Abstract
"Haemophilus somnus" has been identified in the etiology of bovine abortion on the basis of the isolation of the organism from aborted fetal and placental tissues. To investigate the role of hematogenous dissemination of "H. somnus" in the pathogenesis of abortion and to monitor the humoral immune response to infection, 19 pregnant cows (gestation ages, 1.4 to 7 months) were challenged intravenously (11 cows) or intrabronchially (8 cows). Five cows challenged intravenously aborted, and one cow challenged intrabronchially resorbed her fetus. "H. somnus" was isolated in large numbers from aborted tissues, and placental lesions were similar to those reported in a field case of "H. somnus" abortion. Antibody titers in serum were measured by the microagglutination test (MAT) and by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). A response to challenge was measured by MAT; it was also measured by ELISA within the immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), IgG2, and IgM isotypes. On comparison of pre- and postchallenge antibody titers, the greatest and most persistent response was detected within the IgG2 isotype. Prechallenge antibody titers (measured by MAT and by IgG2 ELISA) were lower in animals that aborted than in normal calving animals, indicating that IgG2 antibody may have a role in limiting hematogenous dissemination of "H. somnus."
Full text
PDF

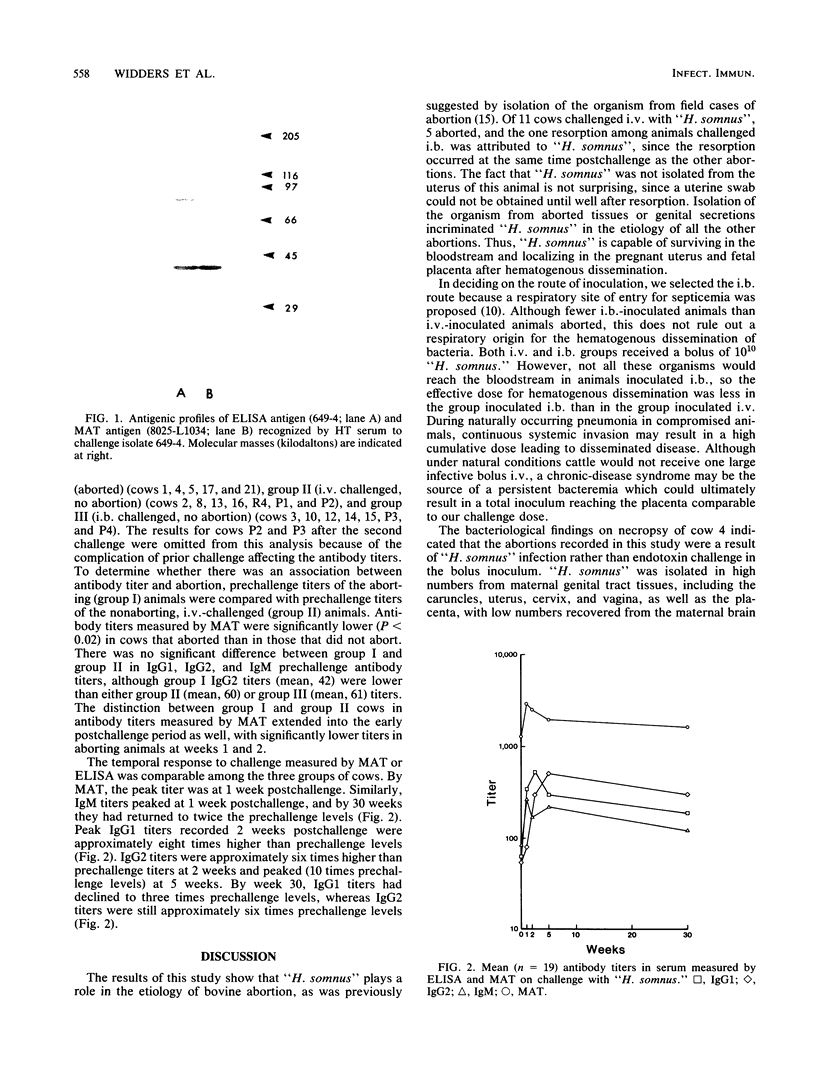


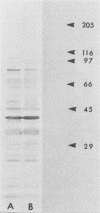
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corbeil L. B., Watt B., Corbeil R. R., Betzen T. G., Brownson R. K., Morrill J. L. Immunoglobulin concentrations in serum and nasal secretions of calves at the onset of pneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Apr;45(4):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G., Brownlie J. Surface receptors for immunoglobulin on bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Jul;29(1):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Stephens L. R., Thorsen J. Occurrence of "Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):215–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. D., Little P. B., Stephens L. R., Barnum D. A., Doig P. A., Thorsen J. Prevalence and distribution of Haemophilus somnus in the male bovine reproductive tract. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J. Biologic activities of bovine IgG subclasses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J. Biologic activities of bovine IgG subclasses. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. B., Van Camp S. D., Barnum D. A. The effects of intra-amniotic inoculation of Hemophilus somnus on the bovine fetus and dam. Vet Pathol. 1983 Sep;20(5):574–583. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panciera R. J., Dahlgren R. R., Rinker H. B. Observations on septicemia of cattle caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Pathol Vet. 1968;5(3):212–216. doi: 10.1177/030098586800500303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell J. R., Renshaw H. W. Haemophilus somnus complex: in vitro interactions of Haemophilus somnus, leukocytes, complement, and antiserums produced from vaccination of cattle with fractions of the organism. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):759–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee K. J., Stephens L. R. Selective medium for isolation of Haemophilus somnus from cattle and sheep. Vet Rec. 1985 Feb 23;116(8):215–217. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.8.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Humphrey J. D., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Vaccination of cattle against experimentally induced thromboembolic meningoencephalitis with a Haemophilus somnus bacterin. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Aug;43(8):1339–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dreumel A. A., Kierstead M. Abortion associated with Hemophilus somnus infection in a bovine fetus. Can Vet J. 1975 Dec;16(12):367–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]