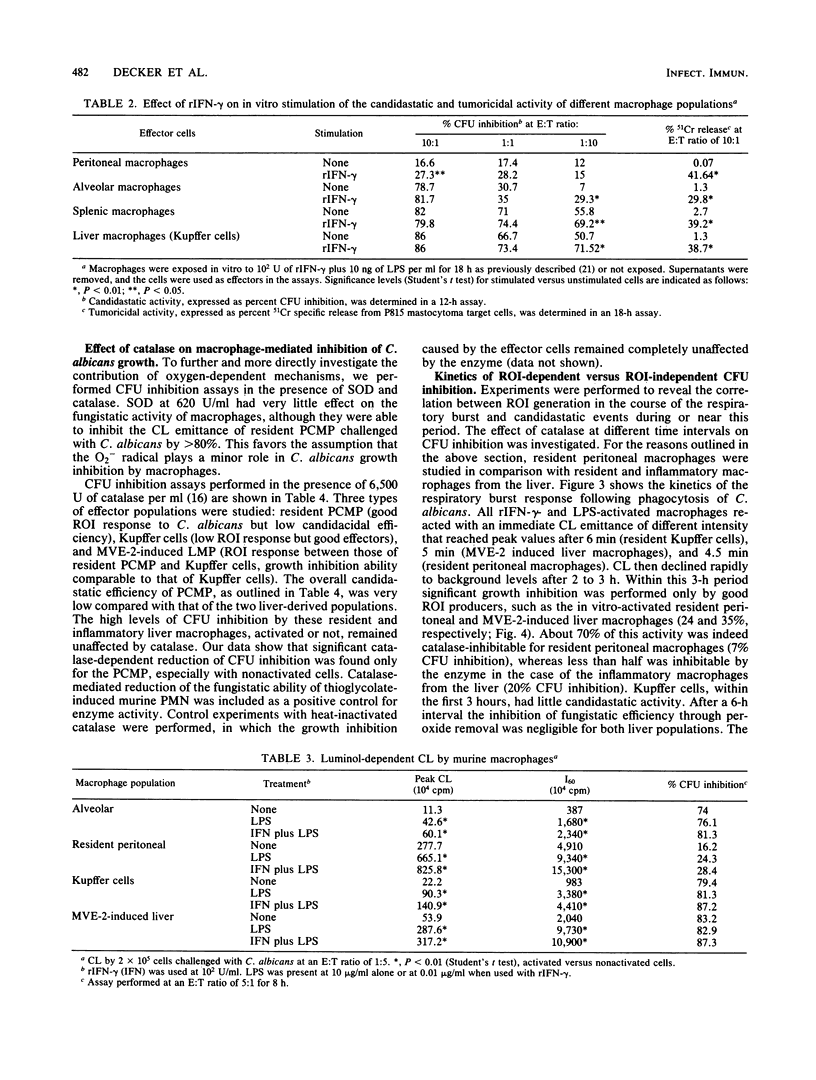
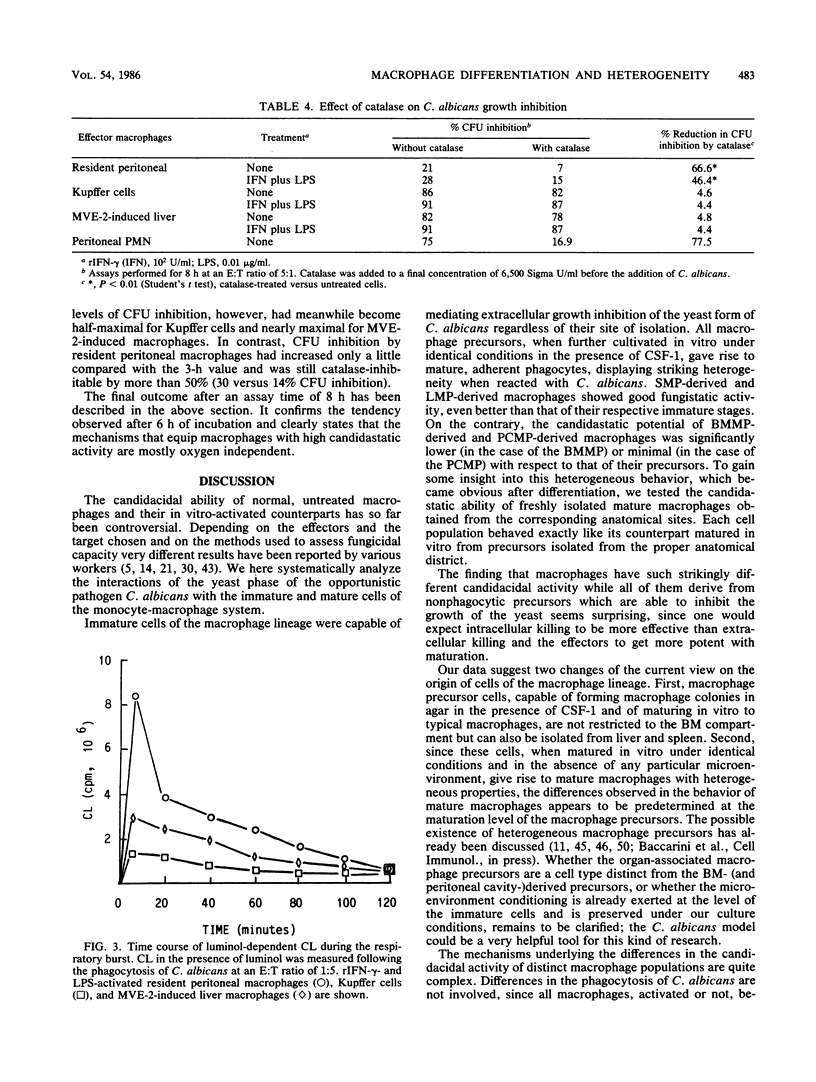
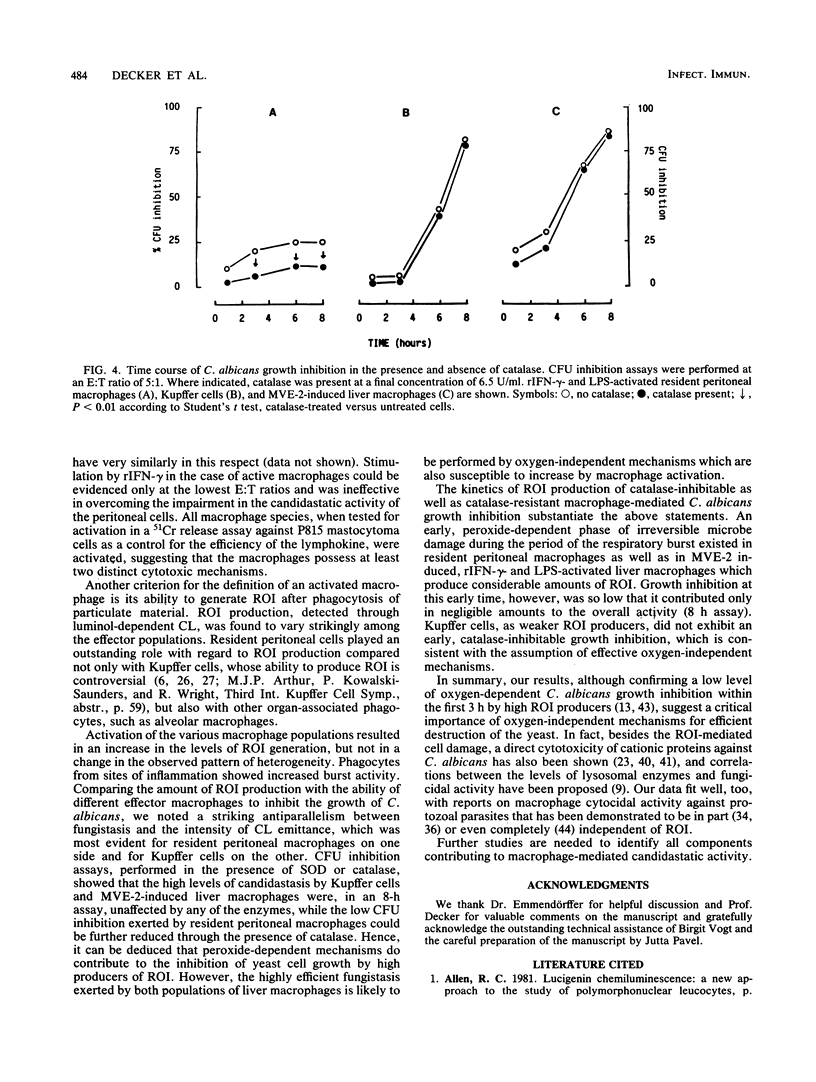
Mature mononuclear phagocytes have been receiving much attention as effectors of spontaneous candidacidal activity, although with controversial results due to differences in the effector populations and the methods used in different laboratories. We here systematically compare the fungistatic activity of immature and mature cells of the murine macrophage series. The results show that nonadherent, nonphagocytic precursor cells (isolated either [90% purity] from bone marrow liquid cultures or from the organs of mice in which inflammatory conditions had been elicited in vivo) exerted a strong extracellular candidastatic activity. In contrast, mature macrophages, either obtained from different anatomical areas (spleen, liver, lung, peritoneal cavity) or matured in vitro from the precursor populations, displayed striking heterogeneity in their ability to inhibit the growth of Candida albicans, depending on the anatomical site they were derived from. Lymphokine activation did not alter the fungistatic pattern of the untreated cells. The different macrophage populations behaved very differently also in the production of reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) in response to phagocytosis of C. albicans. The amounts of ROI generated, however, showed no correlation with candidastatic ability. Low levels of candidastatic activity exerted by resident peritoneal macrophages (good ROI producers) were inhibited by catalase, whereas high levels of growth inhibition by Kupffer cells (poor ROI producers) after 8 h of assay were hardly influenced by the enzyme. Our data suggest the existence of two different effector mechanisms in macrophage-mediated C. albicans growth inhibition, a rather inefficient ROI-dependent one, and a second, very efficient oxygen-independent mechanism. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccarini M., Bistoni F., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. In vitro natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Candida albicans: macrophage precursors as effector cells. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2658–2665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini M., Bistoni F., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Organ-associated macrophage precursor activity: isolation of candidacidal and tumoricidal effectors from the spleens of cyclophosphamide-treated mice. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):837–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini M., Bistoni F., Puccetti P., Garaci E. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Candida albicans induced by cyclophosphamide: nature of the in vitro cytotoxic effector. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini M., Blasi E., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Phagocytic killing of Candida albicans by different murine effector cells. Sabouraudia. 1983 Dec;21(4):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar R., Schirmer R., Ernst M., Decker K. Superoxide release by zymosan-stimulated rat Kupffer cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):171–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Baccarini M., Blasi E., Marconi P., Puccetti P., Garaci E. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies of modulation of resistance to experimental Candida albicans infection by cyclophosphamide in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):46–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.46-55.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Beaman B. L., Donovan R. M., Goldstein E. Intracellular acid phosphatase content and ability of different macrophage populations to kill Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):375–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.375-383.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Fungal infections in the cancer patient. S Afr Med J. 1977 Dec 10;52(25):1009–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursuker I., Goldman R. On the origin of macrophage heterogeneity: a hypothesis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Mar;33(3):207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codish S. D., Tobias J. S. Managing systemic mycoses in the compromised host. JAMA. 1976 May 10;235(19):2132–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings N. P., Pabst M. J., Johnston R. B., Jr Activation of macrophages for enhanced release of superoxide anion and greater killing of Candida albicans by injection of muramyl dipeptide. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1659–1669. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Poor A. H. Effect of mouse phagocytes on Candida albicans in in vivo chambers. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1110-1116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Baccarini M., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Liver-associated macrophage precursors as natural cytotoxic effectors against Candida albicans and Yac-1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(6):693–699. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. A role for oxygen-dependent mechanisms in killing of Leishmania donovani tissue forms by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):850–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Lagrange P. H., Michel J. C. Systemic candidiasis in mice. II.--Main role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in resistance to infection. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1980 Jan-Feb;131C(1):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indiveri F., Wilson B. S., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Detection of human histocompatibility (HLA) antigens with an indirect rosette microassay. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(2):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Starkey P. M., Gordon S. Quantitative analysis of total macrophage content in adult mouse tissues. Immunochemical studies with monoclonal antibody F4/80. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):475–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ferrari L. G., Patterson-Delafield J., Sorrell T. Fungicidal activity of rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages against Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1001–1008. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1001-1008.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ladra K. M., Hake R. B. Nonoxidative fungicidal mechanisms of mammalian granulocytes: demonstration of components with candidacidal activity in human, rabbit, and guinea pig leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1226–1234. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1226-1234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E., Fleischmann J. Increased content of microbicidal cationic peptides in rabbit alveolar macrophages elicited by complete Freund adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):775–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.775-778.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):313–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.313-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Steinman R. M., Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Liver macrophages in murine listeriosis. Cell-mediated immunity is correlated with an influx of macrophages capable of generating reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1503–1512. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Domzig W., Roder J. Promonocytes have the functional characteristics of natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1883–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiti P. K., Kumar R., Mohapatra L. N. Candidacidal activity of mouse macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):477–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.477-482.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi P., Bistoni F., Boncio L., Bersiani A., Bravi P., Pitzurra M. Utilizzazione di soluzione salina ipertonica di cloruro di potassio (3M KC1) per l'estrazione di antigeni solubili da Candia albicans. Ann Sclavo. 1976 Jan-Feb;18(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Cassone A. Inducibility of germ-tube formation in Candida albicans at different phases of yeast growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):439–442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerpohl H. G., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Fischer H. Studies on the activation of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages by the macrophage cytotoxicity factor (MCF). Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):213–217. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cartelli D. M. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence for oxygen-dependent and -independent leishmanicidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):32–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI110972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Juangbhanich C. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. II. The role of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):950–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Carriero S. M., Harris A. M., Jaffee E. A. Human mononuclear phagocyte antiprotozoal mechanisms: oxygen-dependent vs oxygen-independent activity against intracellular Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1982–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham R. K., Ortaldo J. R., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Direct comparison of three isotopic release microtoxicity assays as measures of cell-mediated immunity to Gross virus-induced lymphomas in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Apr;58(4):1061–1067. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.4.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., LeBlanc P. A., Murasko D. M. Comparative effects of various classes of mouse interferons on macrophage activation for tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):977–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins in rabbit alveolar macrophages: a potential host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.180-192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Szklarek D., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins of rabbit alveolar macrophages: amino acid composition and functional attributes. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):723–731. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.723-731.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Klingenstein R. J., Richman J. A., Strober W., Berzofsky J. A. The murine Kupffer cell. I. Characterization of the cell serving accessory function in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahay J. N., Chatterjee S. S., Stanbridge T. N. Inhaled corticosteroid aerosols and candidiasis. Br J Dis Chest. 1979 Apr;73(2):164–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada M., Johnston R. B., Jr Macrophage microbicidal activity. Correlation between phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism and the killing of Candida by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):85–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., James S., Sher A. The respiratory burst is not required for killing of intracellular and extracellular parasites by a lymphokine-activated macrophage cell line. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jun;15(6):553–558. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Volkman A. The effect of bone marrow depletion on prostaglandin E-producing suppressor macrophages in mouse spleen. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3897–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Volkman A. The effect of hemopoietic microenvironment on splenic suppressor macrophages in congenitally anemic mice of genotype Sl/Sld. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3905–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Functionally different subpopulations of mouse macrophages recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):134–140. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. M. Dual origin of mouse spleen macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1273–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


