Abstract
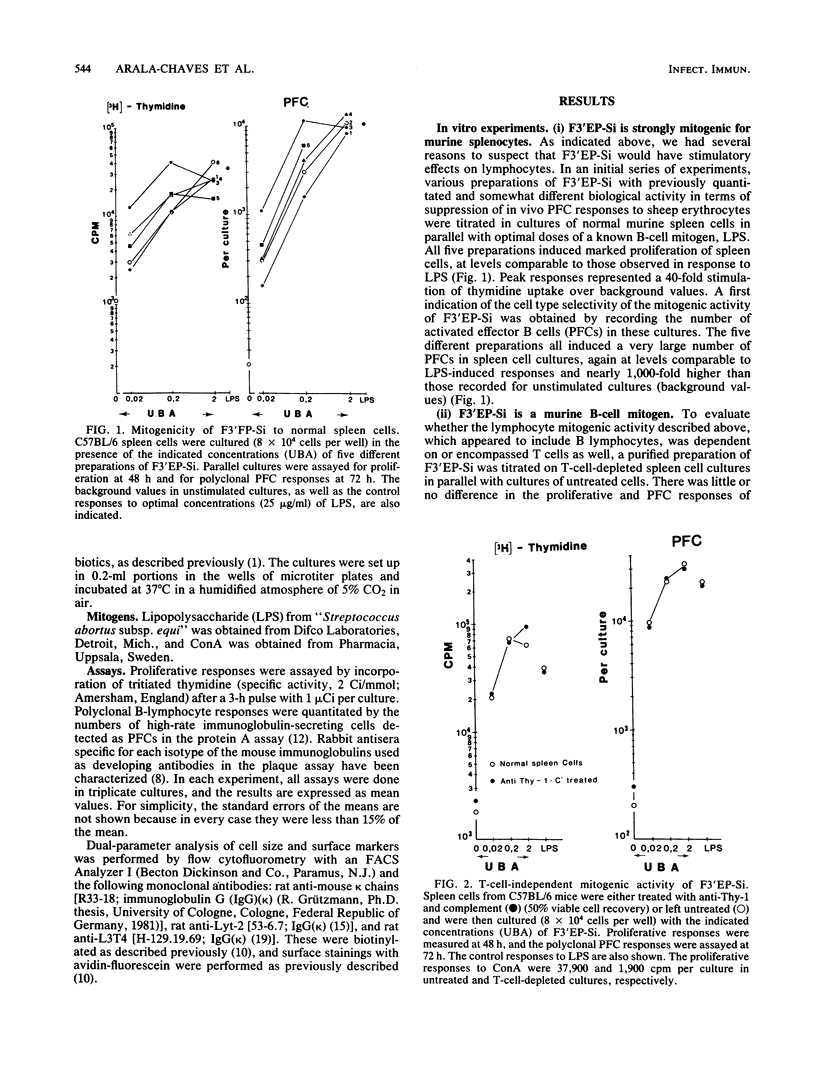
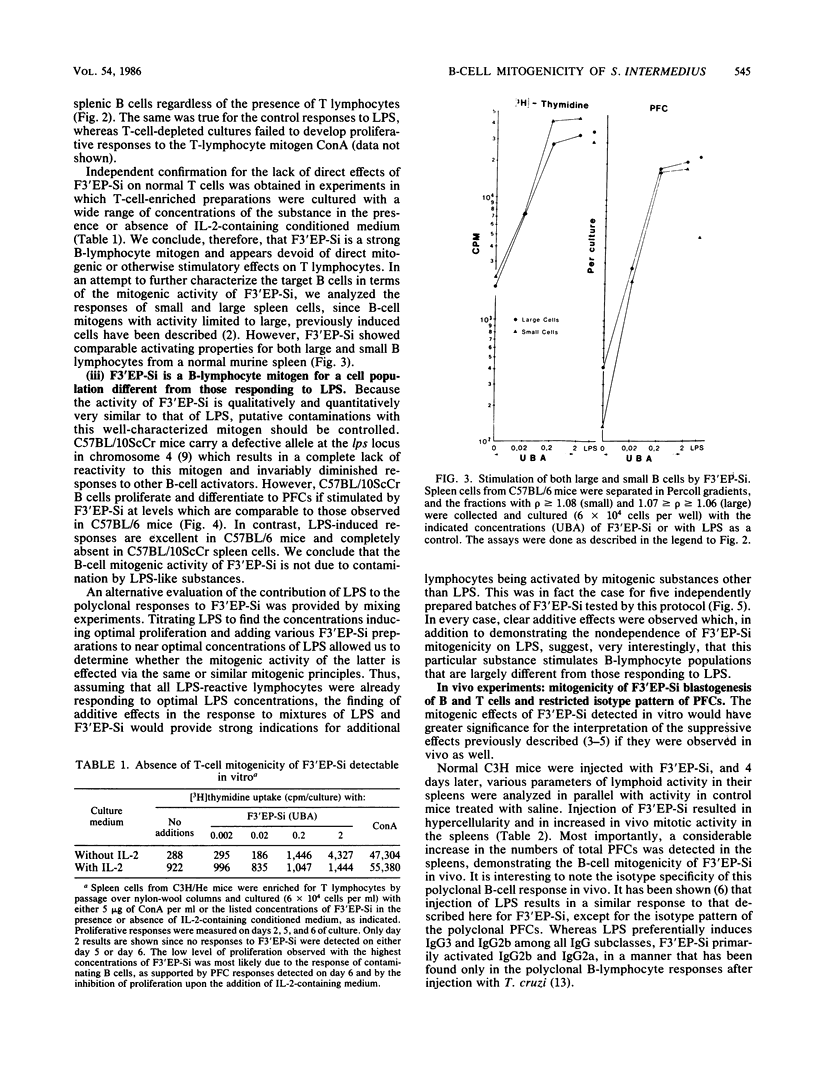
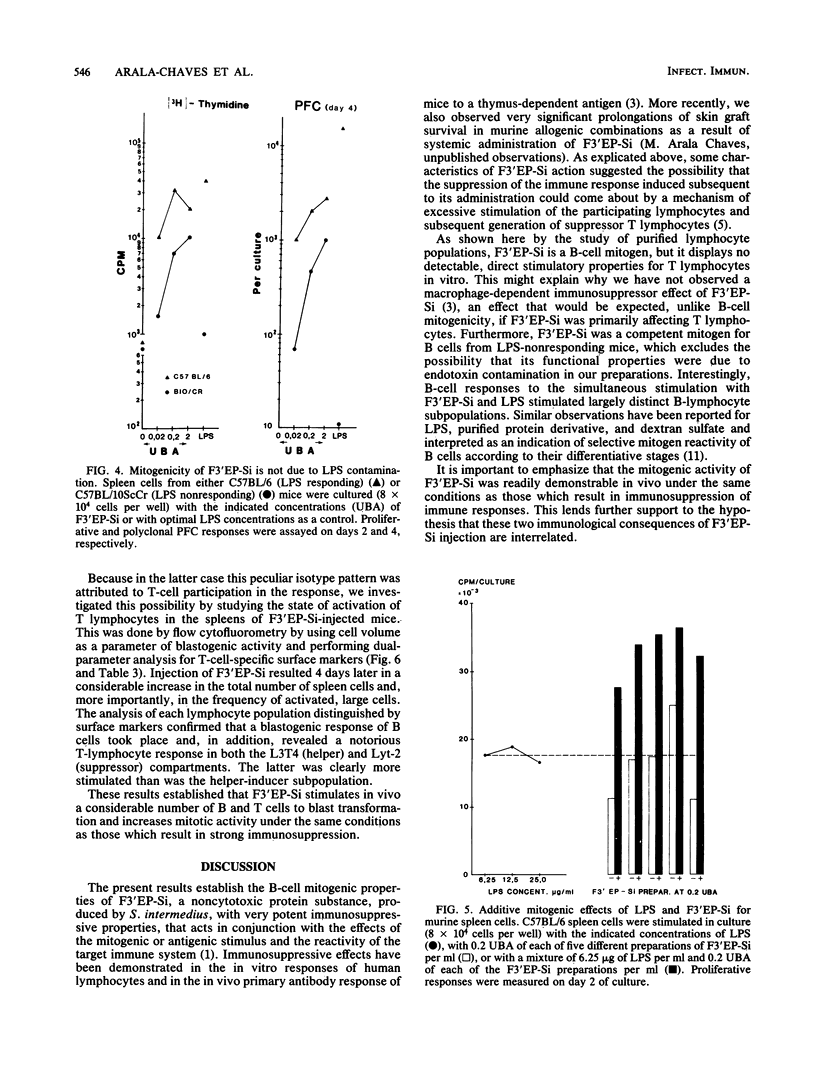
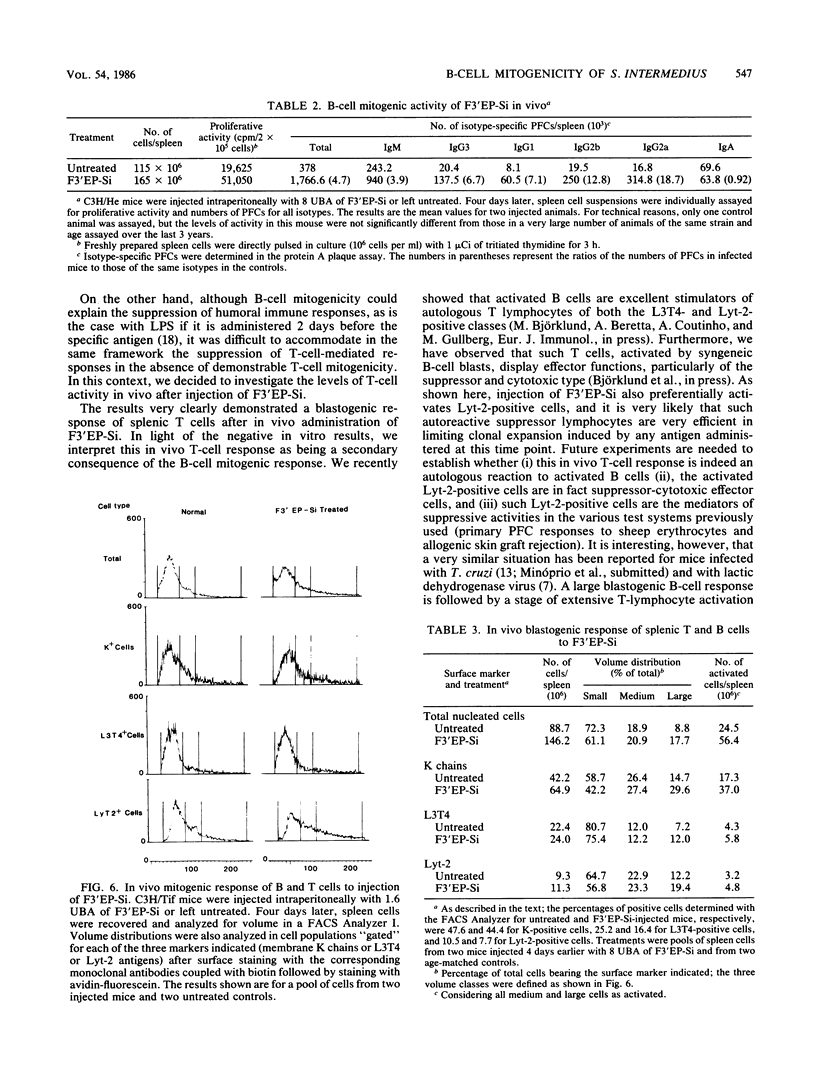
A noncytotoxic protein substance, produced by Streptococcus intermedius, with very potent immunosuppressive properties (F3'EP-Si) was tested for lymphocyte mitogenic activity. Although devoid of T-cell mitogenicity, F3'EP-Si stimulated proliferation and led to high numbers of plaque-forming cells in cultures of normal or T-cell-depleted, small or large splenic B cells from both lipopolysaccharide-responding and -nonresponding mice. The B-cell mitogenic activity of F3'EP-Si was quantitatively comparable to that of lipopolysaccharide, and the simultaneous exposure to both mitogens stimulated additive B-cell responses. Injection of F3'EP-Si into normal mice resulted in increased numbers of spleen cells, higher rates of mitotic activity, and very large numbers of plaque-forming cells, predominantly of the immunoglobulin G2a and -b isotypes. In preliminary experiments, the analysis of surface markers among the lymphocytes participating in the blastogenic response in vivo revealed a T-cell component in the response to F3'EP-Si. These observations are discussed in the context of the immunosuppressive activity of this and other microbial substances.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Clonal growth and maturation to immunoglobulin secretion in vitro of every growth-inducible B lymphocyte. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. The purified protein derivative of turberculin, a B-cell mitogen that distinguishes in its action resting, small B cells from activated B-cell blasts. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Higerd T. B., Porto M. T., Munoz J., Goust J. M., Fudenberg H. H., Loadholt C. B. Evidence for the synthesis and release of strongly immunosuppressive, noncytotoxic substances by Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):871–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI109553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Porto M. T., Arnaud P., Saraiva M. J., Geada H., Patrick C. C., Fudenberg H. H. Fractionation and characterization of the immunosuppressive substance in crude extracellular products released by Streptococcus intermedius. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):294–302. doi: 10.1172/JCI110247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arala-Chaves M. P., Santarém M. M., Azevedo C., Soares J. O., Granjo E. Evidence for the generation of specific T suppressor lymphocytes by Streptococcus intermedius. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Mar-Apr;19(2):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund M., Coutinho A. Isotype commitment in the in vivo immune responses. II. Polyclonal plaque-forming cell responses to lipopolysaccharide in the spleen and bone marrow. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jan;13(1):44–50. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutelier J. P., Van Snick J. Isotypically restricted activation of B lymphocytes by lactic dehydrogenase virus. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):250–255. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Benner R., Björklund M., Forni L., Holmberg D., Ivars F., Martinez-A C., Pettersson S. A "trans" perspective on the control of immunoglobulin c gene expression. Immunol Rev. 1982;67:87–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb01057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Imperio Lima M. R., Joskowicz M., Coutinho A., Kipnis T., Eisen H. Very large and isotypically atypical polyclonal plaque-forming cell responses in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):201–203. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A. Selective triggering of B cell subpopulations by mitogens. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Nov;4(11):771–776. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson S. D., Zamfirescu P. L., Drew S. I., Wilbur S. Two-step separation of human peripheral blood monocytes on discontinuous density gradients of colloidal silica-polyvinylpyrrolidinone. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(3-4):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira P., Larsson E. L., Forni L., Bandeira A., Coutinho A. Natural effector T lymphocytes in normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7691–7695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson U. Lipopolysaccharide-induced suppression of the primary immune response to a thymus-dependent antigen. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres A., Naquet P., Van Agthoven A., Bekkhoucha F., Denizot F., Mishal Z., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Pierres M. A rat anti-mouse T4 monoclonal antibody (H129.19) inhibits the proliferation of Ia-reactive T cell clones and delineates two phenotypically distinct (T4+, Lyt-2,3-, and T4-, Lyt-2,3+) subsets among anti-Ia cytolytic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos C., Lamoyi E., Feoli M., Rodriguez M., Perez M., Ortiz-Ortiz L. Trypanosoma cruzi: immunosuppressed response to different antigens in the infected mouse. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Aug;45(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Scott P. A., Asofsky R., Sher F. A. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in anti-IgM-treated mice: enhanced resistance due to functional depletion of a B cell-dependent T cell involved in the suppressor pathway. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2072–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J. P., Rabesandratana H., Huguet M. F., Cannat A., Serre A. Brucella fractions behave as nonspecific mitogens and polyclonal B-cell activators for human lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):310–316. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.310-316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



