Abstract
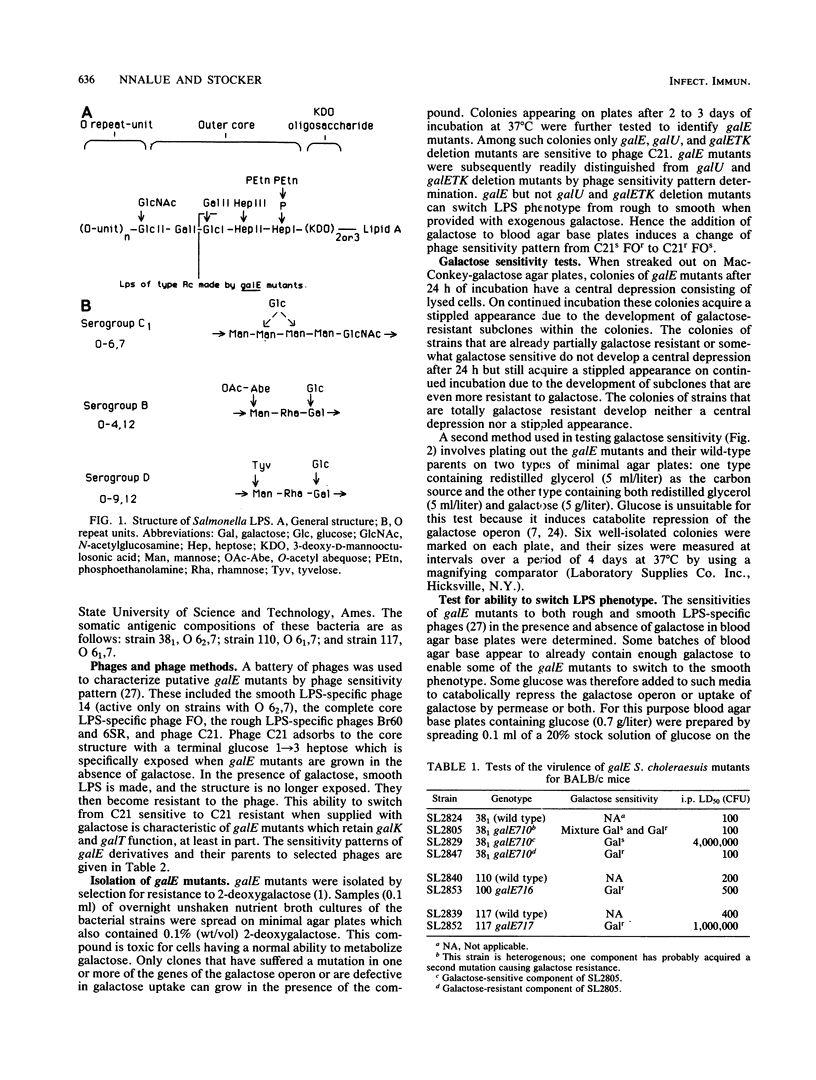
galE mutants were isolated from three mouse-virulent strains of Salmonella choleraesuis (of group C1, O antigen 6,7) by selection for resistance to 2-deoxygalactose. The galE derivative of strain 381 comprised two components: galactose sensitive, thought to be the original mutant; and galactose resistant, presumably by a second mutation reducing galK or galT function or both. The galactose-sensitive component had an intraperitoneal 50% lethal dose for BALB/c mice of ca. 4 X 10(6) CFU, whereas the galactose-resistant component was about as virulent as its gal+ parent, with a 50% lethal dose of ca. 100 CFU. The galE mutant of strain 110 was somewhat sensitive to galactose, as shown by retardation of growth; its 50% lethal dose, ca. 500 CFU, was not much greater than the ca. 200 CFU value for its parent. The galE mutant of strain 117 showed the same partial sensitivity to galactose as strain 110 galE, but was nonvirulent (50% lethal dose of ca. 10(6) CFU versus ca. 400 CFU for its parent). Growth on galactose-supplemented medium restored the smooth phenotype, as indicated by phage sensitivity to three of the four galE strains, but only partially so for the strain 117 galE mutant. The retention of parental virulence by galE mutants of S. choleraesuis which are galactose resistant or somewhat galactose sensitive contrasts with the greatly reduced virulence of galactose-resistant galE mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella typhi; this difference may result from the absence of galactose from the O repeat unit in the lipopolysaccharide of group C1 salmonellae.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Positive selection of mutants with deletions of the gal-chl region of the Salmonella chromosome as a screening procedure for mutagens that cause deletions. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.259-266.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Boyer F. A proposed mechanism for natural immunity to enterobacterial pathogens. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):292–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlabac V. The sensitivity of smooth and rough mutants of Salmonella typhimurium to bactericidal and bacteriolytic action of serum, lysozyme and to phagocytosis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(5):439–449. doi: 10.1007/BF02869196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. II. Bacteriolysis induced by galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. Nature. 1959 Oct 10;184(Suppl 15):1168–1169. doi: 10.1038/1841168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Fürer E. Immunity in experimental salmonellosis. II. Basis for the avirulence and protective capacity of gal E mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):663–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.663-673.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in Experimental Salmonellosis I. Protection Induced by Rough Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.309-315.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Woodard W. E., DuPont H. L., Snyder M. J., Levine M. M., Libonati J. P. Evaluation of a UDP-glucose-4-epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhi as a liver oral vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):717–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., MacPhee D. G., Stocker B. A. Properties of a Salmonella typhimurium mutant with an incomplete deficiency of uridinediphosphogalactose-4-epimerase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.155-161.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V. Uridinediphosphogalactose-4-epimerase deficiency in Salmonella typhimurium and its correction by plasmoid-borne galactose genes of Escherichia coli K-12: effects on mouse virulence, phagocytosis, and serum sensitivity. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):177–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.177-188.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L. Conversions antigéniques chez les Salmonella XI.--Conversions dans le groupe N (0:30) Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Jul;115(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., SATO I., TANAKA T. Experimental salmonellosis. Intracellular growth of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes of mice, and cellular basis of immunity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:863–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.863-868.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. W., Roantree R. J. Analyses of lipopolysaccharides extracted from penicillin-resistant, serum-sensitive salmonella mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROANTREE R. J., STEWARD J. P. MUTATIONS TO PENICILLIN RESISTANCE IN THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE THAT AFFECT SENSITIVITY TO SERUM AND VIRULENCE FOR THE MOUSE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:630–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.630-639.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster C. W., Rundell K. Resistance of Salmonella typhimurium mutants to galactose death. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):103–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.103-109.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Serie C., Germanier R., Lackany A., Cerisier Y., Guerin N., Sallam S., Geoffroy P., el Tantawi A. S., Guesry P. A controlled field trial of liver oral typhoid vaccine Ty21a. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(3):469–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Sérié C., Cerisier Y., Sallam S., Germanier R. A controlled field trial of live Salmonella typhi strain Ty 21a oral vaccine against typhoid: three-year results. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):292–295. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



